Did this video help you?
Enzymes & pH: Extended (CIE IGCSE Biology: Co-ordinated Sciences (Double Award))
Revision Note
Enzymes & pH: Extended
Extended Tier Only
- The optimum pH for most enzymes is 7
- Some are produced in acidic conditions, such as the stomach; these have a lower optimum pH (pH 2)
- Some are produced in alkaline conditions, such as the duodenum, and have a higher optimum pH (pH 8 or 9)
- If the pH is too high or too low, the bonds that hold the amino acid chain together to make up the protein can be destroyed
- This will change the shape of the active site, so the substrate can no longer fit into it, reducing the rate of activity
- Moving too far away from the optimum pH will cause the enzyme to denature and activity will stop

Effect of pH on enzyme activity
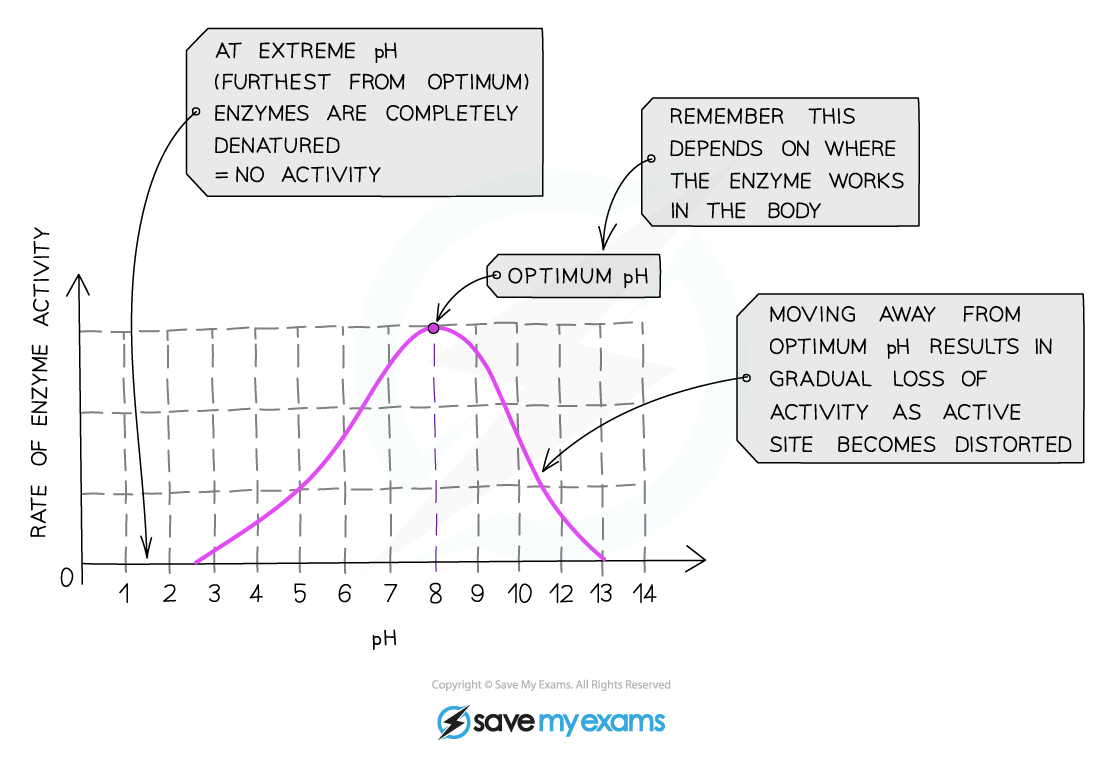
Graph showing the effect of pH on rate of activity for an enzyme from the duodenum

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
