Enthalpy Change & Activation Energy (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences (Double Award)): Revision Note
Exam code: 0654 & 0973
Did this video help you?
Enthalpy change & activation energy
Extended Tier Only
For atoms or particles to react with each other in a chemical system they must collide together
A number of factors affect the success of a collision:
Energy
Orientation
Number of collisions per second - the frequency of collisions
What is activation energy?
In terms of the energy of collisions, there is a minimum amount of energy required for a successful collision
A successful collision is where the particles in the reactant(s) are rearranged to form the products
This minimum amount of energy is called the activation energy, Ea
Different reactions have different activation energies, depending on the chemical identities involved
Reactions with higher activation energies require more energy to start than those with lower activation energies
What is enthalpy change?
The transfer of thermal energy during a reaction is called the enthalpy change, ΔH, of the reaction.
ΔH is:
Positive for an endothermic reaction
Negative for an exothermic reaction
Reaction pathway diagrams
Extended Tier Only
Reaction pathway diagrams are graphical representations of the relative energies of the reactants and products in chemical reactions
On a reaction pathway diagram:
Progress of the reaction is shown on the x-axis
Energy is shown on the y-axis
The difference in energy between the energy of reactants and products is the overall enthalpy change of a reaction
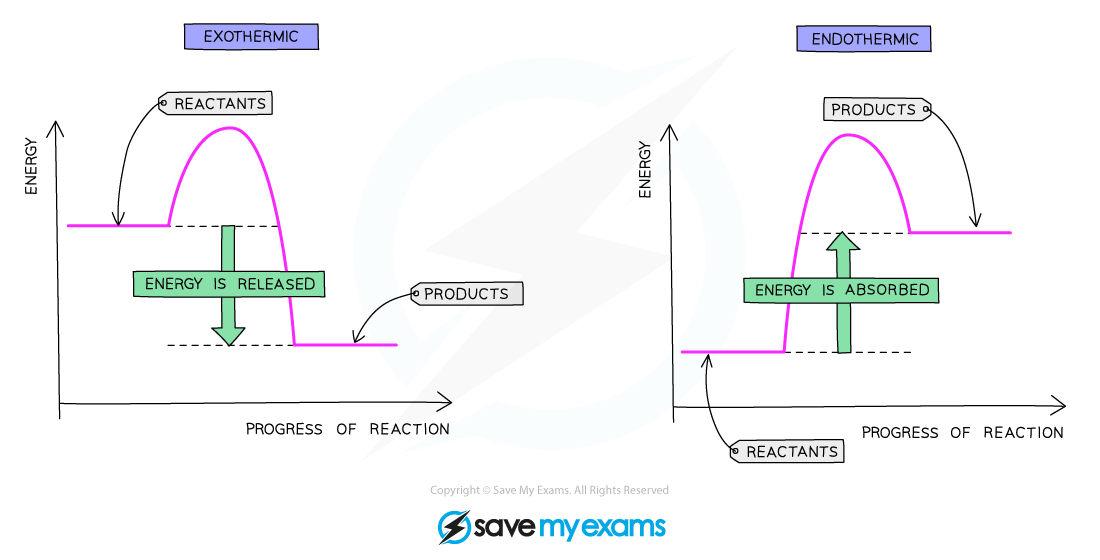
Reaction pathway diagram of an exothermic reaction and an endothermic reaction
Exothermic reactions
Energy is given out to the surroundings
The energy of the products will therefore be lower than the energy of the reactants
The enthalpy change is negative
This is represented on the reaction profile with a downwards-arrow as the energy of the products is lower than the reactants
The activation energy is the energy difference between the reactants and the highest point on the curve
The reaction pathway diagram for an exothermic reaction is:

The reaction pathway diagram for exothermic reactions
Endothermic reactions
Energy is taken in from the surroundings
The energy of the products will be higher than the energy of the reactants
The enthalpy change is positive
This is represented on the reaction profile with an upwards-arrow as the energy of the products is higher than the reactants
The activation energy is the energy difference between the reactants and the highest point on the curve
The reaction pathway diagram for an endothermic reaction is:

The reaction pathway diagram for endothermic reactions.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You must be able to draw these pathway diagrams and label the following parts:
Reactants
Products
Enthalpy change of the reaction, ΔH
Activation energy, Ea

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?