The Cosine Rule is a formula used in trigonometry to find missing sides or angles in any triangle, not just right-angled ones. It is particularly useful when you know two sides of a triangle and the angle between them, or when you know all three sides but want to find an angle.
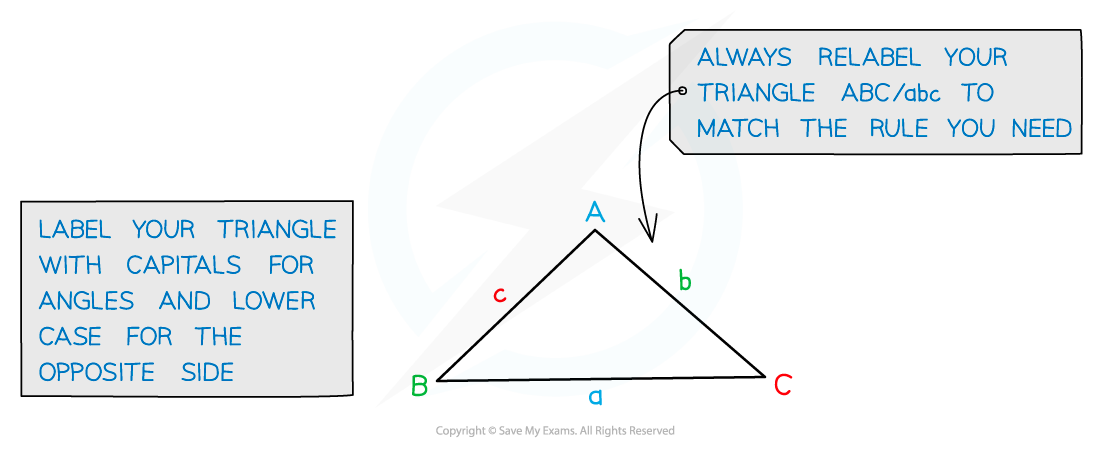
The Cosine Rule states that in any triangle:
where:
c is the side opposite to angle C,
a and b are the other two sides, and
C is the included angle between sides a and b.
By rearranging the formula, you can also find an angle if you know all three sides. The Cosine Rule helps solve problems involving triangles in a straightforward way and is an important part of the GCSE Maths curriculum.
Examiner-written GCSE Maths revision resources that improve your grades 2x
- Written by expert teachers and examiners
- Aligned to exam specifications
- Everything you need to know, and nothing you don’t

Share this article


 written revision resources that improve your
written revision resources that improve your