What is nuclear fission?
In IGCSE Physics, nuclear fission is the splitting of a large, unstable nucleus into two smaller nuclei and energy is released in the process.
Nuclear fission begins when the heavy nucleus absorbs an extra neutron, causing it to become unstable and break apart. Two smaller daughter nuclei are produced, as well as two or three neutrons, which can go on to trigger further fission reactions in a chain reaction.
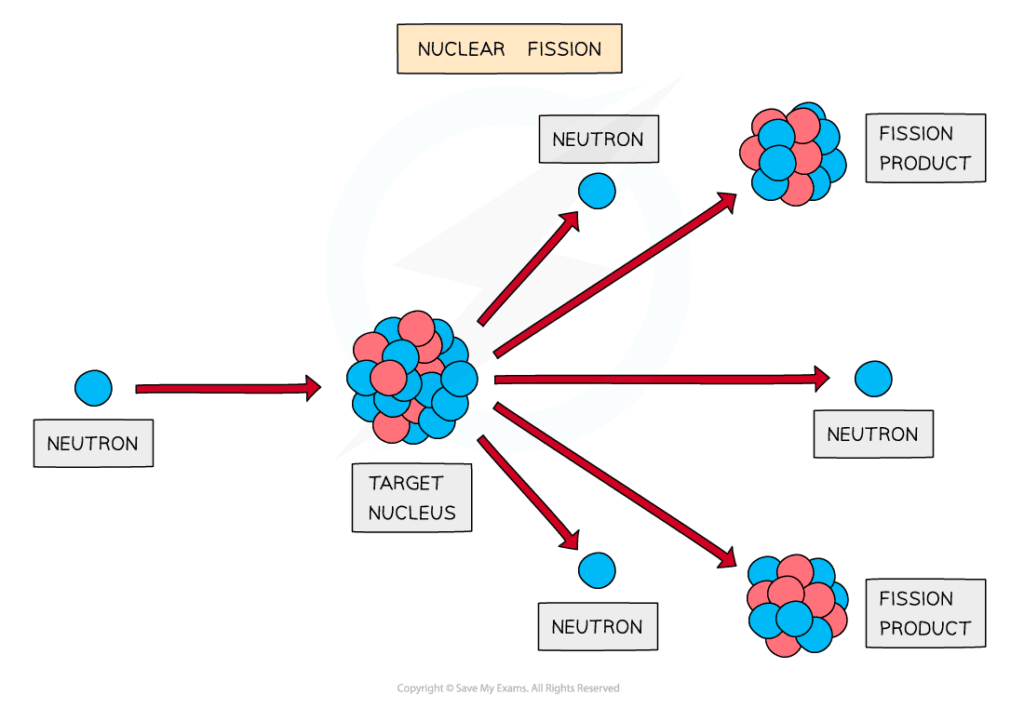
This chain reaction is the principle behind nuclear power plants, where the energy released from fission is used to heat water, produce steam, and drive turbines to generate electricity.
Examiner-written IGCSE Physics revision resources that improve your grades 2x
- Written by expert teachers and examiners
- Aligned to exam specifications
- Everything you need to know, and nothing you don’t

Share this article


 written revision resources that improve your
written revision resources that improve your