Did this video help you?
Linear Graphs (CIE IGCSE Additional Maths)
Revision Note
Equations of a Straight Line
How do I find the gradient of a straight line?
- Find two points that the line passes through with coordinates (x1, y1) and (x2, y2)
- The gradient between these two points is calculated by
- The gradient of a straight line measures its slope
- A line with gradient 1 will go up 1 unit for every unit it goes to the right
- A line with gradient -2 will go down two units for every unit it goes to the right

What are the equations of a straight line?
- This is the gradient-intercept form
- It clearly shows the gradient m and the y-intercept (0, c)
-
- This is the point-gradient form
- It clearly shows the gradient m and a point on the line (x1, y1)
- This is the general form
- You can quickly get the x-intercept
and y-intercept

How do I find an equation of a straight line?
- You will need the gradient
- If you are given two points then first find the gradient
- It is easiest to start with the point-gradient form
- then rearrange into whatever form is required
- multiplying both sides by any denominators will get rid of fractions
- then rearrange into whatever form is required

Examiner Tip
- Quickly sketching the graph of the straight line(s) can be helpful if you are struggling with an exam question
- Ensure you state equations of straight lines in the format required
- Usually
or
- Check whether coefficients need to be integers (they usually are for
)
- Usually
Worked example
Find the equation of the straight line with gradient 3 that passes through (5, 4).
We know that the gradient is 3 so the line takes the form
To find the value of c, substitute (5, 4) into the equation
Replace c with −11 to complete the equation of the line
y = 3x − 11
You may find it helpful to sketch the information given
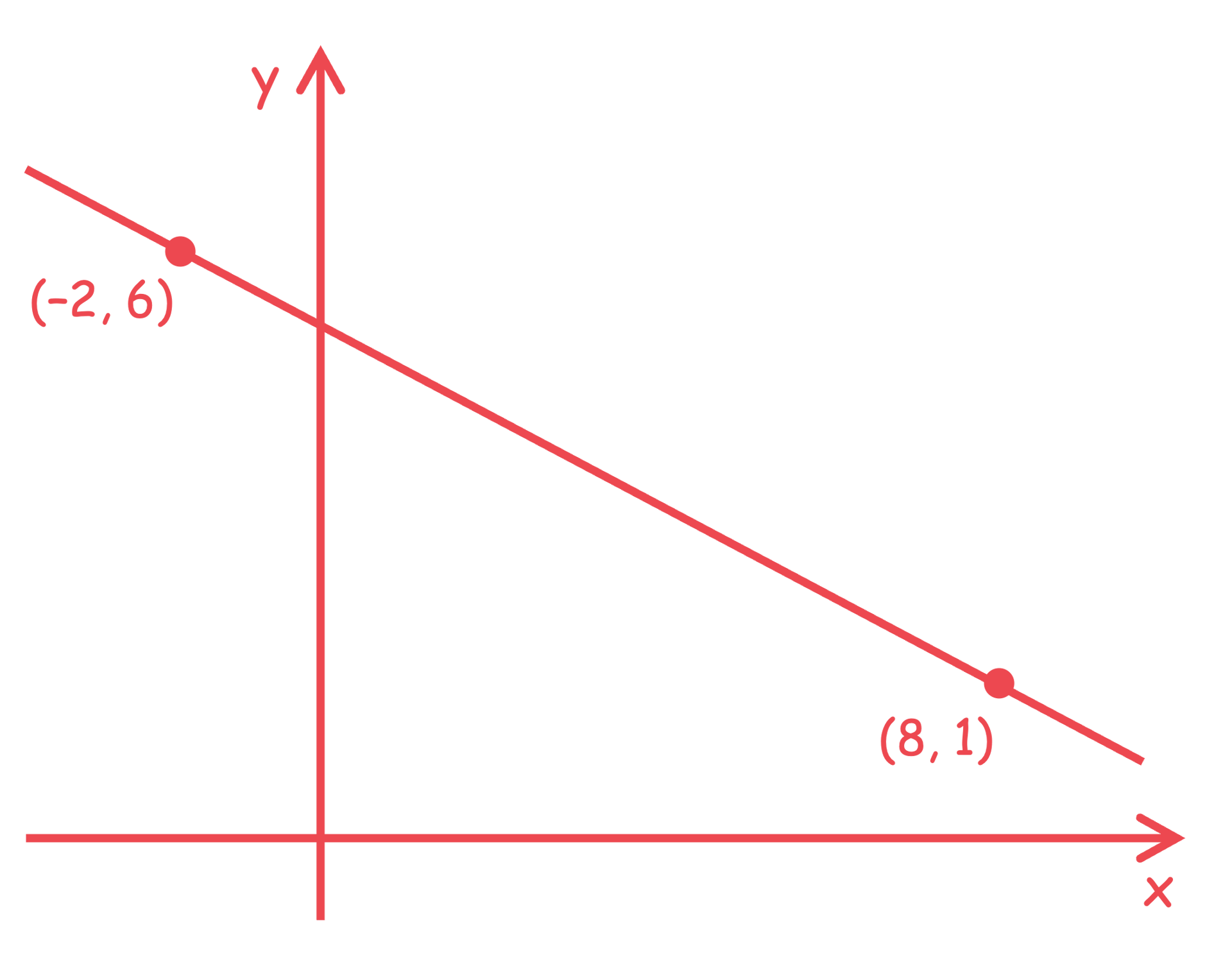
To find the value of c, substitute either of the given points into this equation. Here we will pick (8, 1) as it is doesn't contain negative numbers so is easier to work with
Replace c with −11 to complete the equation of the line
Midpoint of a Straight Line
How do I find the midpoint of a line (segment)?
- The midpoint of a line will be the same distance from both endpoints
- You can think of a midpoint as being the average (mean) of two coordinates
- The midpoint of
and
is

- M is often used as the midpoint between two points (x1, y1) (x2, y2)
- It is the average of both the x and y coordinates
Worked example
The coordinates of A are (−4, 3) and the coordinates of B are (8, −12).
Find M, the midpoint of AB.
The midpoint can be found using M =
Fill in the values of x and y from each coordinate
Simplify
M = (2, −4.5)
Length of a Straight Line
How do I calculate the length of a line?
- The distance between two points with coordinates
and
can be found using the formula
- This formula is really just Pythagoras’ Theorem
, applied to the difference in the
-coordinates and the difference in the
-coordinates;

- You may be asked to find the length of a diagonal in 3D space
- This can be answered using 3D Pythagoras
Examiner Tip
- Work with the square of a distance for as long as possible as this avoids early rounding errors
- In the non-calculator paper your answer may need to be left as a surd
- Only square root when forced to or for a final answer, and use the ANS button (and other memory features) on your calculator
Worked example
Point A has coordinates (3, -4) and point B has coordinates (-5, 2).
Calculate the distance of the line segment AB.
Using the formula for the distance between two points,
Substituting in the two given coordinates:
Simplify:
Answer = 10 units

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
