What is the limit of proportionality?
In GCSE Physics, the limit of proportionality refers to the point on a force-extension graph where a material stops obeying Hooke's law. Hooke's law states that the extension of a material is directly proportional to the applied force, meaning that if the force doubles, the extension doubles as well.
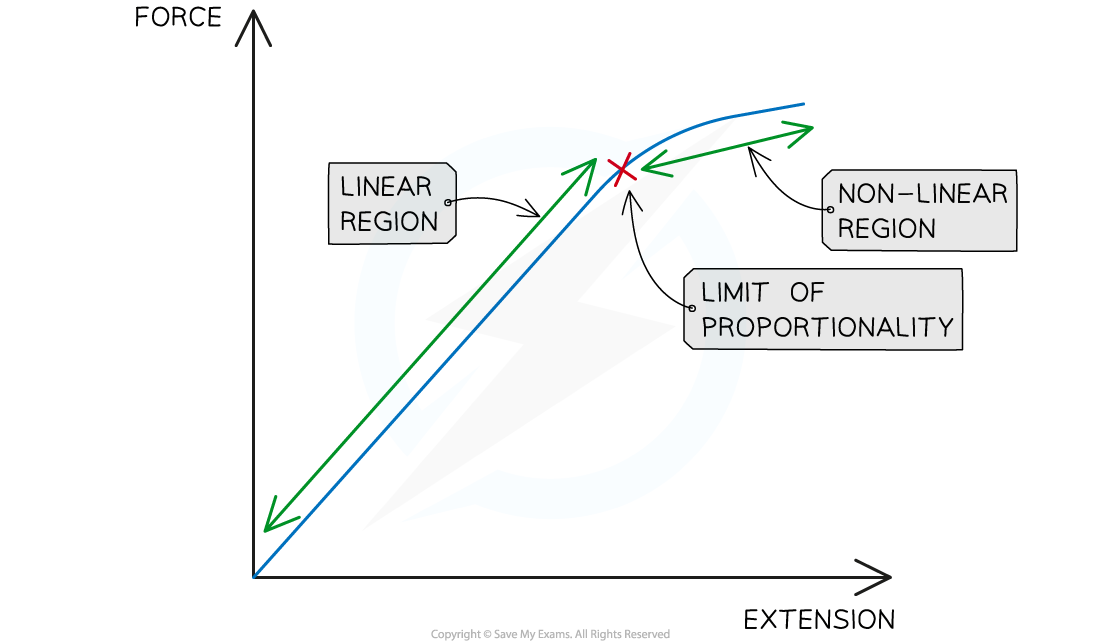
Beyond the limit of proportionality, Hooke's law no longer applies; the extension and force applied are no longer directly proportional.
Examiner-written GCSE Physics revision resources that improve your grades 2x
- Written by expert teachers and examiners
- Aligned to exam specifications
- Everything you need to know, and nothing you don’t

Share this article
 written revision resources that improve your
written revision resources that improve your