Importance of Cell Differentiation (Edexcel IGCSE Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 4BI1
Did this video help you?
Cell Differentiation & Specialised Cells
The structural differences between different types of cells enable them to perform specific functions within an organism
Cell differentiation is an important process by which a cell changes to become specialised
Cell differentiation is how cells develop the structure and characteristics needed to be able to carry out their functions
Specialised cells are those that have developed certain characteristics that allow them to perform particular functions. Developing these characteristics is controlled by genes in the nucleus
As an organism develops, cells differentiate to form different types of cells
When a cell differentiates, it develops a structure and composition of subcellular structures which enables it to carry out a certain function
E.g. to form a nerve cell the cytoplasm and cell membrane of an undifferentiated cell must elongate to form connections over large distances

When a cell differentiates, it develops a structure and composition that enables it to carry out a particular function.
Differentiation and development
Stem cells are undifferentiated (unspecialised) cells that can divide by mitosis to form more stem cells or cells that go on to differentiate to become specialised cells
As a multicellular organism develops, its cells differentiate to form specialised cells
In animals, most cells differentiate at an early stage of development
As a result, animal cells lose their ability to differentiate early in the life of the organism
Specific cells in various locations throughout the body of an animal retain the ability to differentiate throughout the life of the animal
These undifferentiated cells are called adult stem cells and they are mainly involved in replacing and repairing cells, such as blood or skin cells
Plants differ from animals in that many types of plant cells retain the ability to fully differentiate throughout the life of a plant, not just in the early stages of development
Examples of specialised cells
Ciliated cell
Ciliated cells move mucus in the trachea and bronchi
They have hair-like extensions called cilia, which beat to transport mucus and trapped particles toward the throat

Ciliated epithelial cells
Nerve cell
Nerve cells conduct impulses and are long, allowing communication between different parts of the body and the central nervous system
Their axons are covered in a fatty sheath that insulates and speeds up nerve transmission

A nerve cell
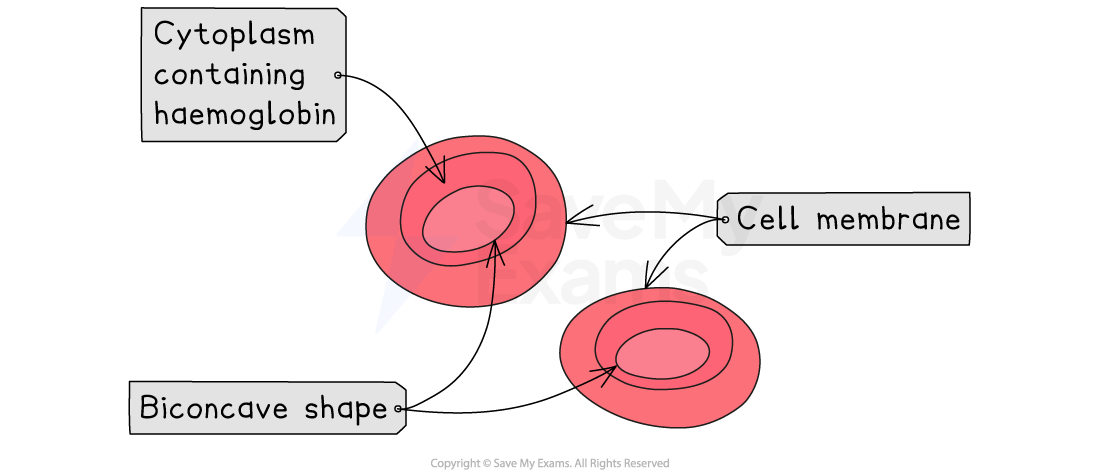
Red blood cell
Red blood cells transport oxygen efficiently due to their biconcave shape, which provides a high surface area to volume ratio for oxygen diffusion
Red blood cells are packed with the protein haemoglobin, which transports oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. Red blood cells do not have a nucleus, maximising space for haemoglobin to transport oxygen
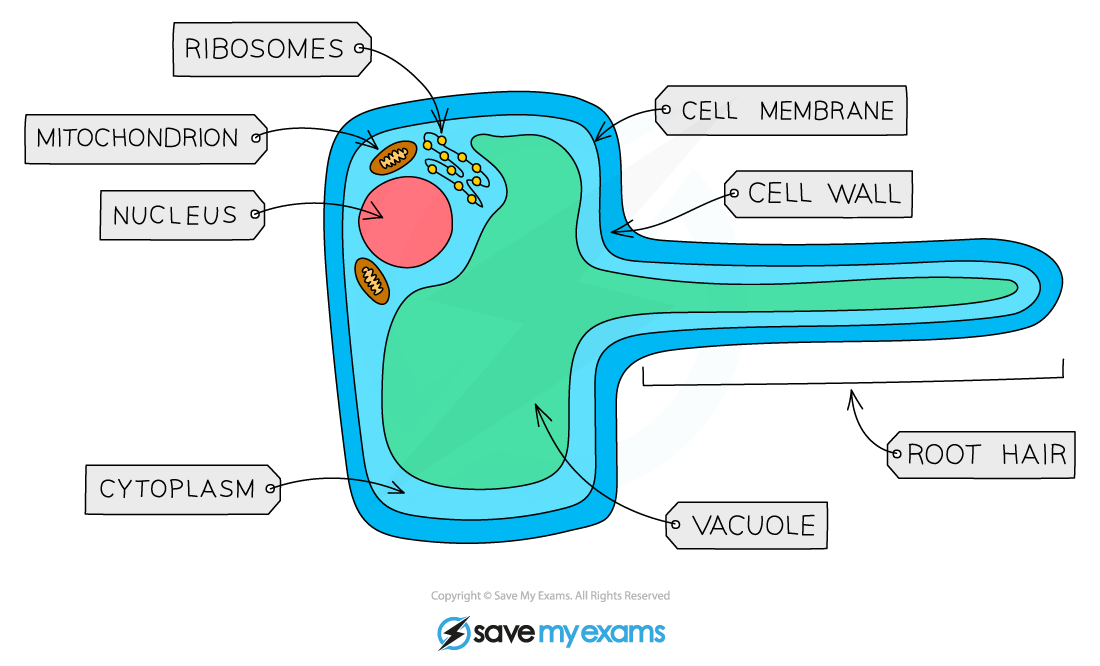
Root hair cell
Root hair cells absorb water and mineral ions from the soil
Root hair cells have long extensions to increase surface area for maximum absorption, and their thin walls help water move quickly through them
Root hair cell
Palisade mesophyll cell
Palisade mesophyll cells are found in the leaf and are adapted for photosynthesis
Palisade mesophyll cells contain many chloroplasts
The cells are column-shaped and tightly packed together beneath the upper epidermis of the leaf to maximise light absorption for photosynthesis

Palisade mesophyll cell

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?