The Electromagnetic Spectrum (WJEC GCSE Science (Double Award)) : Revision Note
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum (em) is a collection of waves that share the following properties:
They are all transverse
They can all travel through a vacuum
They all travel at the same speed in a vacuum
They all transfer energy
There are 7 types of electromagnetic waves, which all together form a continuous spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is arranged in a specific order based on the wavelengths or frequencies
The Electromagnetic Spectrum from Longest Wavelength to Shortest Wavelength

Visible light is just one small part of a much bigger spectrum: The electromagnetic spectrum
The relationship between frequency and wavelength of waves across the electromagnetic spectrum is
The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength
The lower the frequency, the longer the wavelength
This means that radio waves have a lower frequency, and a longer wavelength than UV waves
This can be seen from the wave equation
Where:
= speed of the wave in metres per second (m/s)
= frequency of the wave in hertz (Hz)
= wavelength of the wave in metres (m)
Since all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, this is constant
Therefore, in the equation, in keeping v constant, if f increases then λ must decrease
Relationship Between Wavelength and Frequency
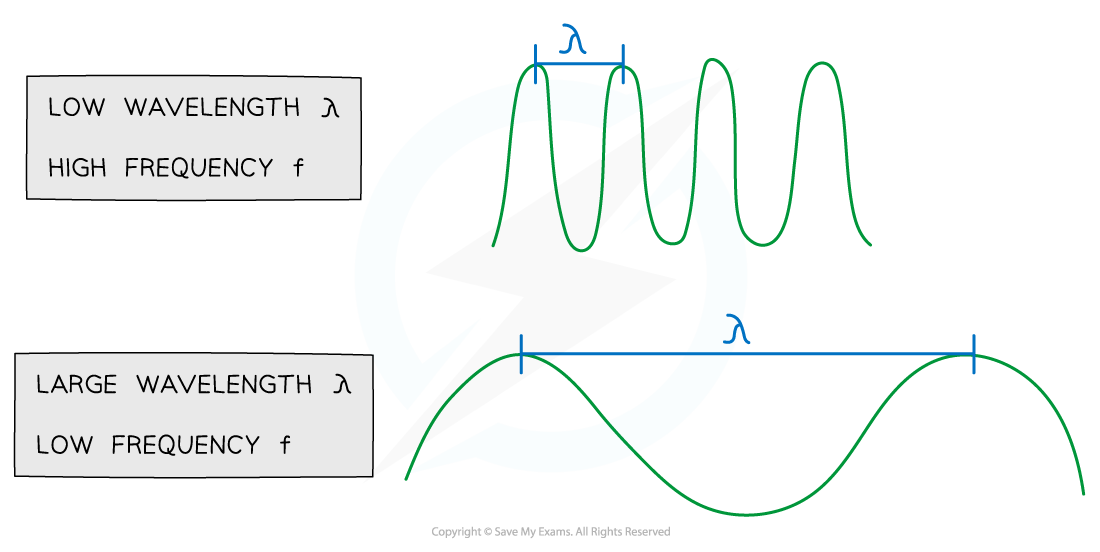
The larger the wavelength, the lower the frequency. The speed remains the same
The higher the frequency, the higher the energy of the wave
Waves with higher energy are:
Highly ionising
Harmful to cells and tissues causing cancer (e.g. UV, X-rays, Gamma rays)
For more information, see our revision note on Radiation
Waves with lower energy are:
Useful for communications and they are used to transmit information, for example:
Radio waves are used in long-range communications, such as for radio and television
Microwaves are used in mobile phones and satellite communications as they can penetrate the Earth's surface
Infra-red waves and visible light are used in optical fibres as they can undergo total internal reflection
Less harmful to humans
Worked Example
One region of the electromagnetic spectrum has wavelengths in the range 110-11 to 1
10-9 m. The wave speed of electromagnetic waves is 3
108 m/s.
Calculate the maximum frequency of this region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Answer:
Step 1: Deduce the wavelength which would have the maximum frequency within this range
The maximum frequency will have the shortest wavelength
The shortest wavelength in this region is 1
10-11 m
Step 2: List the known quantities
Wavelength,
= 1
10-11 m
Wave speed = 3
108 m/s
Step 3: Write out the equation relating wave speed, frequency and wavelength
Step 4: Rearrange for frequency and calculate the answer
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Foundation Tier students would be provided with the rearranged equation but Higher Tier students would be expected to rearrange this.
If you are not quite sure which wavelength would give the maximum frequency, you could calculate the frequency for both the shortest and longest wavelength to see which one gives the maximum value.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
