Box plot - GCSE Maths Definition
Reviewed by: Dan Finlay
Last updated
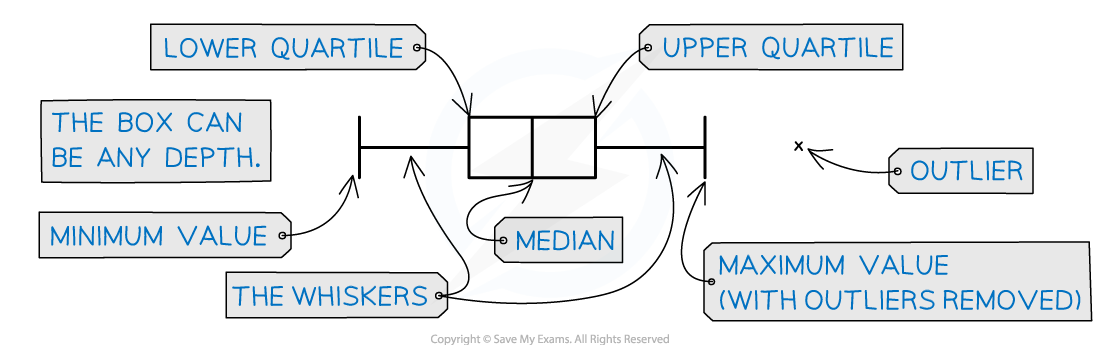
A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical method used in statistics to display the distribution of a data set. It provides a visual summary of key data points: the minimum, lower quartile, median, upper quartile, and maximum. The 'box' represents the interquartile range, which contains the middle 50% of the data, while the 'whiskers' extend to the smallest and largest values excluding any outliers. Box plots are useful for comparing different sets of data and identifying any skewness, variation, and potential outliers, making them an essential tool for GCSE Maths students to analyse data effectively.
Examiner-written GCSE Maths revision resources that improve your grades 2x
- Written by expert teachers and examiners
- Aligned to exam specifications
- Everything you need to know, and nothing you don’t

Share this article

 written revision resources that improve your
written revision resources that improve your