Water: Chemical Tests (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 0620 & 0971
Chemical tests for water
Chemical tests for water
The presence of water is commonly tested for using anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride or anhydrous copper(II) sulfate
Cobalt(II) chloride
Anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride, CoCl2, is blue
Hydrated cobalt(II) chloride, CoCl2•6H2O is pink
So, anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride can be used to test for water
This test is usually done with cobalt chloride paper
anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride + water hydrated cobalt(II) chloride
CoCl2 (s) + 6H2O (l) CoCl2•6H2O (s)
The presence of water causes a colour change from blue to pink
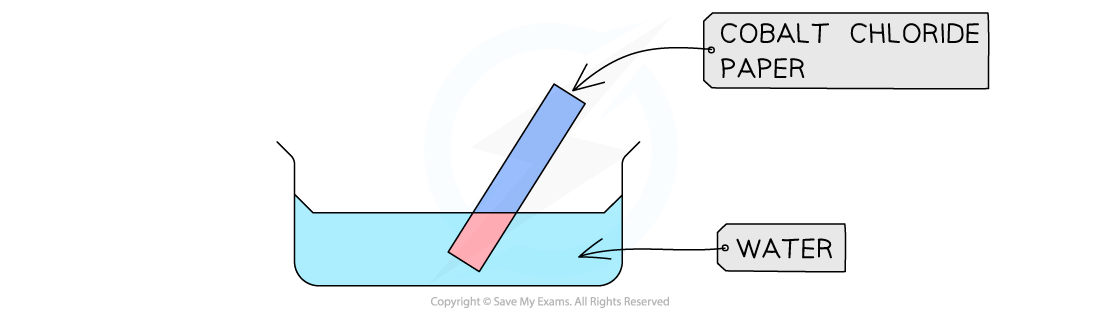
Cobalt chloride paper changes from blue to pink in the presence of water
Copper(II) sulfate
Anhydrous copper(II) sulfate, CuSO4 is white
Hydrated copper(II) sulfate, CuSO4•5H2O, is blue
So, anhydrous copper(II) sulfate can be used to test for water
anhydrous copper(II) sulfate + water hydrated copper(II) sulfate
CuSO4 (s) + 5H2O (l) CuSO4•5H2O (s)
The presence of water causes a colour change from white to blue
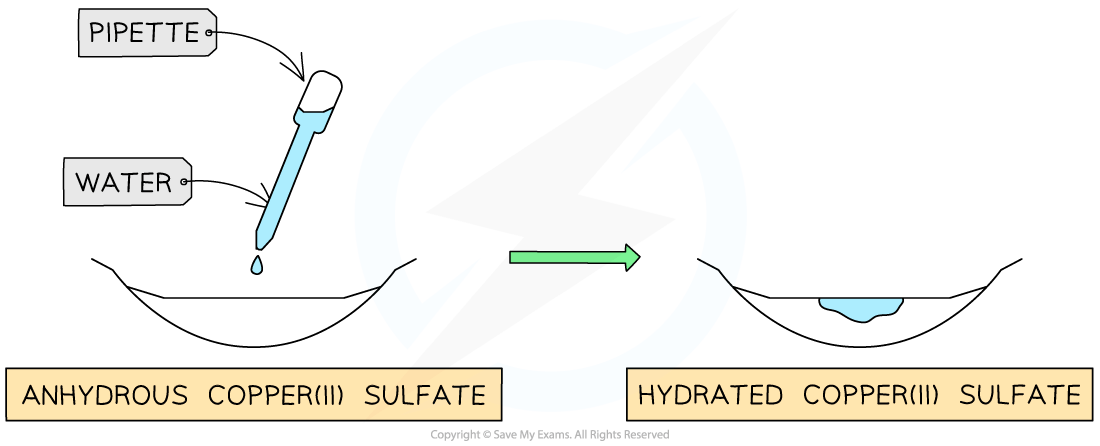
Anhydrous copper(II) sulfate changes from white to blue in the presence of water
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Core students do not need to know the symbol equations.
Purity of water
Testing for purity
Pure substances boil and melt at specific and sharp temperatures
Water has a boiling point of 100 °C and a melting point of 0 °C
Mixtures have a range of boiling and melting points as they consist of different substances that melt or boil at different temperatures
Therefore, boiling and melting point data can be used to determine the purity of water
Impurities tend to increase the boiling point of water
So, impure water will boil at temperatures above 100 oC
Impurities tend to decrease the melting point of water
So, impure water will melt at temperatures below 0 oC
What is distilled water?
Distilled water is water that has been heated to form a vapour, and then condensed back to a liquid
This means that it contains very few impurities
Distilled water is used in practical chemistry because of its high purity
Tap water is not typicaly used because it contains more impurities which could interfere with chemical reactions

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?