Group VII Properties (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 0620 & 0971
Did this video help you?
Group VII properties & trends
These are the Group VII non-metals that are poisonous and include fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine and astatine
Halogens are diatomic
This means that they form molecules containing two atoms
The formulae of the halogens are:
Fluorine = F2
Chlorine = Cl2
Bromine = Br2
Iodine = I2
Astatine = At2
All halogens have seven electrons in their outer shell
They form halide ions by gaining one more electron to complete their outer shells
Fluorine is not allowed in schools so observations and experiments tend to only involve chlorine, bromine and iodine
Properties of the halogens
Physical state, colour and density
At room temperature (20 °C), the physical state of the halogens changes as you go down the group
Chlorine is a pale yellow-green gas
Bromine is a red-brown liquid
Iodine is a grey-black solid
This demonstrates that the density of the halogens increases as you go down the group:

Examiner Tips and Tricks
Solid iodine, iodine in solution and iodine vapour are different colours.
Solid iodine is dark grey-black
Iodine vapour is purple
Aqueous iodine is brown.
Reactivity
The reactivity of Group 7 elements decreases as you go down the group
This is the opposite trend to Group 1
When a halogen reacts, it needs to gain one outer electron to achieve a full outer shell of electrons
As you go down Group 7, the number of electron shells increases
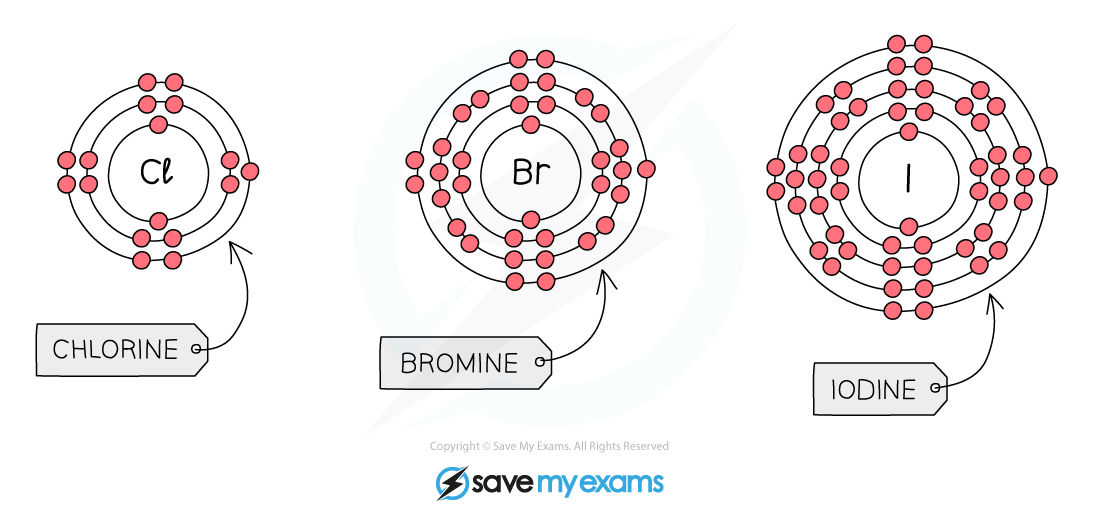
The increasing number of electron shells has two main effects:
The atomic radius increases, so the outer shell is further from the nucleus
There is more electron shielding from the inner shells
These factors reduce the force of attraction between the nucleus and an incoming electron
Therefore, it becomes harder to attract an electron
This means that the reactivity of the halogens decreases down the group
Predicting group VII properties
You may be given information about some elements and asked to predict the properties of other elements in the group
The information you might be given could be in relation to melting/boiling point or physical state/density so it is useful to know the trends in properties going down the group
Predicting melting and boiling point
The melting and boiling point of the halogens increases as you go down the group
Fluorine is at the top of Group 7
It has the lowest melting and boiling point
Astatine is at the bottom of Group 7
It has the highest melting and boiling point
Predicting physical states and density
The halogens become denser as you go down the group
Fluorine is at the top of Group 7
It is a gas
Astatine is at the bottom of Group 7
It is a solid
Predicting colour
The colour of the halogens becomes darker as you go down the group
Fluorine is at the top of Group 7 so the colour will be lighter
Fluorine is yellow
Astatine is at the bottom of Group 7 so the colour will be darker
Astatine is black
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are doing the extended course you can be asked to identify trends in chemical or physical properties of the Group 7 elements, given appropriate data.
Firstly, make sure that you have placed the elements and associated data in either ascending or descending order according to their position in Group 7. Then look for any general patterns in the data.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
