Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2021
Last exams 2026
Depreciation (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Accounting): Revision Note
Exam code: 0452 & 0985
Introduction to depreciation
What is depreciation?
Depreciation is applied to non-current assets to represent the reduction in their value
Depreciation is the financial measure of how the value of an asset decreases over time
The value of a non-current asset depreciates due to:
Wear and tear of the asset
The asset becoming outdated or obsolete
The reduction in the expected useful lifetime of the asset
The asset being used up or depleted
Depreciation is an expense that accounts for the estimated loss in value of an asset during a given period
It is an expense that does not involve spending money
It is used to spread the cost of the assets over their expected useful life
You need to know three methods to calculate depreciation
Straight-line method
Reducing balance method
Revaluation method
The accounting principle of consistency states that when a business chooses a method of depreciation for a type of non-current asset, it must use that method each year unless there is a valid reason to change to a different method
Different methods can be used for different types of non-current assets
Why are non-current assets depreciated?
Depreciation is used so that the business adheres to the following accounting principles:
Matching
The capital expenditure of a non-current asset is matched against the income that it has contributed to
Suppose that a business buys a vehicle for $30 000 and expects it to be useful for 8 years
The full $30 000 should not be charged as an expense straightaway
Instead, the expense should be spread out over the 8 years that it is contributing to income
Prudence
The value of the assets should not be overstated
Depreciation allows the business to report a more realistic estimation for the valuation of its assets
Is depreciation charged in the years of purchase and sale?
Different businesses will have different policies for dealing with depreciation for the year in which the asset is purchased and the year in which the asset is sold or disposed of
The business could:
Charge a full year’s worth of depreciation
Charge no depreciation
Charge a proportion of the full year’s worth of depreciation
The exam question will specify which rules should be used
Straight-line depreciation
What is the straight-line method of depreciation?
The straight-line method of depreciation assumes that a non-current asset loses value at a constant rate over its useful life
This means that the expense for its depreciation is the same each year
The net book value can reach $0
This is when the asset is fully depreciated
You could be given the depreciation rate as a percentage of its original value
E.g. depreciation could be charged at 20% of its original cost
Or you could be expected to calculate the depreciation using:
The number of years that the non-current asset will be used
The expected value of the non-current asset at the end of its working life
This value could be $0
The expected value is also called the residual value
This method is usually used when the asset will be equally valuable for each year of its use
For example, fixtures and fittings, equipment, etc

How do I calculate depreciation using the straight-line method?
If you are given the percentage for the depreciation
Find the percentage of the original amount
This will be the yearly depreciation charge
If you are not given the percentage
Calculate the expected loss in value during the expected life of the non-current asset
The original value minus the expected value at the end of its life
Divide the loss by the number of years it will be used
This will be the yearly depreciation charge
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The straight-line method is similar to simple interest calculations used in maths.
Worked Example
Abi purchases machinery for $18 000. Machinery is depreciated at 15% per annum using the straight-line method.
Calculate the net book value of the machinery after 3 years.
Answer:
Calculate the yearly expense due to depreciation
15% × $18 000 = $2 700
Calculate the total depreciation after 3 years
3 × $2 700 = $8 100
Subtract the depreciation from the original value
$18 000 - $8 100 = $9 900
Worked Example
Taiki purchases a vehicle for $30 000. He expects to use the vehicle for 3 years, after which he estimates that it will have a value of $12 000.
Calculate the yearly expense due to the depreciation of the vehicle.
Answer:
Calculate the loss in value over the 3 years
$30 000 - $12 000 = $18 000
Divide this by the number of years
$18 000 ÷ 3 = $6 000
Reducing balance depreciation
What is the reducing balance method of depreciation?
The reducing balance method of depreciation assumes that the non-current asset loses value at a rate proportional to its current value
This means that the expense for its depreciation gets smaller each year as the current value decreases
You will be told the percentage of the current value to use for depreciation
This method is usually used when a non-current asset initially loses value at a fast rate
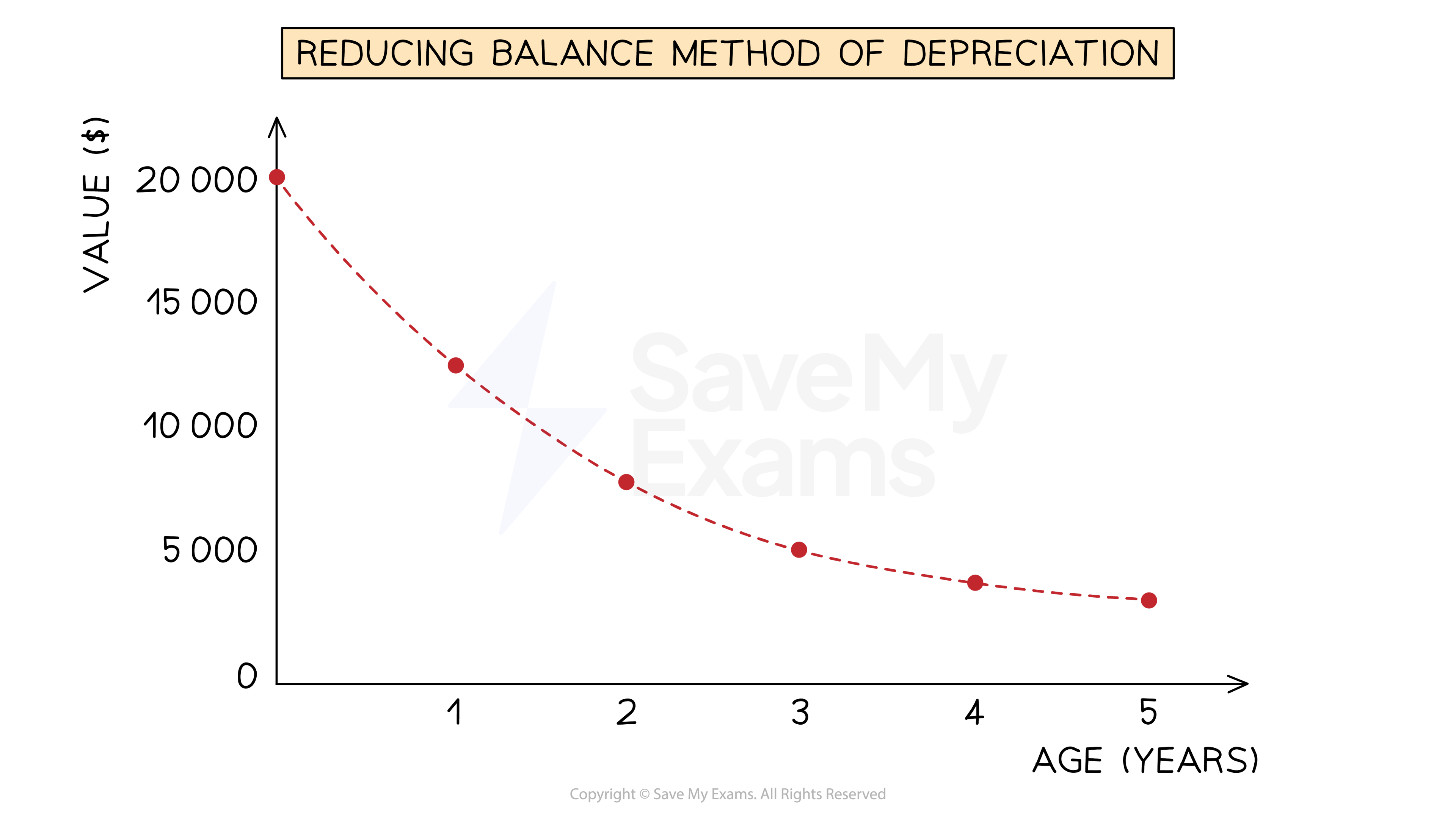
How do I calculate depreciation using the reducing balance method?
Find the percentage of the current net book value
This will be the depreciation charge for that year
If you need to calculate the depreciation for multiple years, then calculate one year at a time
Find the depreciation charge for one year using the net book value at that start of the year
Subtract this amount from the net book value at the start of the year to find the new net book value
Find the depreciation charge for the next year using the net book value at the start of that year
Continue this process
If you just need to find the current net book value then you can use some maths skills
Subtract the percentage from 100%
Write this as a decimal
Raise this to the power of the number of years
Multiply this by the original value
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The reducing balance method is similar to compound interest calculations used in maths.
Amounts should always be given to the nearest dollar in exams.
Worked Example
Abi purchases a vehicle for $16 000. Machinery is depreciated at 25% per annum using the reducing balance method.
Calculate the net book value of the machinery after 3 years.
Answer:
Method 1: Year-by-year
Find the depreciation charged in each year by finding the percentage of the net book value at that time
Subtract that year’s depreciation from the net book value to find the net book value at the end of the year
End of year | Depreciation charge | Net book value |
0 | - | $16 000 |
1 | 25% × $16 000 = $4 000 | $16 000 - $4 000 = $12 000 |
2 | 25% × $12 000 = $3 000 | $12 000 - $3 000 = $9 000 |
3 | 25% × $9 000 = $2 250 | $9 000 - $2 250 = $6 750 |
Method 2: Compound interest
Subtract the percentage from 100%
100% - 25% = 75%
Write this as a decimal
75% = 0.75
Raise this to the power of the number of years
0.753
Multiply this by the original value
$16 000 × 0.753 = $6 750
Revaluation depreciation
What is the revaluation method of depreciation?
The revaluation method of depreciation involves performing a valuation of assets at the end of the financial year to determine the reduction in value
This method is commonly used for assets of smaller value
Such as loose tools, packing cases

How do I calculate depreciation using the revaluation method?
A revaluation of the non-current asset will be given in the question
You need to identify two numbers:
The net book value before the revaluation
The net book value after the revaluation
The depreciation charge is the value before minus the value after
Worked Example
Abi purchased fixtures and fittings for $5 000 on 1 March 2023. On 29 February 2024, at the end of the financial year, the fixtures and fittings were valued at $3 650.
Calculate the depreciation charged for the financial year ending on 29 February 2024.
Answer:
Value before the revaluation is $5 000
Value after the revaluation is $3 650
Calculate the difference
$5 000 - $3 650 = $1 350

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
