Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2018
Last exams 2026
Promotion (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
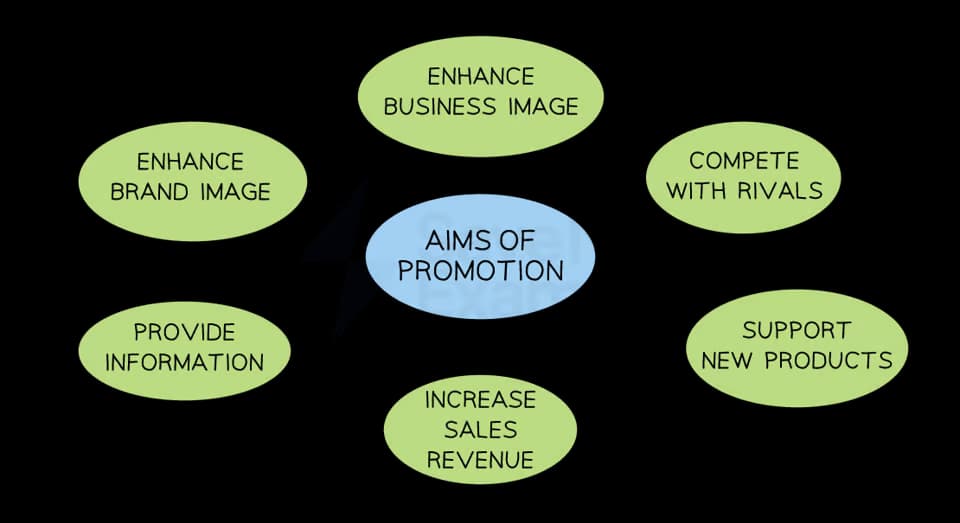
The aims of promotion
Promotion plays a crucial role in generating customer awareness, interest and desire for a product
It communicates a businesses value proposition to potential customers and helps to differentiate the product or business from competitors
Types of promotion
Above-the-line promotion refers to advertising aimed at reaching a wide audience through traditional mass media channels
Advertising may use media such as television, radio, newspapers, magazines and outdoor sites such as billboards
Below-the-line promotion includes marketing communications over which a business has direct control and which do not make use of mass media
These channels include direct marketing, sales promotions, personal selling and public relations (PR)
Businesses have a wide choice of promotional tools and techniques
They must select the most appropriate methods for their product, target audience and budget

Explaining the different promotional methods
1. Advertising
Promotion through paid channels such as television, radio, print media, online advertising and outdoor advertising
Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
|
|
2. Direct marketing
Communicating directly with customers through email, text message, social media or post
Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
|
|
3. Sales promotions
Temporary incentives or discounts such as free samples, buy one get one free (bogof), discount coupons, loyalty cards,] and rebates (customers have to mail in to receive money back)
Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
|
|
4. Personal selling
A salesperson interacts with potential customers one-on-one either in person or through digital channels
Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
|
|
5. Sponsorship
Agreement where a business provides financial or other support to an event, team, or organisation in exchange for marketing exposure
Can take many forms, such as logo placement or naming rights (For example, Arsenal's Emirates Stadium)
Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
|
|
6. Public relations (PR)
Building relationships with the public and manage business reputation
Include media relations, product launches, crisis management and community outreach
Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
|
|
7. Digital communications
Promotions or communication delivered electronically, such as social media, search engine optimisation (SEO) or social media apps such as Instagram and Twitter
Can be used for building brand awareness, generating leads or driving sales
Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
|
|
Spending the marketing budget effectively
A marketing budget is the plan for marketing spending over a specific time period
A budget helps the business to determine how much can be spent on advertising, sales promotions and other promotional activity
It allows the effectiveness of the marketing department to be assessed
The size of the marketing budget can be calculated in several ways
Using market and competitor averages
E.g., using a proportion of sales revenues
Using the businesses marketing objectives
E.g., How much needs to be spent to increase market share by 5%
Using figures from the the previous year and adjusted for known changes in the marketing activities this year
E.g. the budget may have increased this year due to the development of a new product
A small budget limits the media a business can use for advertising or the techniques it can use
Smaller businesses often find it difficult to use promotion to compete with larger businesses
Online promotional activity may be the most cost-effective way to reach large or targeted audiences
A business will need to compare the cost of promotional activity with increases in sales it generates
Over time businesses will determine the most effective methods for their specific circumstances
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you can select suitable promotional strategies for particular products and explain why they are suitable. Remember that advertising does not necessarily increase sales and profits. More subtle promotional efforts can achieve outstanding results too.
Advertising may increase sales, but if prices have been reduced and advertising expenditure increased, then profits may not increase.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?