Organic Formulae (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 0620 & 0971
Displayed formulae
Organic Chemistry is the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds.
Organic compounds are those which contain carbon
For conventional reasons metal carbonates, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide are not included in organic compounds
Many of the structures you will be drawing are hydrocarbons
A hydrocarbon is a compound that contains only hydrogen and carbon atoms
Organic compounds can be represented in a number of ways:
Displayed Formulae
General Formulae
Structural Formulae
The displayed formula shows the spatial arrangement of all the atoms and bonds in a molecule
For example:

This displayed formula tells us several things about the compound
It has 5 carbon atoms
It has 12 hydrogen atoms
It has only single bonds
Structural formulae
Extended tier only
In structural formulae, enough information is shown to make the structure clear, but most of the actual covalent bonds are omitted
Only important bonds are always shown, such as double and triple bonds
Identical groups can be bracketed together
Side groups are also shown using brackets
Straight chain alkanes are shown as follows:


Structural isomers
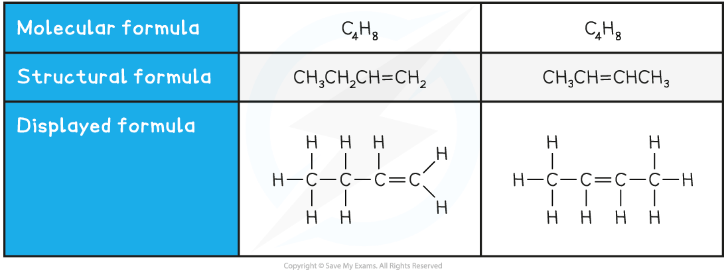
Structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae
The molecular formula is the actual number of atoms of each element in a compound
Compounds with the same molecular formula can have different structural formulae due to the different arrangement of their atoms in space
Two examples of structural isomers are shown below
Table showing structural isomerism in C4H10
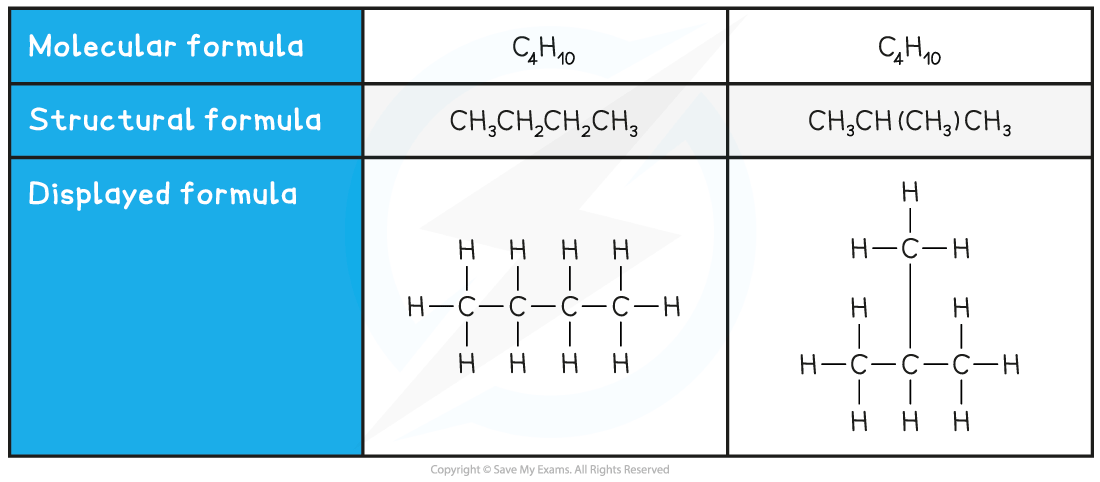
Table showing structural isomerism in C4H8
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember: Only double and triple bonds are shown in structural formulae.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
