Locating Agents & Rf Values (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 0620 & 0971
Did this video help you?
Locating agents
Extended tier only
For chromatography to be useful, the chemist needs to be able to see the components move up the paper
This is not the case for colourless substances such as amino acids or sugars
Locating agents can be used to see the spots
These are substances which react with the sample and produce a visible / coloured spot for the product(s)
The chromatogram is treated with the agent after the chromatography run has been carried out, making the sample runs visible to the naked eye
Retention factor (Rf) values
Extended tier only
Rf values are used to identify the components of mixtures
The Rf value of a particular compound is always the same
However, it does depend on the solvent used
If the solvent is changed then the Rf value changes
Calculating the Rf value allows chemists to identify unknown substances because it can be compared with the Rf values of known substances under the same conditions
The retention factor, Rf, is calculated by the equation:
Rf =
The Rf value:
Is a ratio
Has no units
Will always be less than 1
Worked Example
A student obtained the following chromatogram when carrying out chromatography.
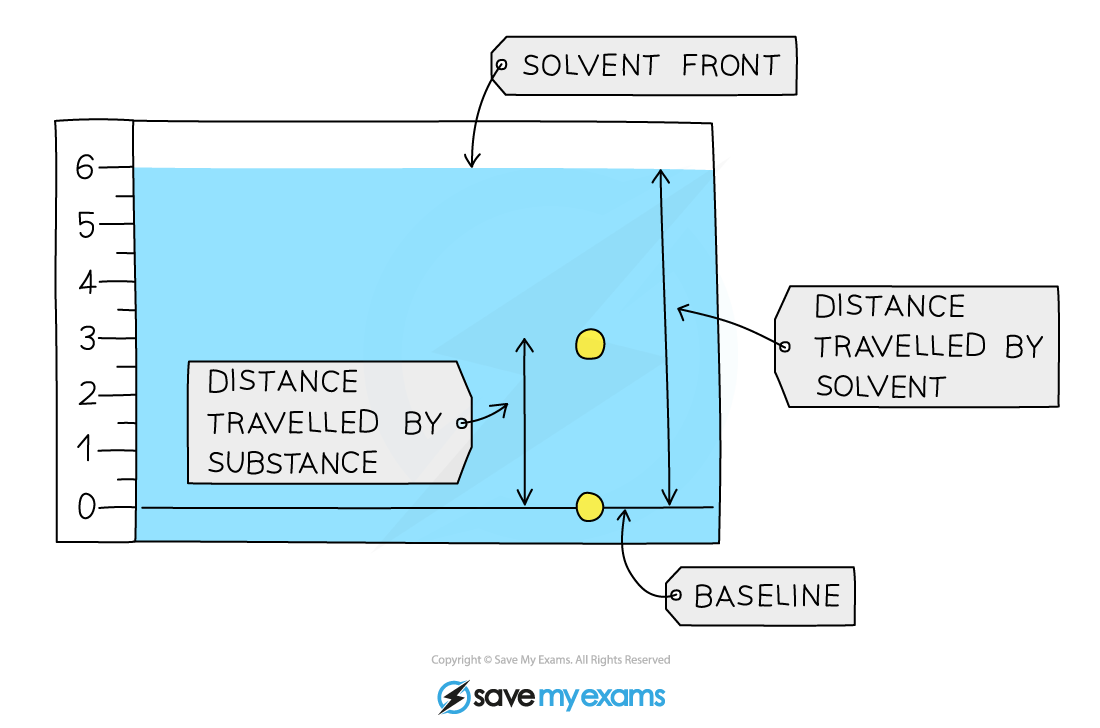
Calculate the Rf value of the substance.
Answer:
The Rf value of the substances in the chromatogram above can be calculated by:
Rf =
=
= 0.5
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When you calculate Rf values in exams, make sure to use your ruler carefully to measure the distance moved by the solvent and the substance, or use any scale provided on the diagram.
Mark schemes can be strict about the values accepted, so it's important to be as accurate as possible when determining these distances.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?