Estimating Speeds & Accelerations (OCR GCSE Combined Science A (Gateway)) : Revision Note
Typical Speeds
The table below gives some typical speeds (in m/s) for various everyday scenarios
Typical Speeds Table

Note that typical speeds of a person walking, running or cycling depends on a variety of factors, such as:
Age
Terrain
Fitness
Distance
Similarly, typical speeds of transportation systems like cars or planes will depend on their:
Shape
Design
Cost
Purpose
Worked Example
A student claims that people typically walk at 6 m/s.
a) State whether or not you agree with this claim and explain your reasoning.
b) Suggest a factor that can affect the typical speeds of a person walking.
Answer:
Part (a)
The student’s claim is incorrect because 6 m/s is too fast
The typical speed that people walk at is about 1.5 m/s
Part (b)
Some factors that can affect the typical speeds of a person walking are:
The terrain might be wet, rocky or steep
The age of the person
The fitness of the person
The length of the walk or journey
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You may be asked to recall typical values of speed for a person walking, running or cycling, or comment on typical values of speed for different types of transportation system - so learn the values in this table and have an idea about how they compare to each other.
Estimating Accelerations
The acceleration of an object is a measure of how quickly its velocity changes
A typical family car, for example, takes around 10 seconds to go from 0 m/s to 27 m/s (roughly 60 mph)
This is an acceleration of about 2.7 m/s2
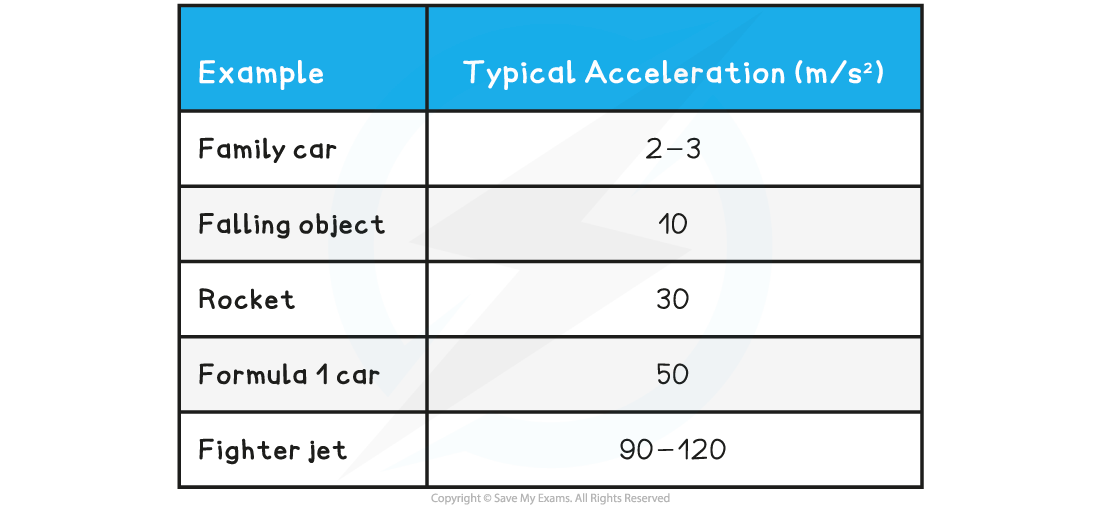
The table below gives some other typical accelerations:
Typical Accelerations Table
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You should be able to estimate the magnitude of everyday accelerations. Memorise the examples given in the table to develop a sense of the magnitude of different accelerating objects.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
