What is atomic number?
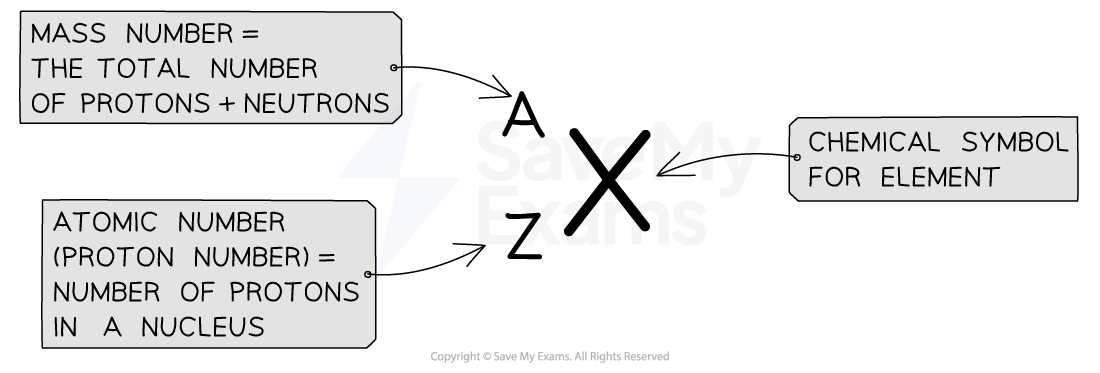
In IGCSE chemistry, the atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and is unique to each element. It determines the element’s identity and position in the Periodic Table.
For example, hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, meaning it has one proton, while oxygen has an atomic number of 8, meaning it has eight protons. In a neutral atom, the atomic number also equals the number of electrons, which balance the positive charge of the protons. The atomic number is essential in understanding chemical properties and reactions in IGCSE Chemistry.
Atomic Number Revision Resources to Ace Your Exams
For more information about atomic number check out the following resources:
Examiner-written IGCSE Chemistry revision resources that improve your grades 2x
- Written by expert teachers and examiners
- Aligned to exam specifications
- Everything you need to know, and nothing you don’t

Share this article

 written revision resources that improve your
written revision resources that improve your