Relative Atomic Mass (Oxford AQA IGCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 9202
Relative Atomic Mass
Relative atomic mass has the symbol Ar
This is the average mass of the atoms of an element measured relative to carbon-12
For example:
Carbon has an Ar of 12 and hydrogen has an Ar of 1 on the periodic table
So, 1 atom of carbon has the same mass as 12 atoms of hydrogen
Comparing hydrogen and carbon

Examiner Tips and Tricks
Defining relative atomic mass is a common exam question.
The best answers work through the term backwards and include the required extra detail:
Mass - the average mass
Atomic - of an atom
Relative - compared to carbon-12
The relative atomic mass of any element is shown on the periodic table
It is the mass number
The mass number that is shown on the periodic table is an average value of all the isotopes of an element
This is calculated from the mass number and relative abundances of all the isotopes of a particular element
The isotopes of carbon are carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14
But, the percentage of carbon-12 is so high that the average value of all isotopes shown on the periodic table is 12
Using isotopes for the Ar of carbon

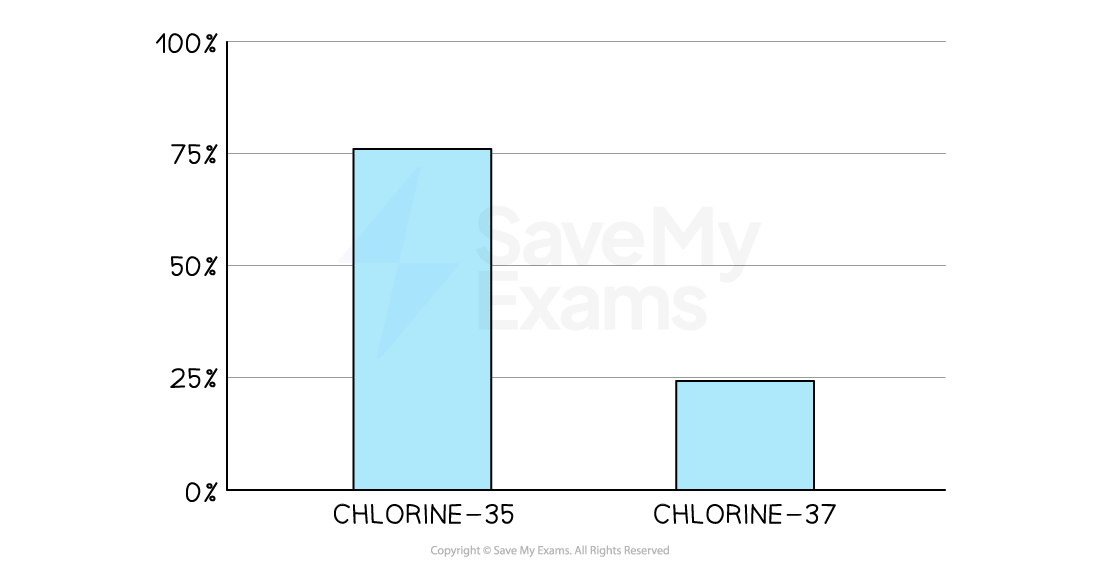
The isotopes of chlorine are chlorine-35 and chlorine-37
The percentage of chlorine-35 is roughly three quarters of all chlorine atoms
So, the average value of all chlorine atoms shown on the periodic table is 35.5
Using isotopes for the Ar of chlorine
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You will not be asked to use isotopes and their abundances to calculate values for relative atomic mass.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?