Principles of Lean Production (Edexcel IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 4BS1
Introduction to lean production
Lean production involves the minimisation of the resources used in production
Less time is required as the production process is organised in the most efficient way
Fewer materials are used as there is a focus on waste reduction
Less labour is used as lean production is typically capital intensive
The space required for production is reduced as a result of just in time stock management
A small number of trusted suppliers work closely with the business
The use of lean production is likely to lead to a competitive advantage
Lower unit costs are achieved due to minimal wastage so prices may be lower than those offered by competitors
High quality output is likely as a result of supplier reliability and carefully managed production processes
The result should be increased profit margins
Lean production uses strategies such as Just in Time stock control and Kaizen
Just-in-time (JIT) stock management
Just-in-time (JIT) stock management is a process in which raw materials are not stored onsite but ordered as required and delivered by suppliers 'just in time' for production
Careful coordination is required to ensure that raw materials and components are delivered by suppliers at the moment that they are to be used
Close relationships with suppliers need to be developed
Suppliers may need to be in close proximity
Just-in-time is particularly useful for businesses that operate in dynamic markets
Products may need frequent design changes that require different components
Holding large amounts of stock risks wastage through obsolescence
Where significant competition exists lean production can ensure a high level of quality to achieve a competitive advantage
Advantages and disadvantages of just-in-time stock management
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Kaizen
Kaizen involves taking continuous steps to improve productivity through the elimination of all types of waste in the production process
Changes are small and ongoing rather than significant one-off’s
They are constantly reviewed to ensure that they achieve the desired positive impact on productivity and always focused on meeting customers' needs
Kaizen requires a long-term cultural and management commitment to change
All workers must be actively involved in making improvements, not just management
Ongoing training and development is vital
The impact of Kaizen on productivity over time
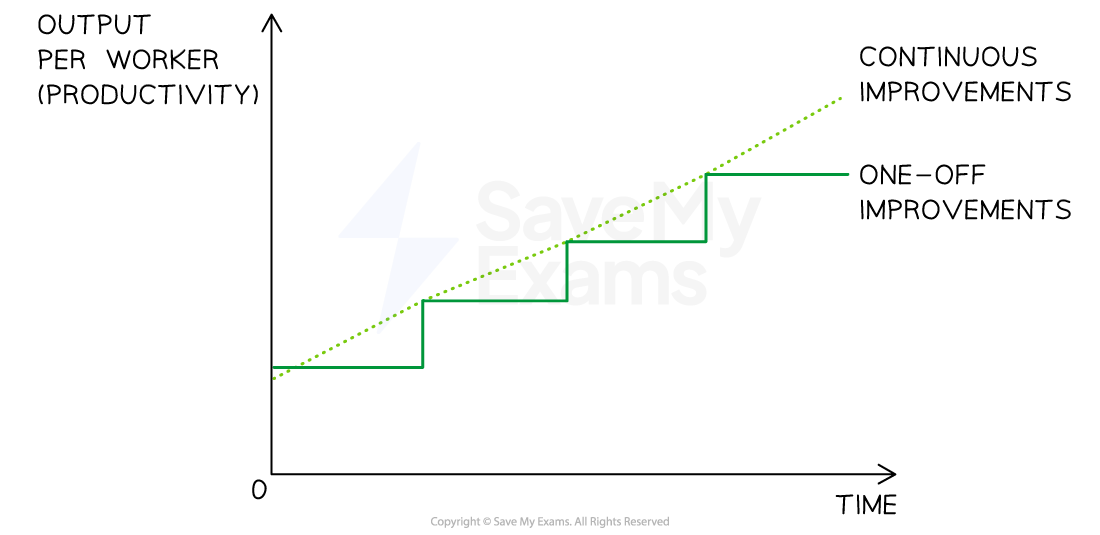
Elements of Kaizen commonly include
Zero defects in manufacturing
High levels of automation
High levels of cooperation between workers and management
Employees are likely to work in teams and be empowered to work creatively
Staff training and computer inventory management systems may also reduce wastage as fewer errors are likely to be made
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In the exam, you could be asked to justify whether a business should improve efficiency by adopting just-in-time or kaizen. A great evaluation point is that, in most cases, the two elements of lean production are adopted together.
The importance of using resources effectively
Lean production is focused on the effective use of resources and, in particular, the elimination of waste throughout the business
Waste refers to anything that prevents a business from being efficient
Seven key types of waste are minimised in lean production
The seven wastes

Transportation: Unnecessary movement of materials or products
Inventory: Excess raw materials, work-in-progress, or finished goods
Motion: Unnecessary movement of people or equipment
Waiting: Delays or idle time in the production process
Overproduction: Producing more than what is required by the customer
Overprocessing: Using more resources than necessary to produce a product
Defects: Products or services that do not meet customer requirements
Benefits of reducing waste
Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
Competiveness |
|
Lower costs |
|
Better customer service |
|
Environmental benefits |
|

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?