Asexual Reproduction (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 0610 & 0970
Did this video help you?
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction does not involve sex cells or fertilisation
Only one parent is required so there is no fusion of gametes and no mixing of genetic information
As a result, the offspring are genetically identical to the parent and to each other (clones)
Asexual reproduction is defined as a process resulting in genetically identical offspring from one parent
Examples of Asexual Reproduction
Bacteria produce exact genetic copies of themselves in a type of asexual reproduction called binary fission:
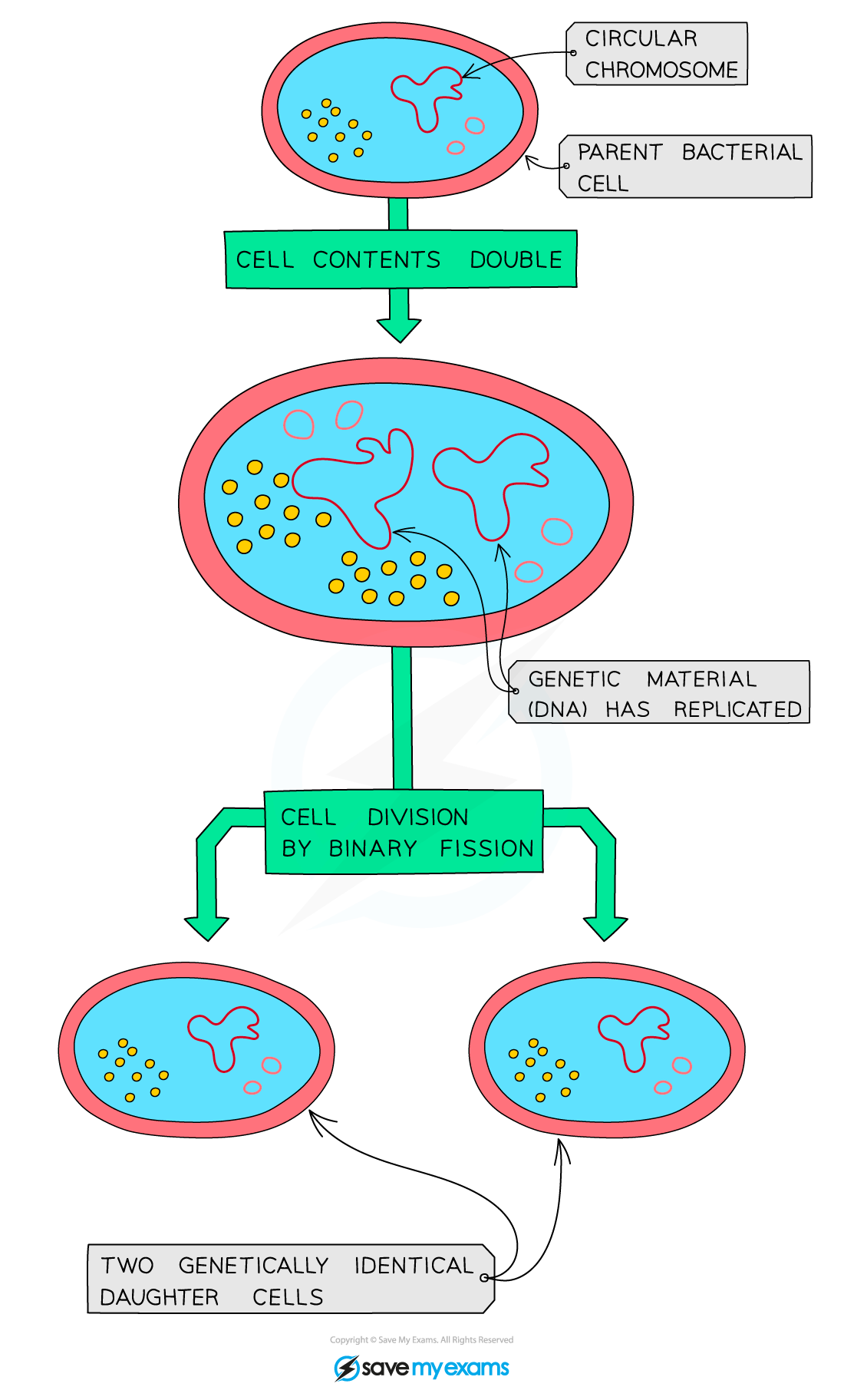
Bacteria produce exact genetic copies of themselves in a type of asexual reproduction called binary fission
Plants can reproduce asexually using bulbs and tubers; these are food storage organs from which budding can occur, producing new plants which are genetically identical to the parent plant:

Some plants develop underground food storage organs that will develop into next years plants - they can take different forms, such as bulbs or tubers
Some plants grow side shoots called runners that contain tiny plantlets on them (a good example of this are strawberry plants. These will grow roots and develop into separate plants, again being genetically identical to the parent plant:

Some plants grow side shoots called runners that contain tiny plantlets on them. These will grow roots and develop into separate plants.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction: Extended
Species Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Wild species | Rapid population growth | Limited genetic variation in population - offspring are genetically identical to their parents |
Can exploit suitable environments quickly | Vulnerability to habitat changes e.g. temperature changes, droughts or new predators | |
More time and energy-efficient | Disease is likely to affect the whole population as there is no genetic variation | |
Reproduction is completed much faster than sexual reproduction | No recombination of genes means evolution is slow | |
Crop plants | Crops can be produced with desired characteristics e.g. high yield, disease-resistant, drought resistant | Crops will not adapt to changes in climate if produced asexually |
Crops can be produced with uniform characteristics necessary for commercial sale | The process of asexual reproduction in crops requires human input and management | |
Production of crops can be faster | If a diseased parent plant is used in the reproduction process, the offspring will also be diseased | |
The cost of production will be less than investing in seeds | Vulnerability to disease or pests may result in big financial losses for the farmer |

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?