Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient (Edexcel GCSE Statistics): Revision Note
Exam code: 1ST0
Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient
What is Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient?
Spearman's rank correlation coefficient measures the strength of the correlation between two data sets
i.e., to what extent does one always go up when the other one goes up (or always go down when the other one goes up)
It is not always easy to see this clearly on a scatter diagram
The notation for the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient of a sample is
Spearman's rank correlation coefficient is always a number between -1 and 1
i.e.
The value of
tells you about the type and strength of any correlation
A positive value (
) means there is positive correlation between the data sets
An
value close to 1 means strong positive correlation
If
is zero (
), then there is no correlation
A negative value (
) means there is negative correlation between the data sets
An
value close to -1 means strong negative correlation
In general, the closer to 1 or -1 that
is, the stronger the correlation between the data sets
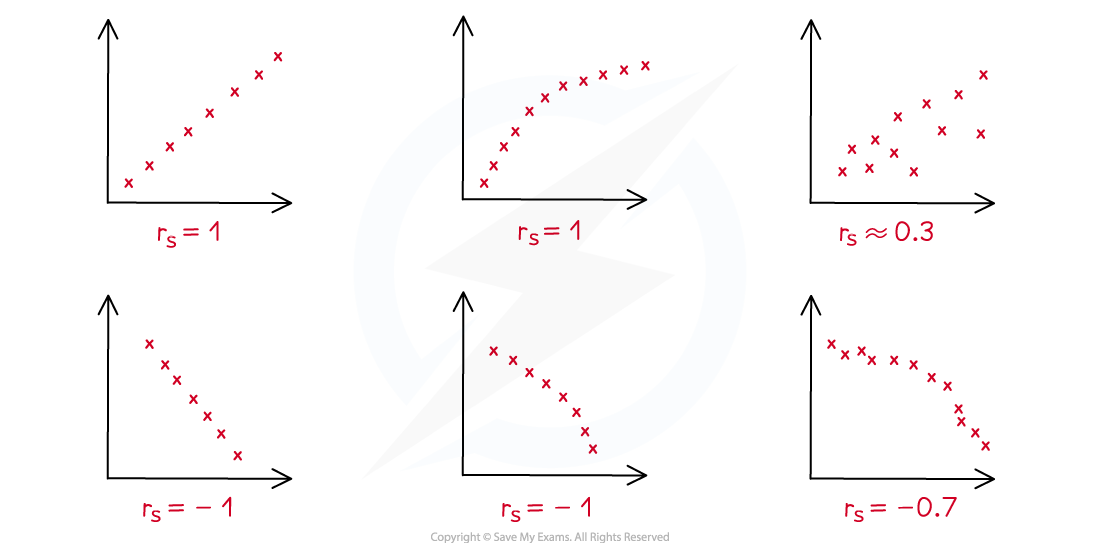
For example, if
is calculated for the rankings of competitors given by two judges in a competition, then
would mean there was perfect agreement between the two judges' rankings
would mean the rankings were in completely opposite orders
would mean there was no agreement in the ranks given (but also not consistent disagreement)
Spearman's rank correlation coefficient does not tell you anything about whether or not the data points lie along a straight line
It only tells you how true it is that one always tends to go up (or down) when the other one goes up
Worked Example
Regina has been watching the judging at a 'best jam' competition at a village fête.
Two judges ranked the 10 different jams that were submitted for the competition.
Regina calculated the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient for the ranks given by the judges.
She got a value of .
(a) What type of correlation is shown by the value ? Select one of the three options below:
Negative correlation No correlation Positive correlation
The value is negative, which means negative correlation
Negative correlation
(b) Interpret Regina’s value.
The value is close to -1, which indicates strong negative correlation
This means there was quite a lot of disagreement between the judges' rankings
-0.8 is close to -1, so there is a strong amount of disagreement between the judges' rankings. One tended to like the jams that the other one didn't like, and vice versa.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?