Acid-Alkali Titrations (Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 4CH1
What is a titration?
Titrations are a method of analysing the concentration of solutions
Acid-base titrations are one of the most important kinds of titrations
They can determine exactly how much alkali is needed to neutralise a quantity of acid – and vice versa
You may be asked to calculate the moles present in a given amount, the concentration or volume required to neutralise an acid or a base
Titrations can also be used to prepare salts
How to carry out a titration
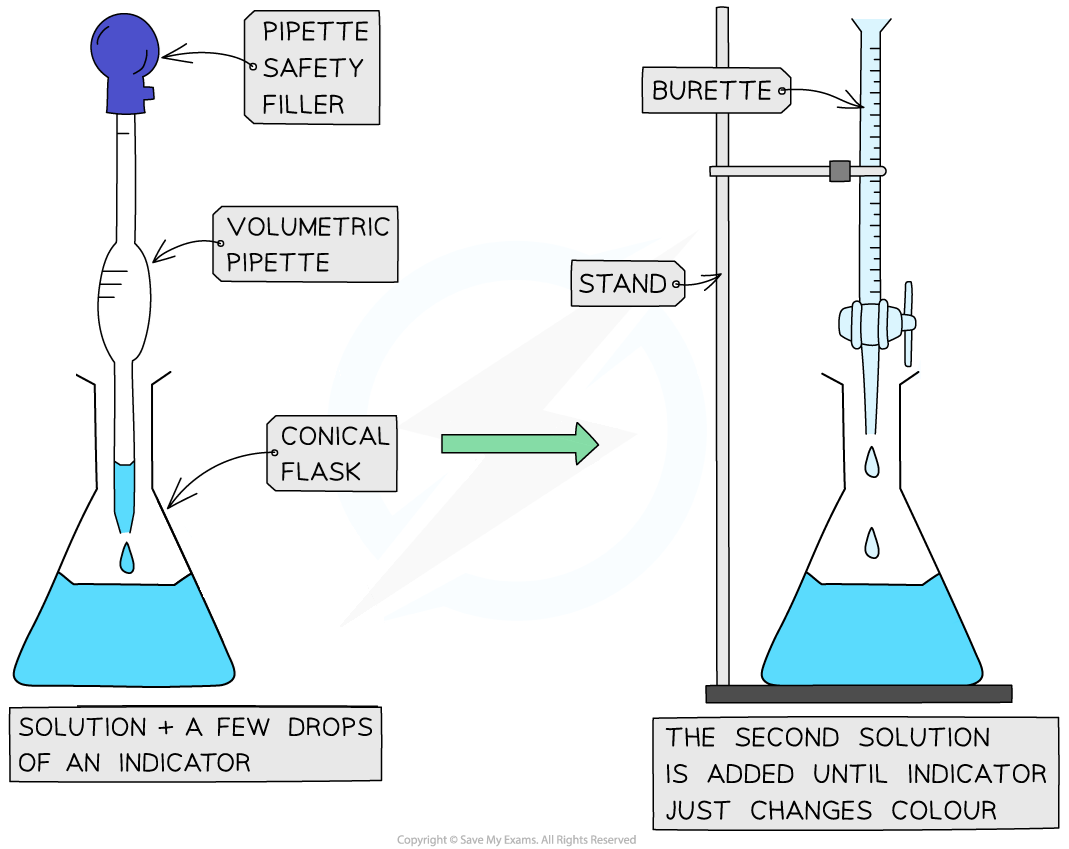

Performing a titration
Method
Use the pipette and pipette filler and place exactly 25 cm3 sodium hydroxide solution into the conical flask
Fill the burette with hydrochloric acid
Ensure an empty beaker is underneath the tap to catch in case the tap is accidentally open
Run a small portion of hydrochloric acid through the burette to remove any air bubbles
The main air bubble is likely to be in the "jet space", which is the area between the tap and the tip of the burette
Record the starting point on the burette to the nearest 0.05 cm3
You can add more hydrochloric acid so that the burette reading starts at 0.0 cm3
Place the conical flask on a white tile
The purpose of the white tile is to make colour changes more obvious
Add a few drops of a suitable indicator to the solution to the conical flask
Ensure the tip of the burette is inside the conical flask
Perform a rough titration by taking the burette reading and running in the solution in 1 – 3 cm3 portions
Remembe to swirl the flask vigorously
Quickly close the tap when the end-point is reached
The end-point wil be indicated by a sharp colour change
Record the final volume
Ensure you read off the meniscus at eye level
Now repeat the titration with a fresh batch of sodium hydroxide
As the rough end-point volume is approached, add the solution from the burette one drop at a time until the indicator just changes colour
Record the volume to the nearest 0.05 cm3
Repeat until you achieve two concordant results (two results that are within 0.1 cm3 of each other) to increase accuracy
Results
Results table for a titration
Rough titre (cm3) | Titre 1 (cm3) | Titre 2 (cm3) | Mean (cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|
15.50 | 14.90 | 15.00 | 14.95 |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Use a funnel to fill the burette but be sure to remove it before starting the practical as it can drip liquid into the burette, making the initial reading false.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?