Calculating Speed (OCR GCSE Combined Science A (Gateway)) : Revision Note
Calculating Speed
For objects that are moving with a constant speed, use the equation below to calculate the speed:


Where:
v = speed in metres per second (m/s)
s = distance travelled in metres (m)
t = time taken in seconds (s)
Calculating Average Speed
In some cases, the speed of a moving object is not constant
For example, the object might be moving faster or slower at certain moments in time (accelerating and decelerating)
Because its speed is not constant, it is moving with non-uniform motion
The average speed of an object is given by the equation:

Total distance is again measured in metres, m
Total time is measured in seconds, s
Average speed is therefore also measured in metres per second, m/s
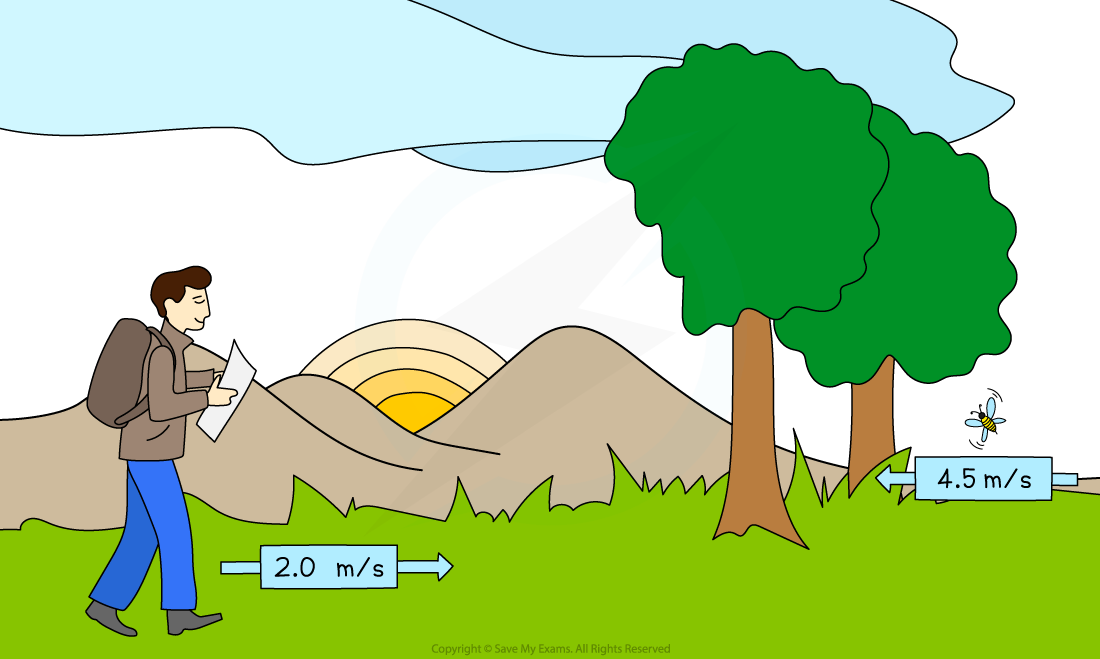
A hiker might have an average speed of 2.0 m/s, whereas a particularly excited bumble bee can have average speeds of up to 4.5 m/s
The equation for average speed can be rearranged with the help of a formula triangle as shown:

Average speed, total distance, time formula triangle
Average Speed & Non-Uniform Motion
The average speed of an object is rarely constant
Hikers change their pace continuously as they walk
Bumblebees buzz around in all directions with varying speed
Cars are constantly speeding up and slowing down throughout a journey
Non-uniform motion refers to motion that is changing
Changing motion can mean the object is changing its speed, direction or both

Race drivers know all about non-uniform motion, especially slowing down for corners and speeding up on the straight sections of track
Worked Example
Florence Griffith Joyner set the women’s 100 m world record in 1988, with a time of 10.49 s. Calculate her average speed during the race.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Distance, s = 100 m
Time, t = 10.49 s
Step 2: Write the relevant equation
Sprinters typically speed up out of the blocks up to some maximum speed
Because Florence’s speed changes over the race, we can calculate her average speed using the equation:
average speed = total distance ÷ time taken
Step 3: Check any unit conversions
Check that all quantities given in the question are in standard units
In this example, they are all in standard units
Step 4: Substitute the values for total distance and time
Average speed = 100 ÷ 10.49 = 9.53288... = 9.53 m/s
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember that average speed is the mean speed of the moving object.
Its speed at a specific moment could be higher or lower - so because the speed changes you need to consider the total distance and time taken.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

