KE, GPE & Elastic Energy (WJEC GCSE Science (Double Award)) : Revision Note
KE, GPE & Elastic Energy
An object can have one of the following forms of energy:
Kinetic energy when it is in motion (KE)
Gravitational potential energy when it is at a height above the Earth's surface (PE)
Elastic energy when it is being stretched or compressed (EPE)
Kinetic energy is defined as:
The energy an object possesses due to its motion
This means that any object that is moving has kinetic energy
If an object speeds up, it gains more kinetic energy
If an object slows down, it loses kinetic energy
Gravitational potential energy is defined as:
The energy an object possesses due to its position
This means:
If an object is lifted up, it gains gravitational potential energy
If an object falls, it loses gravitational potential energy
An example of an energy transfer between gravitational potential and kinetic energy is a ball dropped from a height
Before it is dropped the ball has zero kinetic energy because it is stationary but has maximum gravitational potential energy
As it is dropped the gravitational potential energy is transferred into kinetic energy
As the ball loses gravitational potential energy, it gains kinetic energy
Energy Transfer on a Ball

As it falls the ball loses gravitational potential energy and gains kinetic energy
An example of an energy transfer between kinetic, gravitational potential and elastic energy is the oscillation of a mass on a spring
The total energy of the mass-spring system will remain constant
However, there will be different amounts of each energy form transferred as it moves through its different positions
KE, PE and EPE in a Spring
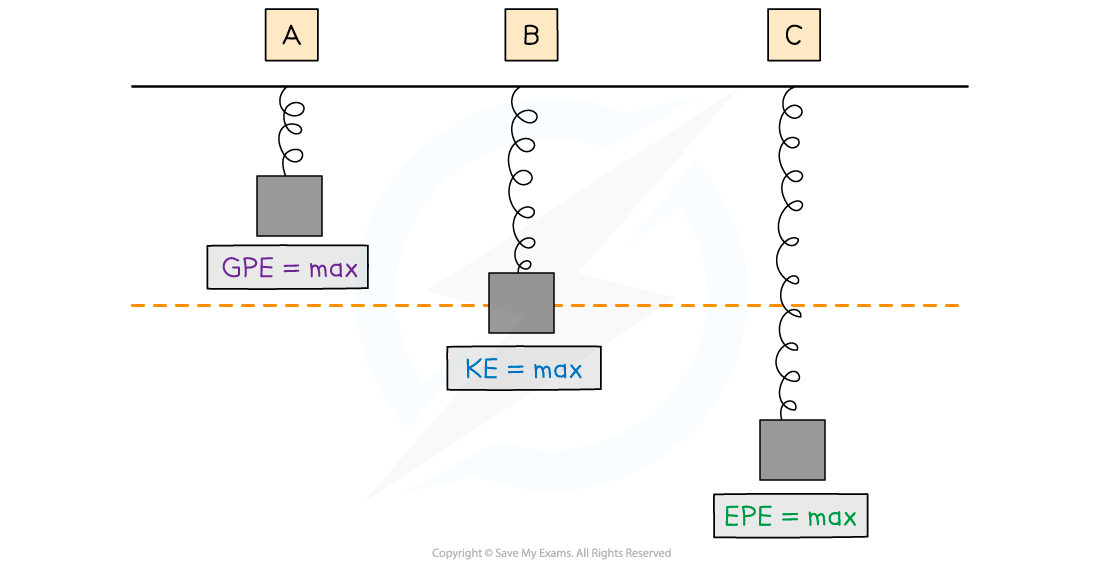
Energy changes take place when a spring is stretched and compressed about its equilibrium point at the orange line
At position A:
The spring has some elastic energy since it is slightly compressed
The spring has zero kinetic energy because it is stationary
The spring has a maximum amount of gravitational potential energy because the mass is at its highest point
At position B:
The spring has some elastic energy since it is slightly stretched
The spring has maximum kinetic energy because it passes through its resting position at maximum speed
The spring has some gravitational potential energy since the mass is still above its lowest point in the oscillation
At position C:
The spring has maximum elastic energy because it is at its maximum extension
The spring has zero kinetic energy since it is stationary
The gravitational potential energy is at a minimum because it is at its lowest point in the oscillation
Worked Example
The diagram below shows a student before and after a bungee jump.

Describe the energy conversions taking place during the jump.
Answer:
Step 1: Consider the energy on the platform before the jump
Before the jump, the bungee jumper has:
Maximum gravitational potential energy because he is at the maximum height
Zero kinetic energy because he is not moving
Zero elastic energy because the bungee chord is unstretched
Step 2: Consider the energy conversion as the bungee jumper falls before the chord extends
During the fall and before the chord extends, the bungee jumper has:
Decreasing gravitational potential energy because he is losing height
Increasing kinetic energy because he is gaining speed
Zero elastic energy because the chord is unstretched
The energy conversions are: gravitational potential energy → kinetic energy
Step 3: Consider the energy conversion as the bungee jumper falls whilst the chord is extended
During the fall and as the chord extends, the bungee jumper has:
Decreasing gravitational potential energy because he is losing height
Decreasing kinetic energy because he is being slowed by the chord as it stretches
Increasing elastic energy because the chord is being stretched
The energy conversions are: gravitational potential energy → kinetic energy → elastic energy
Step 4: Consider the energy transfer of the jumper at the end of the jump
At the bottom of the jump, the bungee jumper has:
Minimum gravitational potential energy because he is at the lowest point of the jump
Zero kinetic energy because he is not moving
Maximum elastic energy because the chord is fully stretched
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In an energy transfer question, think carefully about which energy type has the maximum and minimum values and where. Then work from there to determine the transfers taking place between them. You only need to know about the three energy transfers described here, so don't worry about any others you may come across.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
