Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2018
Last exams 2026
Types of Business Growth (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 0450, 0986 & 0264, 0774
Reasons for business growth
Many firms start small & will grow into large companies or even multi-national corporations
E.g. Amazon and Dell both started in entrepreneurs' garages
Reasons why businesses grow
|
|
|
|
|
|
Methods of business growth
Business growth can be achieved by growing organically, or inorganically (mergers and takeovers)
1. Organic (internal) growth
Organic growth is growth that is driven by internal expansion using reinvested profits or loans
It is usually achieved by:
Gaining a greater market share
Product diversification
Opening new outlets
International expansion (new markets)
Investing in new technology/production machinery
Examples of organic growth
Business | Explanation |
|---|---|
Apple |
|
| |
Disney |
|
Product diversification opens up new revenue streams for a business
Firms may spend money on research and development, or innovation to existing products to help create a new revenue stream
Firms will often grow organically to the point where they are in a financial position to integrate (merge or buy) with others
Integration speeds up growth but also creates new challenges
Evaluating internal growth
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
2. Inorganic (external) growth
Firms will often grow organically to the point where they are in a financial position to integrate (merge or takeover) with others
Integration in the form of mergers or takeovers results in rapid business growth and is referred to as external or inorganic growth
A merger occurs when two or more companies combine to form a new company
The original companies cease to exist and their assets and liabilities are transferred to the newly created entity
A takeover occurs when one company purchases another company, often against its will
The acquiring company buys a controlling stake in the target company's shares (>50%) and gains control of its operations
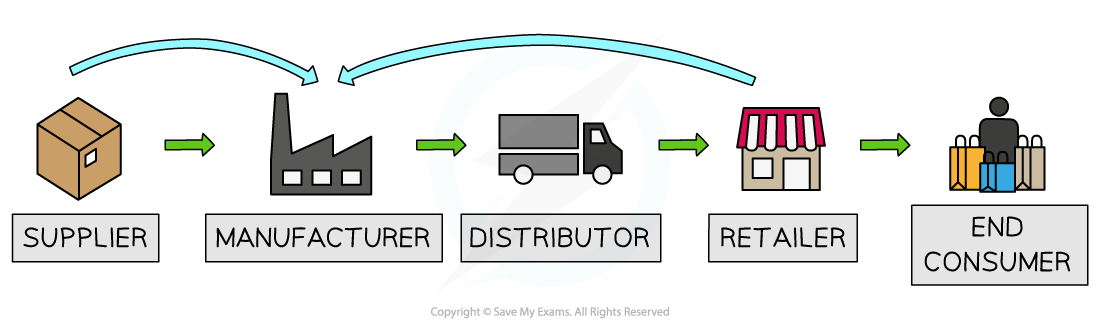
Vertical integration
Vertical integration refers to the merger or takeover of another firm in the supply chain or different stage of the production process
Forward vertical integration involves a merger with or takeover of a firm further forward in the supply chain
E.g. A dairy farmer merges with an ice cream manufacturer
Backward vertical integration involves a merger with or takeover of a firm further backwards in the supply chain
E.g. An ice cream retailer takes over an ice cream manufacturer
Horizontal integration
Horizontal integration is the merger or takeover of a firm at the same stage of the production process
E.g. An ice cream manufacturer merges with another ice cream manufacturer
Evaluating external growth
Type of growth | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Vertical integration |
|
|
Horizontal integration |
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?