Stability of Stars (WJEC GCSE Science (Double Award)) : Revision Note
Stability of Stars
Stars are held together by a delicate balance of inward and outward forces
One of these forces is the gravitational force
This is an attractive force which pulls the outer layers inwards
The other force is due to gas and radiation pressure
This is an outward force which is exerted by the expanding hot gases inside the star
Equilibrium in Stars
When the inward pull of gravity and the outward radiation pressure acting on the star are equal, the star is said to be in equilibrium
Balanced forces in a stable star

Forces acting within a star. The centre red circle represents the star's core and the orange circle represents the star's outer layers
If the temperature of a star increases (for example, if the rate of fusion speeds up), the outward pressure will also increase
This will cause the star to expand
If the temperature drops (for example, if the rate of fusion slows down) the outward pressure will also decrease
This will cause the star to contract
Nuclear Fusion in Stars
In the centre of a stable star, hydrogen nuclei undergo nuclear fusion to form helium nuclei
The equation for the reaction is:
These isotopes of hydrogen,
and
, are known as deuterium and tritium
A huge amount of energy is released in the reaction
This energy provides the radiation pressure that prevents the star from collapsing under its gravity
Nuclear fusion in a stable star
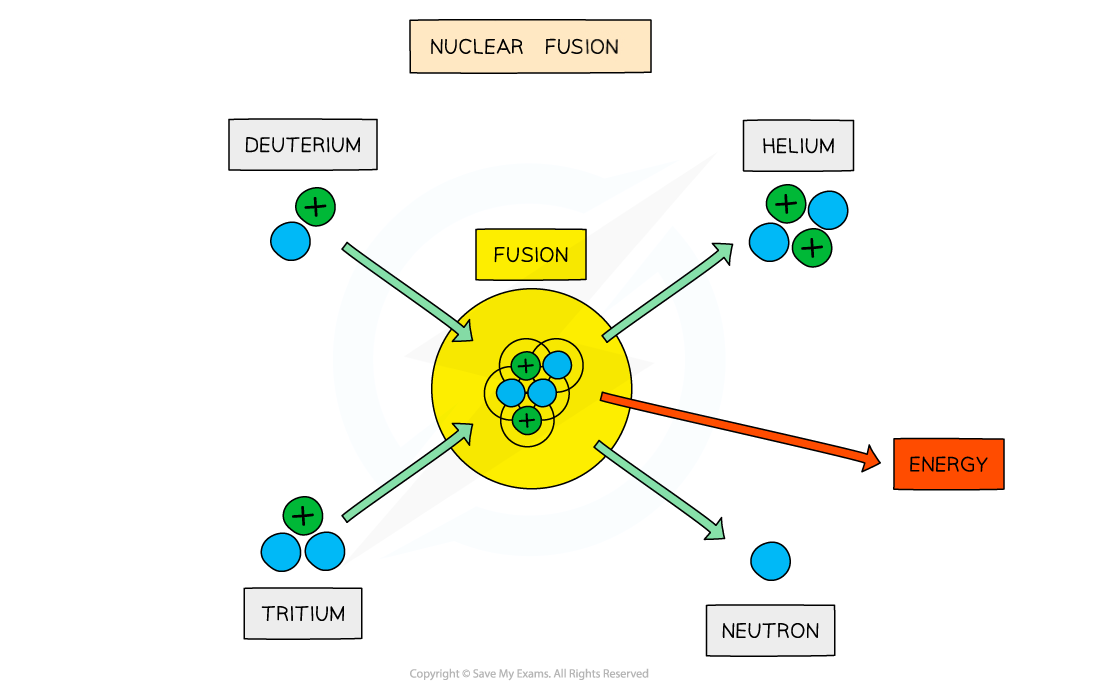
The fusion of deuterium and tritium to form helium with the release of energy
Formation of elements lighter than iron
When the supply of hydrogen begins to run out, fusion reactions of heavier elements begin to take place
For example, two helium nuclei (produced by the fusion of 2 hydrogen nuclei) could fuse together to form a beryllium nucleus
The beryllium nucleus could then fuse with a helium nucleus to form a carbon nucleus
Elements lighter than iron are formed in fusion reactions like the ones above
Formation of elements heavier than iron
Elements heavier than iron are produced in supernova explosions
A supernova occurs at the end of a massive stars life
When the star explodes it releases very large amounts of energy and neutrons
All of the elements which have been produced by the fusion reactions are ejected into space and combine with neutrons to form the heaviest elements
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When you are answering questions about nuclear fusion, remember it is only the nuclei which combine. Do not write about atoms combining.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
