Competing Ions in Electrolysis (Oxford AQA IGCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 9202
Competing Ions in Electrolysis
During the electrolysis of aqueous electrolytes there will be water present
Some water molecules split up into hydrogen and hydroxide ions, H+ and OH–, which participate in the electrolysis reactions
H2O (l) H+ (aq) + OH– (aq)
Rules for identifying products formed at electrodes
Positive Electrode - Anode
Negatively charged OH– ions and non-metal ions are attracted to the positive electrode
If halide ions (Cl-, Br-, I-) and OH- are present then the halide ion is discharged at the anode, loses electrons and forms a halogen (chlorine, bromine or iodine)
If no halide ions are present, then OH- is discharged at the anode, loses electrons and forms oxygen gas
In both cases, the other negative ion remains in solution
Negative Electrode - Cathode
H+ ions and metal ions are attracted to the negative electrode but only one will gain electrons
Either hydrogen or a metal will be produced
If the metal is above hydrogen in reactivity series, hydrogen will be produced – bubbling will be seen at the cathode
The reactivity series
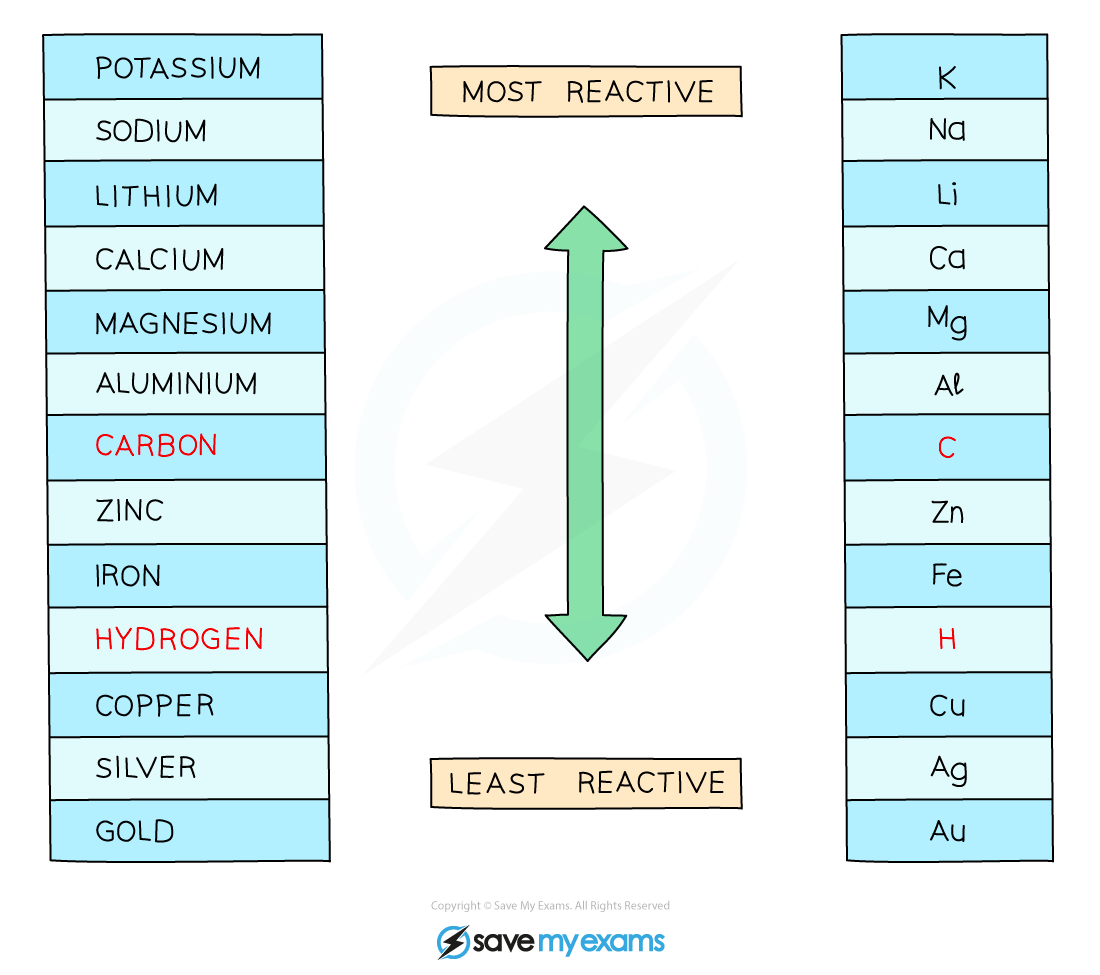
Using Named Electrolytes
You must be able to identify the products at the electrodes from solutions of copper chloride and sodium chloride
The Products of Electrolysing Aqueous Solutions
Aqueous solution | Ions present | Equation at anode | Equation at cathode |
|---|---|---|---|
Sodium chloride, NaCl | H+, OH– , Na+, Cl– | 2Cl– (aq) → Cl2 (g) + 2e– | 2H+ + 2e– → H2 (g) |
Copper(II) chloride, CuCl2 | H+, OH– , Cu2+, Cl– | 2Cl– (aq) → Cl2 (g) + 2e– | Cu2+ (aq) + 2e– → Cu (s) |
Explaining the products:
Copper chloride:
Copper is below hydrogen in the reactivity series so copper(II) ions are preferentially discharged at the cathode; chlorine is a halogen, so is preferentially discharged at the anode
Sodium chloride:
Sodium is above hydrogen in the reactivity series so hydrogen ions are preferentially discharged at the cathode; chlorine is a halogen, so is preferentially discharged at the anode
Worked Example
Name the products formed at the anode and cathode during the electrolysis of the following substances:
Aqueous sodium bromide
Aqueous potassium chloride
Answer:
Aqueous sodium bromide
Anode = bromine gas
Cathode = hydrogen gas
Aqueous potassium chloride
Anode = chlorine gas
Cathode = hydrogen gas

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?