Rates of Reaction Factors (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 0620 & 0971
Rates of reaction factors
Factors that can affect the rate of a reaction are:
The concentration of the reactants in solution or the pressure of reacting gases
Surface area of solid reactants
The temperature of the reaction
The presence of a catalyst
Changes in these factors directly influence the rate of a reaction
It is of economic interest to have a higher rate of reaction as this implies a higher rate of production and hence a more efficient and sustainable process
The effect of increased concentration or pressure
Graph showing the effect of concentration on rate of reaction

Increasing the concentration of a solution or gas pressure increases the rate of reaction
Explanation:
Compared to a reaction with a reactant at a low concentration (or pressure), the line graph for the same reaction at a higher concentration (or pressure):
Has a steeper gradient at the start
Becomes horizontal sooner
Forms the same amount of product
This shows that increasing the concentration (or pressure) increases the rate of reaction
The effect of increasing surface area
Graph showing the effect of surface area on rate of reaction
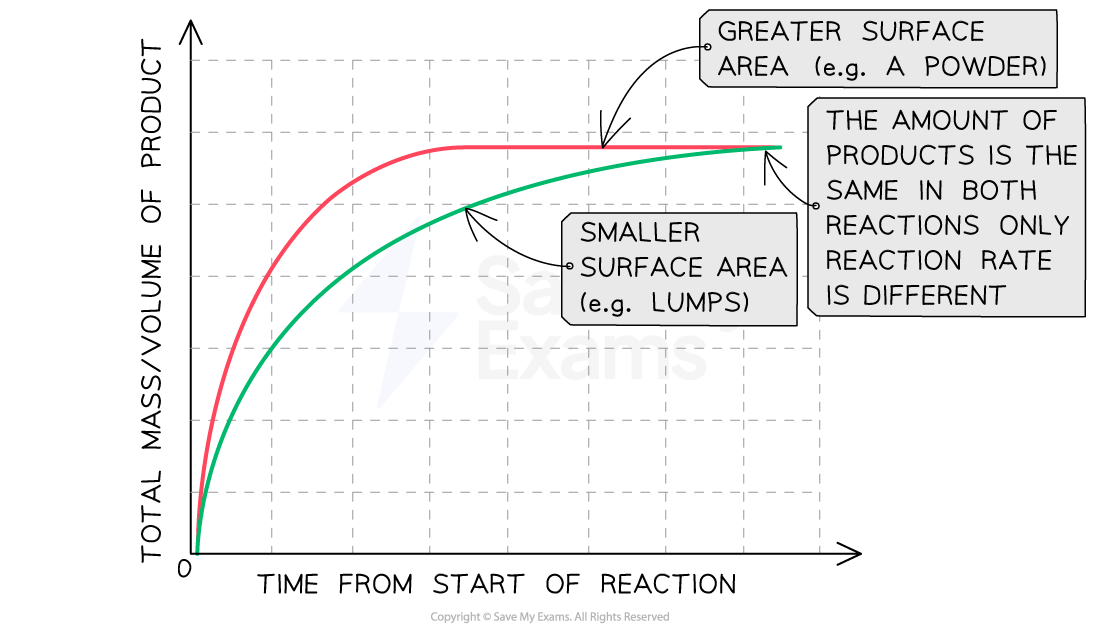
Increasing the surface area increases the rate of reaction
Explanation:
Compared to a reaction with lumps of reactant, the line graph for the same reaction with powdered reactant:
Has a steeper gradient at the start
Becomes horizontal sooner
Forms the same amount of product
This shows that increasing the surface area increases the rate of reaction
Increasing surface area can sometimes be described as decreasing solid particle size
Surface area and particle size
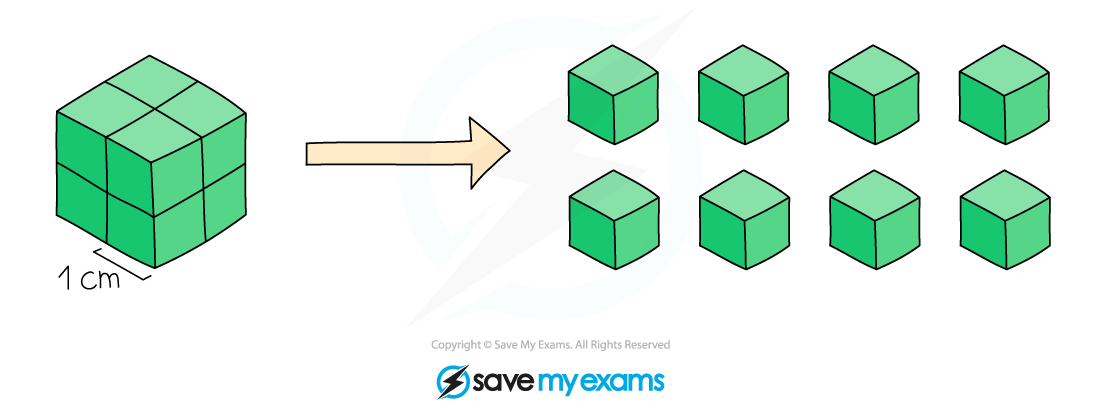
Surface area increases as particle size decreases. A 2 cm3 cube has a surface area of 24 cm2 and the same cube cut up into 8 cubes has a surface area of 48 cm2
The effect of increasing temperature
Graph showing the effect of temperature on rate of reaction
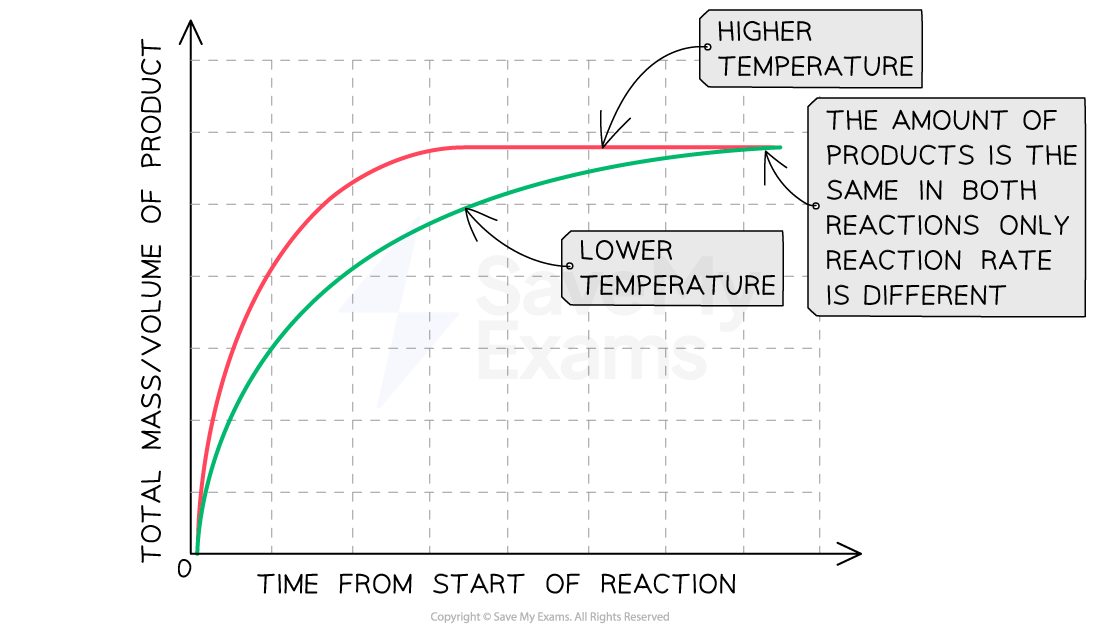
Increasing the temperature increases the rate of reaction
Explanation:
Compared to a reaction at a low temperature, the line graph for the same reaction at a higher temperature:
Has a steeper gradient at the start
Becomes horizontal sooner
Forms the same amount of product
This shows that increasing the temperature increases the rate of reaction
The effect of using a catalyst
Catalysts are substances which speed up the rate of a reaction without themselves being altered or consumed in the reaction
The mass of a catalyst at the beginning and end of a reaction is the same and they do not form part of the equation
Graph showing the effect of using a catalyst on rate of reaction
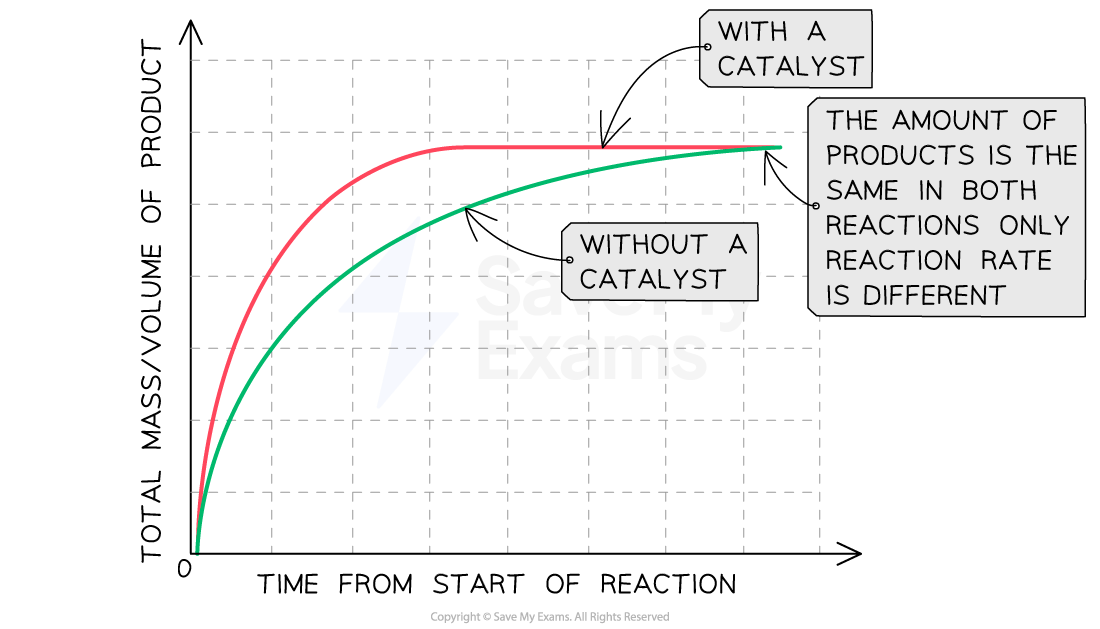
Graph showing the effect of using a catalyst on the rate of reaction
Explanation:
Compared to a reaction without a catalyst, the graph line for the same reaction but with a catalyst has a steeper gradient at the start and becomes horizontal sooner
This shows that with a catalyst, the rate of reaction will increase

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
