The Production of Cloned Mammals (Edexcel IGCSE Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 4BI1
Cloning Mammals
Adult cell cloning
Adult cell cloning is achieved in the following way:
The nucleus is removed from an unfertilised egg cell, producing an enucleated egg cell
The diploid nucleus from a mature adult body cell, such as a skin cell, is inserted into the enucleated egg cell
A very small electric shock stimulates the cell to divide (by mitosis) to form an embryo
These embryo cells contain the same genetic information as the adult skin cell
When the embryo has developed into a ball of cells, it is inserted into the uterus of an adult female (known as the surrogate mother) to continue its development until birth
This process was used to create the first clone (exact genetic copy) of a mammal in 1996
Scientists in Scotland successfully cloned an adult female sheep
The clone was called Dolly
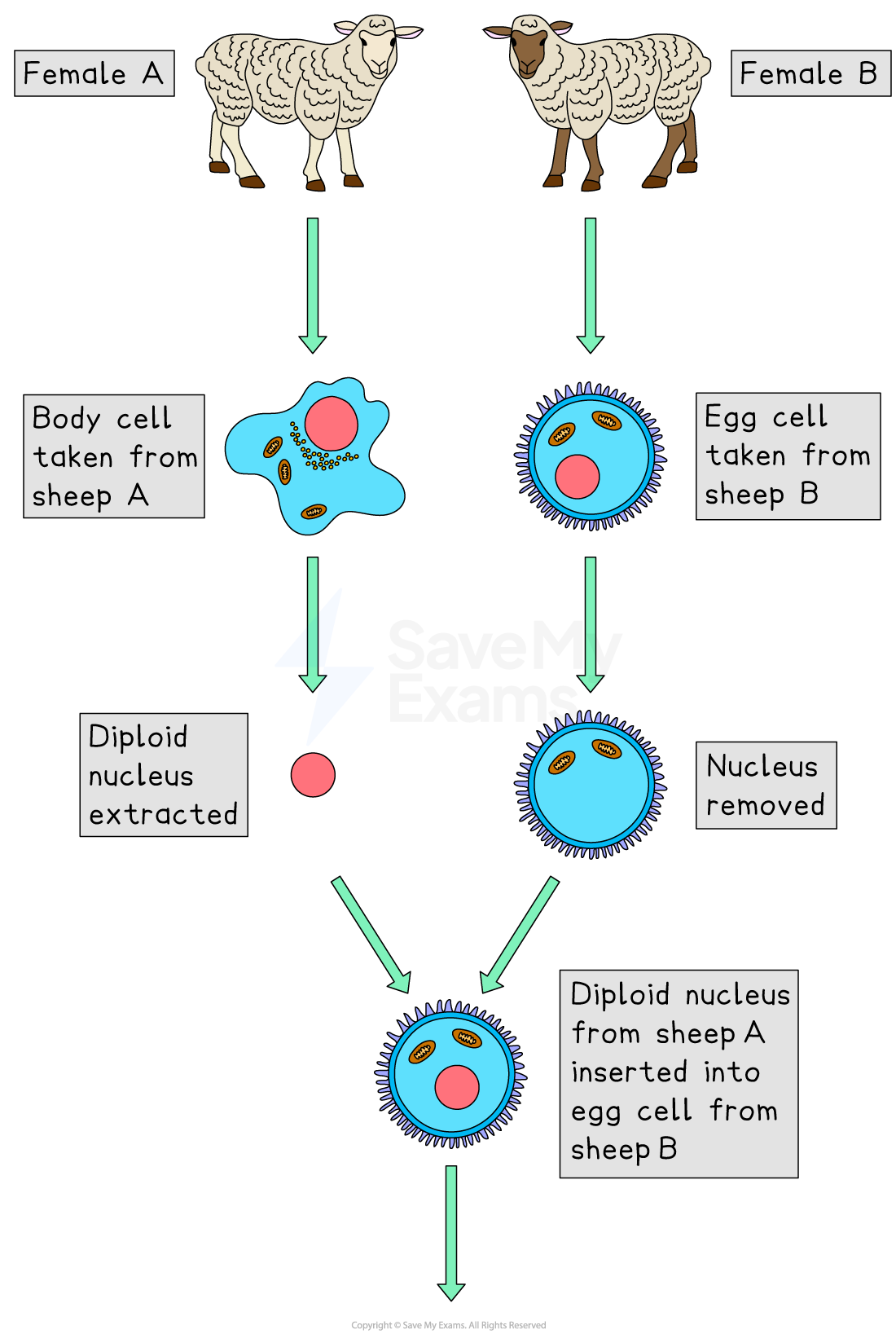

Adult cell cloning: the cloning technique used to produce the first cloned mammal, Dolly the sheep
Benefits & risks of cloning table
Benefits of cloning | Risks of cloning |
|---|---|
Cloning can be used to help preserve endangered species or resurrect extinct animals | Cloning results in a lack of genetic diversity. This can make clones more vulnerable to disease or changes in the environment, leaving the population at risk |
Cloning makes it possible to quickly and cheaply produce commercial quantities of consistently high-quality plants at any time of the year | There is some evidence that cloned animals may not be as healthy as normal ones |
Cloning allows farmers to increase yields by using high-quality livestock and plants | There are ethical concerns about cloning, especially when it comes to humans. Many people believe it is unethical to clone humans. Additionally, cloning in humans has a high rate of failure, with some unsuccessful attempts resulting in stillborn children or children with severe disabilities |
Cloning to Produce Human Proteins
Dolly the sheep was the first cloned mammal produced from an adult cell
Scientists can produce transgenic animals by inserting a foreign gene into their genome
The foreign gene can code for a useful protein, which the animal can then produce in its milk, eggs, or blood
Once a transgenic animal has been created, it can be cloned to produce more animals with the same trait
Uses of transgenic animals include producing useful proteins for medical purposes, such as proteins to treat diseases in humans

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
