Communication Satellites (WJEC GCSE Science (Double Award)) : Revision Note
Communication Satellites
Many important methods of communication rely on long wavelength electromagnetic radiation, including:
Bluetooth, terrestrial television signals & local radio stations (using radio waves)
Signals from mobile phone masts, wireless internet & communication satellites (using microwaves)
Optical fibres (using visible or infra-red waves)
Communication satellites orbit the Earth and can communicate with base stations on the Earth's surface to relay information around the Earth
There are two different types of communication satellites:
Geostationary satellites
Geosynchronous satellites
Different Types of Communication Satellites

Geostationary and geosynchronous satellites orbiitngs around the Earth
Geosynchronous Satellites
The orbital period of a geosynchronous satellite is 24 hours which is in sync with the orbit of the Earth
A geosynchronous satellite will be in the same position above Earth once every 24 hours
It is therefore only in communication with a base station on the surface of Earth once every 24 hours
Geostationary Satellites
A geostationary satellite also has a geosynchronous orbit, i.e. it takes 24 hours to orbit the Earth
A geostationary satellite:
Remains directly above the equator and orbits in the same direction as the Earth spins
Therefore, it always orbits at the same point above the Earth’s surface
Is in constant communication with its base station
A Geostationary Satellite in Orbit
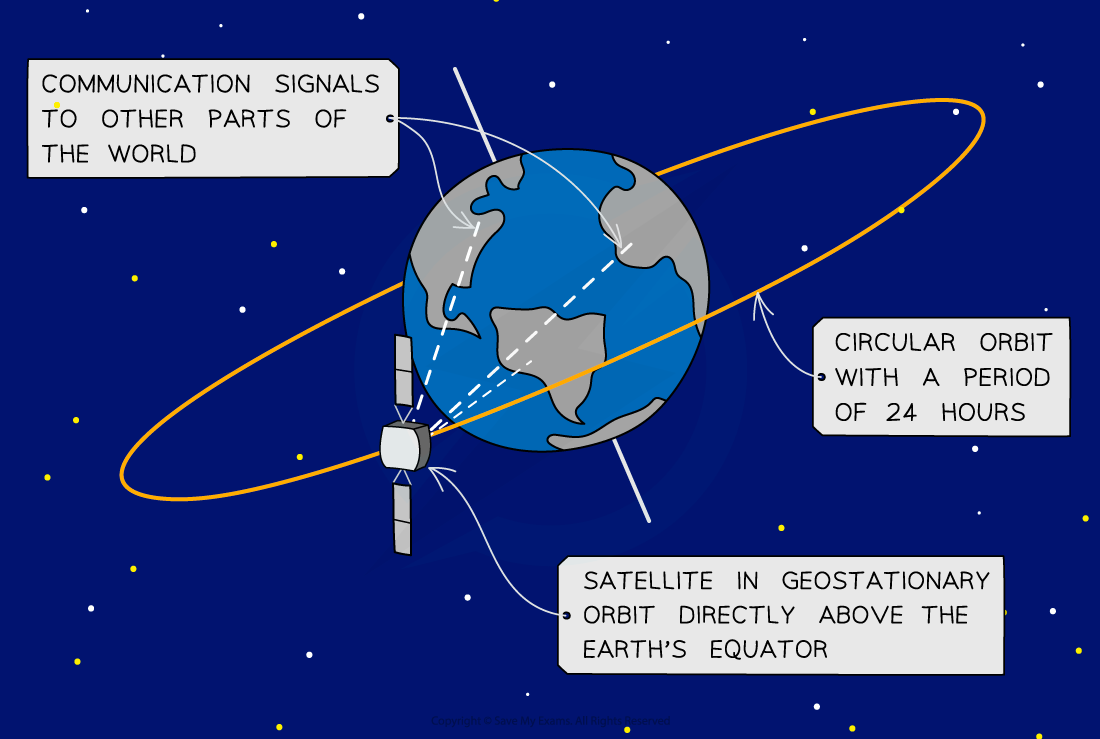
Geostationary satellites orbit the Earth every 24 hours above a fixed position on the Earth's surface
Geostationary satellites are used for telecommunication and television broadcast
Base stations on Earth send the microwave signals to satellites which relay them back to the desired locations
A minimum of 3 satellites located around the Earth is required for global coverage
Signals can be transmitted across the globe by travelling between ground base stations via satellites
Using Geostationary Satellites to Transmit Information

Information can be transmitted across the Earth using three geostationary satellites
Worked Example
Three satellites are positioned in orbit around the Earth to communicate with base stations A, B, and C on the ground, as shown in the diagram. The distance from a base station to a satellite is 36 000 km.

Diagram not drawn to scale
It takes 0.48 s for a signal to travel from base station A to base station C. The diagram shows the path of a signal sent from base station A to a satellite.
a) Complete the diagram to show how the signal reaches base station C.
b) Show that the signal travels at the same speed as the speed of light, 3108 m/s.
Answer:
a) Complete the diagram to show how the signal reaches base station C.
The signal must be sent from the satellite to base station B, up to the other satellite above B and C, before travelling to base station C
The signal cannot travel from one satellite to another, it must travel to a base station first:

b) Show that the signal travels at the same speed as the speed of light, 3108 m/s.
Step 1: List the known quantities:
Distance the signal travels from A to C = 4
36 000 = 144 000 km = 1.44
108 m
Time taken for the signal to travel from A to C = 0.48 s
Step 2: Write out the equation relating speed, distance and time:
Step 3: Calculate the speed of the signal:
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Be careful with terminology, both types of satellites have a geosynchronous orbit. This means they orbit every 24 hours. However, a geostationary satellite remains above a fixed point above the equator on the Earth's surface whereas a geosynchronous satellite will only be above the same position above Earth once every 24 hours.
This is why geostationary satellites can be used for constant communications but geosynchronous satellites are only in communication with a base station once every 24 hours.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
