Oxidation & Reduction (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 0620 & 0971
Did this video help you?
Oxidation & reduction
Roman numerals and oxidation numbers
Transition elements can bond in different ways by forming ions with different charges
When naming, the charge on the ion is shown by using a Roman numeral after the element's name
For example, iron can form different ions
Iron ions with a 2+ charge, Fe2+, are called iron(II) ions
Iron ions with a 3+ charge, Fe3+, are called iron(III) ions
The Roman numeral is the oxidation number of the element
For example, iron reacts with oxygen to form iron oxide
But the name and formula of the product depend on the oxidation state of the iron ions
Iron(II) ions
The iron oxide product contains iron(II) ions, Fe2+
The name of this product is iron(II) oxide
The formula of this product is FeO
Iron(III) ions
The iron oxide product contains iron(III) ions, Fe3+
The name of this product is iron(III) oxide
The formula of this product is Fe2O3
Worked Example
State the oxidation number of the transition metal ion in silver(I) chloride, AgCl.
Name, including Roman numeral, the compound with the formula CoCl2.
Answers:
The oxidation number of the transition metal ion in silver(I) chloride, AgCl, is 1
Remember: The Roman numeral gives the oxidation number of the element before
The name, including Roman numeral, of the chemical with the formula CoCl2 is cobalt(II) chloride
CoCl2 contains two chloride ions, each with a 1- charge
So, the cobalt ion has a 2+ charge
This means the compound contains cobalt(II) ions, Co2+
Therefore, it is called cobalt(II) chloride
What is a redox reaction?
A redox reaction is where oxidation and reduction take place together at the same time in the same reaction
In terms of oxygen:
Oxidation is where oxygen is added to an element or a compound
Reduction is where oxygen is removed from an element or compound
The reaction between zinc oxide and carbon is an example of a redox reaction
Zinc oxide is reduced because it has lost oxygen
Carbon is oxidised because it has gained oxygen
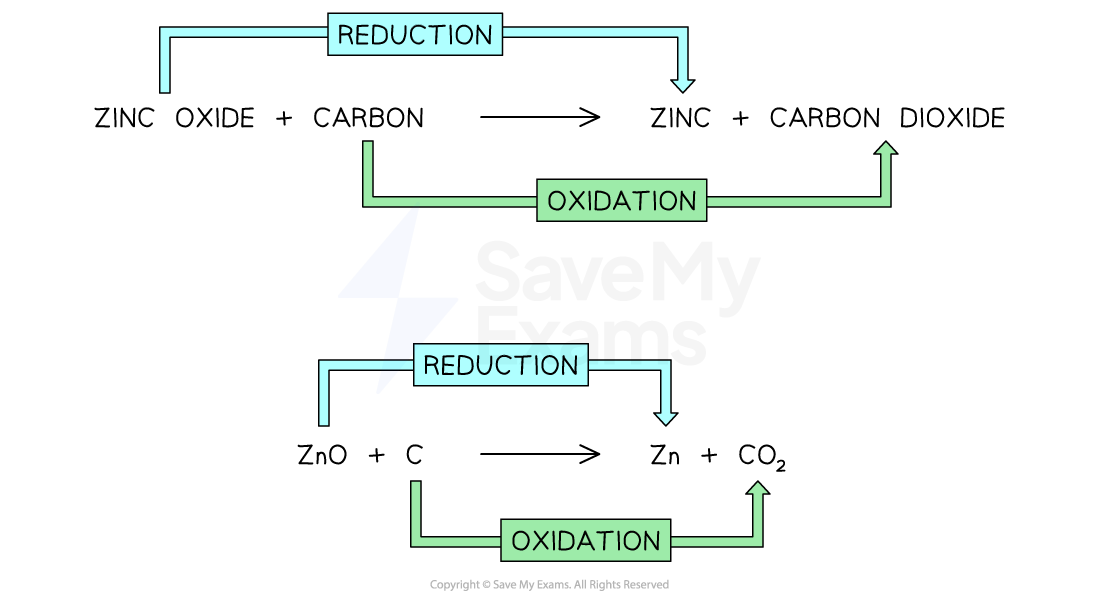
Both reduction and oxidation has occurred in this reaction so it is classed as a redox reaction
Worked Example
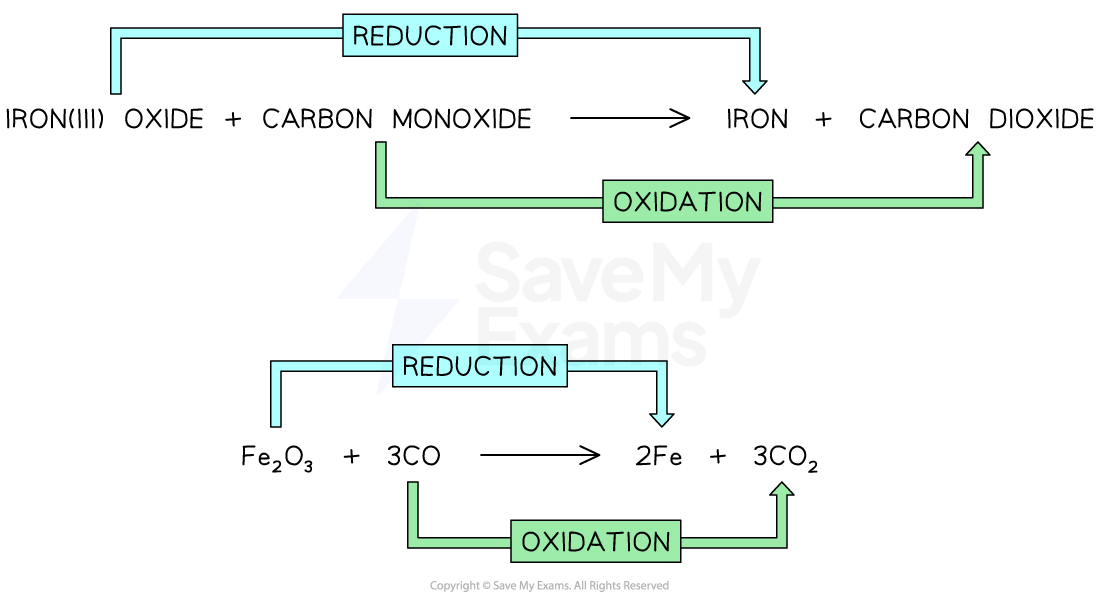
Explain which chemicals that are reduced and oxidised in the reaction between iron(III) oxide and carbon.
iron(III) oxide + carbon monoxide → iron + carbon dioxide
Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
Answer:
Iron(III) oxide loses oxygen, so it is reduced
Carbon monoxide gains oxygen, so it is oxidised
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You may see the term oxidation state used instead of oxidation number.
Although there is a subtle difference between the two terms (this is beyond the scope of this course), they are often used interchangeably.
Usually oxidation number is used to refer to the Roman numerals found within the name.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?