Half-Life (Edexcel GCSE Combined Science) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Half-Life
It is impossible to know when a particular unstable nucleus will decay
But the rate at which the activity of a sample decreases can be known
This is known as the half-life
Half-life is defined as:
The time taken for half the undecayed nuclei to decay or the activity of a source to decay by half
In other words, the time it takes for the activity of a sample to fall to half its original level
Different isotopes have different half-lives and half-lives can vary from a fraction of a second to billions of years in length
Using Half-life
Scientists can measure the half-lives of different isotopes accurately:
Uranium-235 has a half-life of 704 million years
This means it would take 704 million years for the activity of a uranium-235 sample to decrease to half its original amount
Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5700 years
So after 5700 years, there would be 50% of the original amount of carbon-14 remaining
After two half-lives, or 11 400 years, there would be just 25% of the carbon-14 remaining
With each half-life, the amount remaining decreases by half
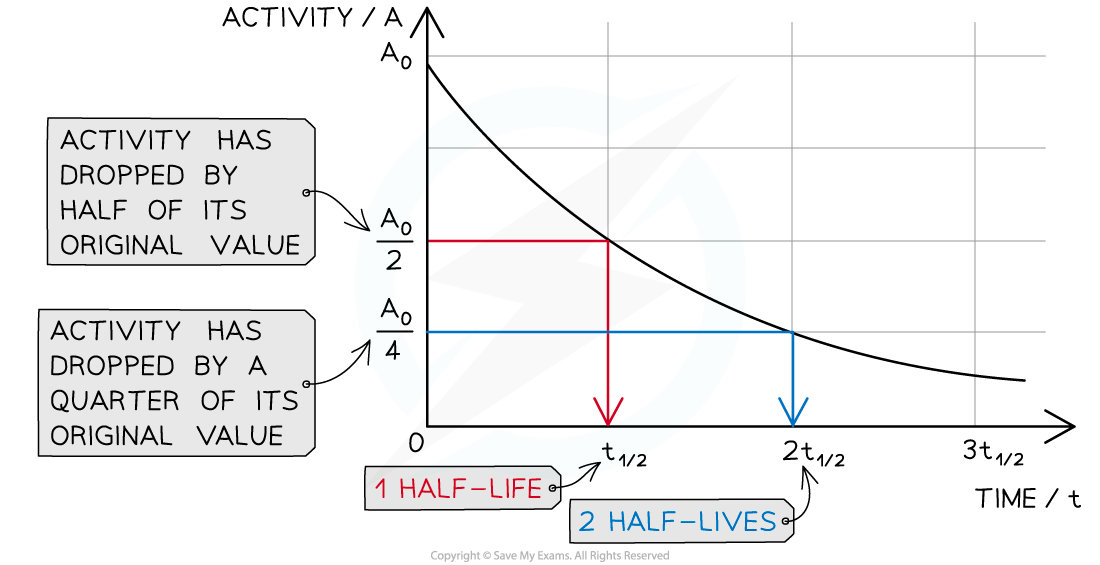
Graph showing how the activity of a radioactive sample changes over time. Each time the original activity halves, another half-life has passed
The time it takes for the activity of the sample to decrease from 100 % to 50 % is the half-life
It is the same length of time as it would take to decrease from 50 % activity to 25 % activity
The half-life is constant for a particular isotope
Half-Life Calculations
To calculate the half-life of a sample, the procedure is:
Measure the initial activity, A0, of the sample
Determine the half-life of this original activity
Measure how the activity changes with time
The time taken for the activity to decrease to half its original value is the half-life
Worked Example
The radioisotope technetium is used extensively in medicine. The graph below shows how the activity of a sample varies with time.
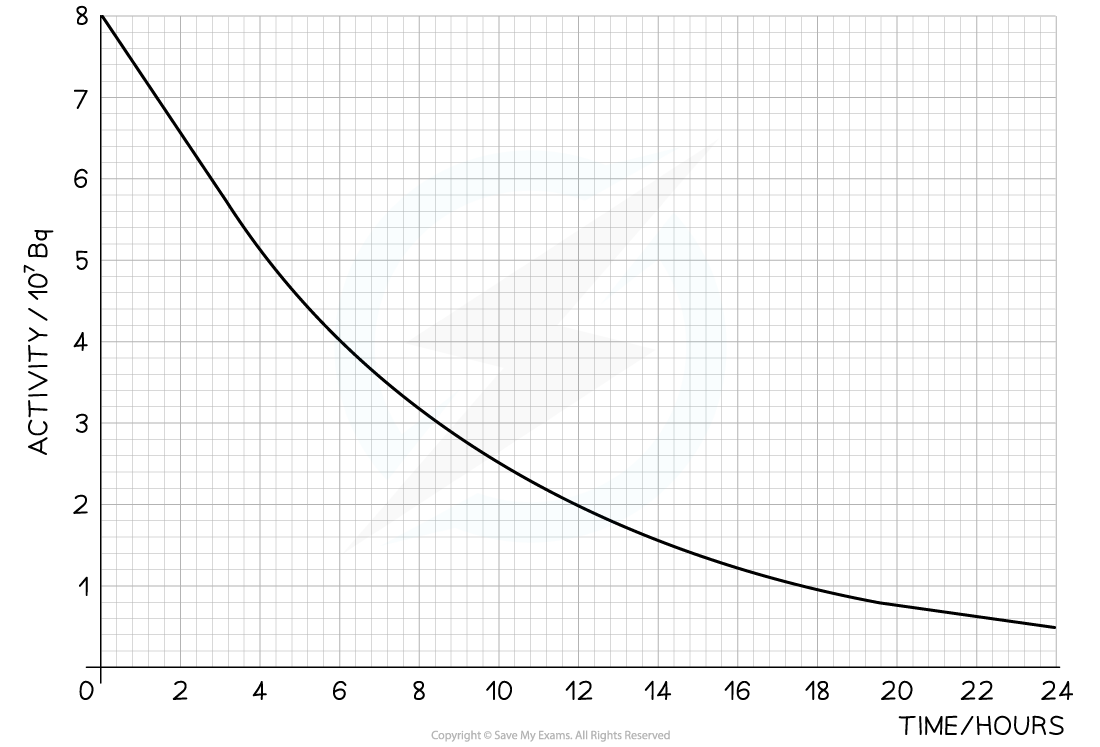
Determine the half-life of this material.
Answer:
Step 1: Draw lines on the graph to determine the time it takes for technetium to drop to half of its original activity

Step 2: Read the half-life from the graph
In the diagram above the initial activity, A0, is 8 × 107 Bq
The time taken to decrease to 4 × 107 Bq, or ½ A0, is 6 hours
The time taken to decrease to 2 × 107 Bq is 6 more hours
The time taken to decrease to 1 × 107 Bq is 6 more hours
Therefore, the half-life of this isotope is 6 hours
Worked Example
A particular radioactive sample contains 2 million un-decayed atoms. After a year, there is only 500 000 atoms left un-decayed. What is the half-life of this material?
Answer:
Step 1: Calculate how many times the number of un-decayed atoms has halved
There were 2 000 000 atoms to start with
1 000 000 atoms would remain after 1 half-life
500 000 atoms would remain after 2 half-lives
Therefore, the sample has undergone 2 half-lives
Step 2: Divide the time period by the number of half-lives
The time period is a year
The number of half-lives is 2
1 year divided by 2 is half a year or 6 months

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
