Isotopes (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 0620 & 0971
Defining isotopes
Isotopes are different atoms of the same element that contain the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
The symbol for an isotope is the chemical symbol (or word) followed by a dash and then the mass number
So C-14 ( or carbon-14) is the isotope of carbon which contains 6 protons, 6 electrons and 14 - 6 = 8 neutrons
It can also be written as 14C or
Table to show the structures of isotopes of hydrogen
Isotope | Atomic Structure | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
Hydrogen - 1 | 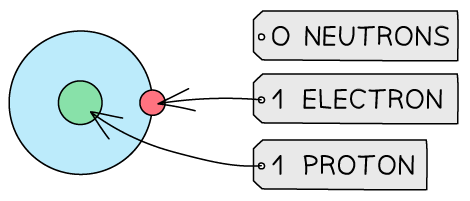 | 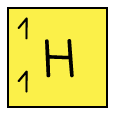 |
Hydrogen - 2 | 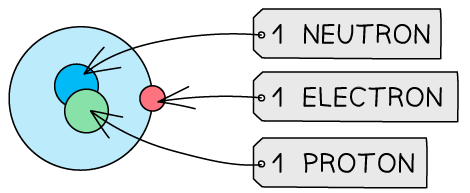 | 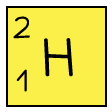 |
Hydrogen - 3 |  | 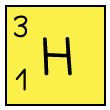 |
Why isotopes share properties
Extended tier only
Isotopes display the same chemical characteristics
This is because they have the same number of electrons in their outer shells, and this is what determines their chemistry
The difference between isotopes is the neutrons which are neutral particles within the nucleus and add mass only
The difference in mass affects the physical properties, such as density, boiling point and melting point
Isotopes are identical in appearance, so a sample of C-14 would look no different from C-12
Calculating relative atomic mass
Extended tier only
Relative atomic mass
Atoms are so tiny that we cannot really compare their masses in conventional units such as kilograms or grams, so a unit called the relative atomic mass (Ar) is used
The relative atomic mass unit is equal to 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom
All other elements are measured by comparison to the mass of a carbon-12 atom and since these are ratios, the relative atomic mass has no units
For example, hydrogen has a relative atomic mass of 1, meaning that 12 atoms of hydrogen would have exactly the same mass as 1 atom of carbon
How do I calculate relative atomic mass?
The relative atomic mass of each element is calculated from the mass number and relative abundances of all the isotopes of a particular element
The equation below is used where the top line of the equation can be extended to include the number of different isotopes of a particular element present
So, if there were 3 isotopes present then the equation would read:
Worked Example
The table shows information about the isotopes in a sample of rubidium
Isotope | Mass Number | Percentage abundance |
1 | 85 | 72 |
2 | 87 | 28 |
Use information from the table to calculate the relative atomic mass of this sample of rubidium.
Give your answer to one decimal place.
Answer:
Relative atomic mass =
Relative Atomic Mass = 85.6
Is mass number and relative atomic mass the same thing?
On the Periodic Table provided in your exam you will see that lithium has a relative atomic mass of 7
Although it seems that this is the same as the mass number, they are not the same thing because the relative atomic mass is a rounded number
Relative atomic mass takes into account the existence of isotopes when calculating the mass
Relative atomic mass is an average mass of all the isotopes of that element
For simplicity relative atomic masses are often shown to the nearest whole number

The relative atomic mass of lithium to two decimal places is 6.94 when rounded to the nearest whole number, the RAM is 7, which is the same as the mass number shown on this isotope of lithium

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?