Effects of Greenhouse Gases (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 0620 & 0971
Effects of greenhouse gases
Extended Tier Only
The Sun emits energy in the form of radiation that enters the Earth’s atmosphere
Some thermal energy is reflected from the Earth's surface
Most thermal energy is absorbed and re-emitted back from the Earth’s surface
The energy passes through the atmosphere where some thermal energy passes straight through and is emitted into space
But some thermal energy is absorbed by greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, and is re-emitted in all directions
This reduces the thermal energy lost into space and traps it within the Earth’s atmosphere, keeping the Earth warm
This process is known as the greenhouse effect
As the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increases due to human activity, more thermal energy is trapped within the Earth's atmosphere causing the Earth’s average temperature to rise (global warming)
This process is called the enhanced greenhouse effect
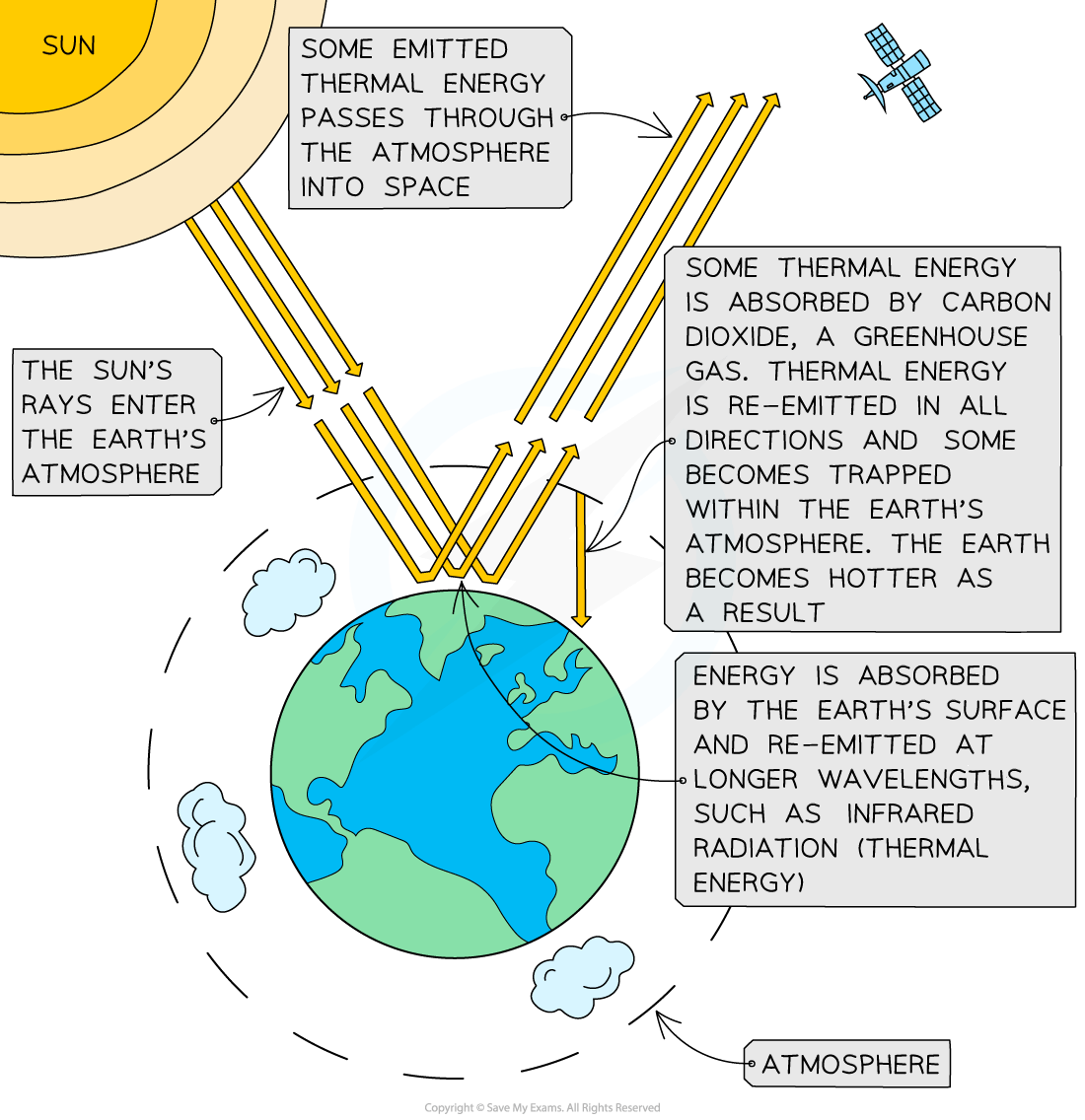
Diagram showing how the greenhouse effect occurs
Consequences of global warming
Climate change due to the increase in Earth’s temperature
Water levels will rise as glaciers melt because of high temperatures, causing flooding in low-lying countries
Extinction of species due to the destruction of natural habitats
Migration of species as they will move to areas that are more habitable (no droughts)
Spread of diseases caused by warmer climate
Loss of habitat due to climate change (animals that live on glaciers or in low-lying countries)

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?