The Ions in Acids & Alkalis (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences (Double Award)): Revision Note
Exam code: 0654 & 0973
Neutralisation reactions
What is a neutralisation reaction?
Acids are a source of hydrogen ions, H+
Bases (or alkalis) are a sources of hydroxide ions, OH–
When they react together in a neutralisation reaction, the H+ ions react with the OH– ions to produce water
This is the net ionic equation of all acid-base neutralisations and is what leads to a neutral solution, since water has a pH of 7:
H+ (aq) + OH– (aq)⟶ H2O (l)
Not all reactions of acids are neutralisations:
For example when a metal reacts with an acid, although a salt is produced there is no water formed so it does not fit the definition of neutralisation
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Not all reactions of acids are neutralisations. For example, when a metal reacts with an acid, although a salt is produced there is no water formed so it does not fit the definition of neutralisation.
Did this video help you?
Hydrogen ion concentration & pH
What is the pH scale?
The pH scale goes from 1 – 14
All acids have pH values of below 7, all alkalis have pH values of above 7
The lower the pH then the more acidic the solution is:
pH 0-2 = strong acid
Extremely acidic substances can have values of below 1
pH 3-6 = weak acid
The higher the pH then the more alkaline the solution is:
pH 8-11 = weak alkali
pH 12-14 = strong alkali
A solution of pH 7 is described as being neutral
The pH scale

The pH scale showing acidity, neutrality and alkalinity
The pH scale and hydrogen ions
We have already seen that acids are substances that contain hydrogen ions in solution
The more hydrogen ions the stronger the acid, but the lower the pH
The higher the concentration of hydroxide ions in a solution the higher the pH
So pH is a measure of the concentration of H+ ions in solution, but they have an inverse relationship
The pH scale is logarithmic, meaning that each change of 1 on the scale represents a change in concentration by a factor of 10
Concentration of hydrogen ions and pH
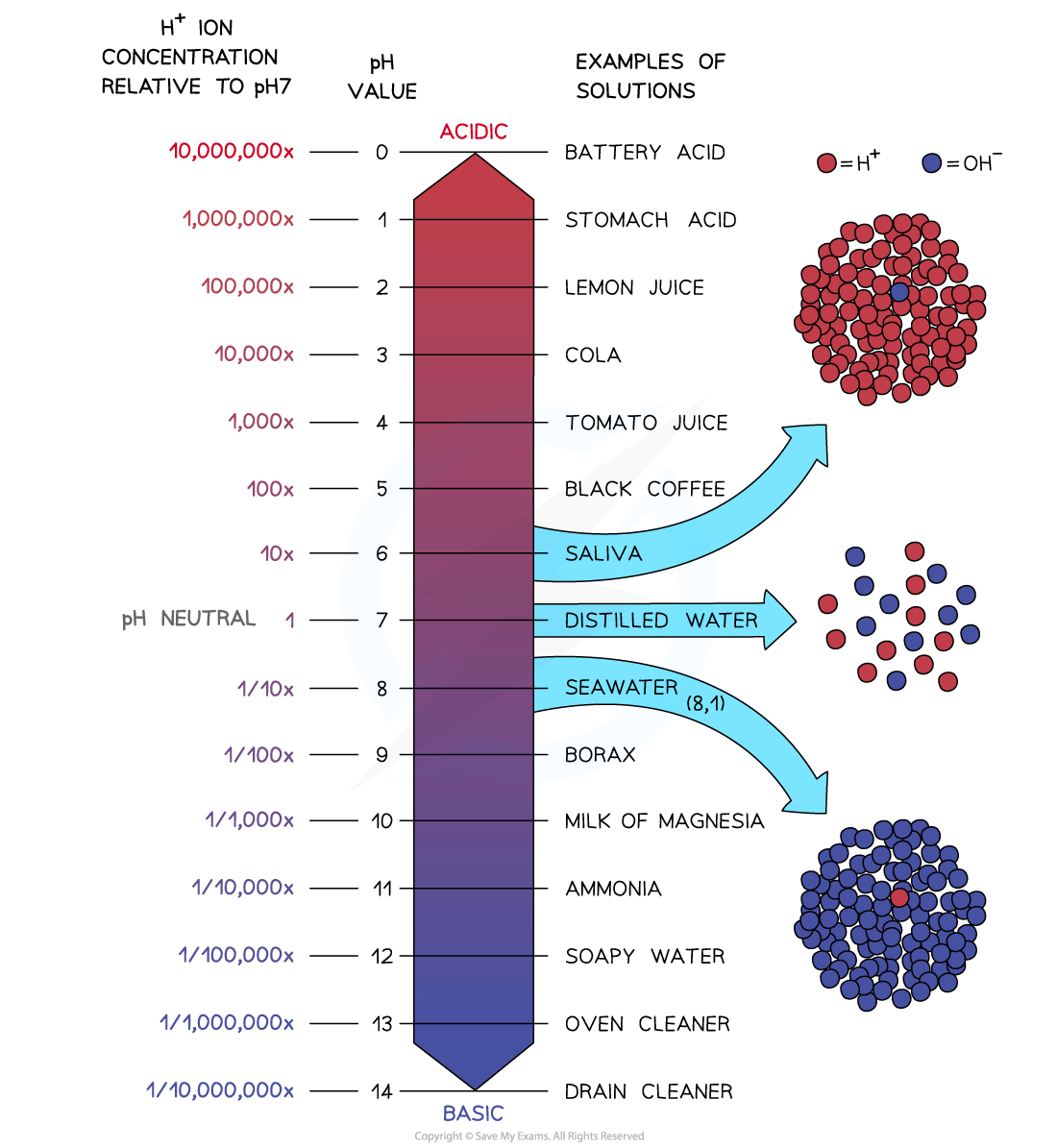
An acid with a pH of 3 has ten times the concentration of H+ ions than an acid of pH 4. An acid with a pH of 2 has 10 x 10 = 100 times the concentration of H+ ions than an acid with a pH of 4
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Acid strength is reflected in how many hydrogen ions are in solution. The more hydrogen ions the lower the pH and vice-versa.
How is universal indicator used?
Universal indicator is a mixture of different indicators which is used to measure the pH
A drop is added to the solution and the colour is matched with a colour chart which indicates the pH which matches specific colours

The pH scale with the Universal Indicator colours which can be used to determine the pH of a solution

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?