Units & Calculations (OCR GCSE Combined Science A (Gateway)): Revision Note
Exam code: J250
Units & Calculations
There are a seemingly endless number of units in Physics
These can all be reduced to seven base units from which every other unit can be derived
These seven units are referred to as the SI Base Units; this is the only system of measurement that is officially used in almost every country around the world
SI Base Quantities Table

The seventh SI base unit is the candela (cd) which is the unit for luminosity
This is not encountered at GCSE
Derived Units
The seven SI base units are then used to derive other common units
The base units of physical quantities such as:
Newtons, N [kg m / s2]
Joules, J [N m]
Pascals, Pa [kg / m s2]
To deduce the base units, it is necessary to use the definition of the quantity
The Newton (N), the unit of force, is defined by the equation:
Force = mass × acceleration
N = kg × m s–2 = kg m s–2
Therefore, the Newton (N) in SI base units is kg m s–2
The Joule (J), the unit of energy, is defined by the equation:
Energy = ½ × mass × velocity2
J = kg × (m s–1)2 = kg m2 s–2
Therefore, the Joule (J) in SI base units is kg m2 s–2
The Pascal (Pa), the unit of pressure, is defined by the equation:
Pressure = force ÷ area
Pa = N ÷ m2 = (kg m s–2) ÷ m2 = kg m–1 s–2
Therefore, the Pascal (Pa) in SI base units is kg m–1 s–2
Common Units Table

Prefix Notation
Physical quantities can span a huge range of values
For example, the diameter of an atom is about 10–10 m (0.0000000001 m), whereas the width of a galaxy may be about 1021 m (1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 m)
This is a difference of 31 powers of ten
Powers of ten are numbers that can be achieved by multiplying 10 times itself
These come under two categories of units:
Multiples eg. 102, 103
Sub-multiples eg. 10−1, 10−2
Each power of ten is defined by a prefix, these are listed in the table below:
Prefixes Table
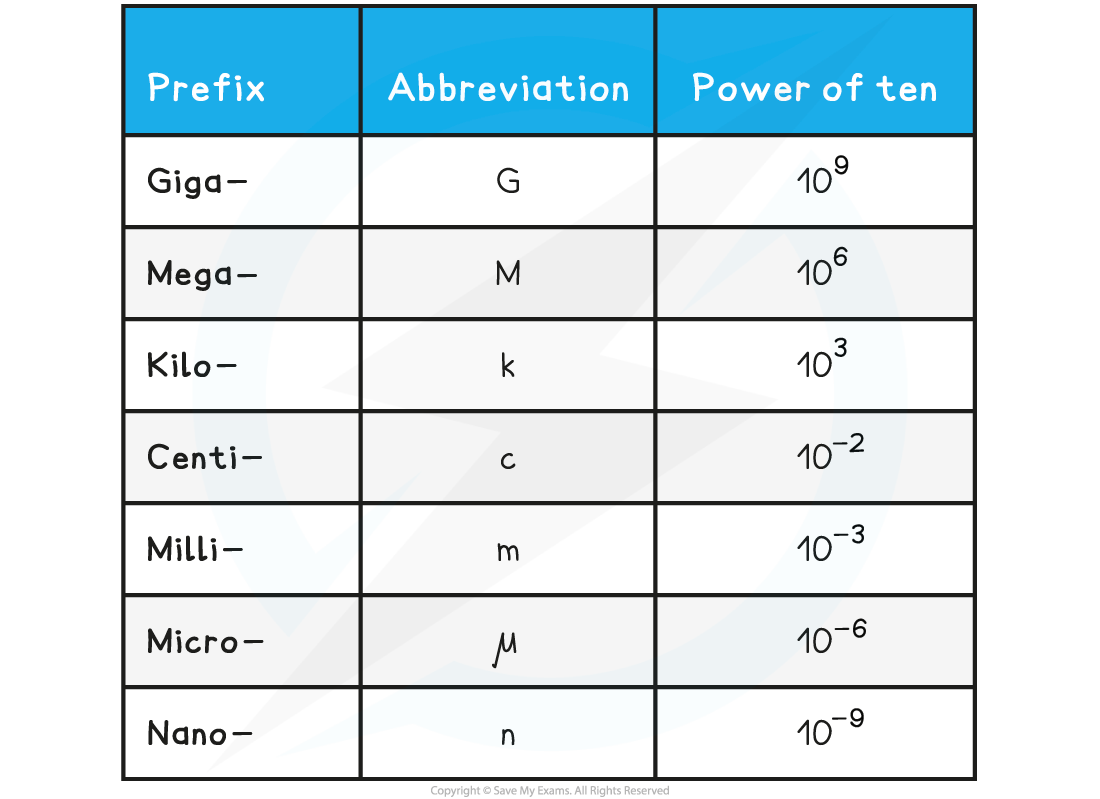
Example conversions:
12 GPa = 12 gigapascals = 12 × 109 Pa (12 000 000 000 Pa)
5 kN = 5 kilonewtons = 5 × 103 N (5000 N)
0.1 μA = 0.1 microamps = 1 × 10–7 A (0.0000001 A)
7 nC = 7 nanocoulombs = 7 × 10–9 C (0.000000007 C)
Unit Conversions
As well as prefix (powers of ten) conversions (eg. km into m) there are also common unit conversions
Time Conversions
One such unit conversion are those for time
The main time conversions are shown in the table below:
Time Conversions Table

A common time unit conversion is between hours and seconds
1 hour = 60 minutes
1 minute = 60 seconds
Therefore 1 hour = 60 × 60 = 3600 seconds
To convert from hours → seconds, multiply by 3600
To convert from seconds → hours, divide by 3600
Hours × 3600 = Seconds
Temperature Conversions
Another common temperature unit conversion is between Kelvin and degrees Celsius (ºC)
The scale is defined as: 0 K = −273.15 ºC
To convert from Kelvin → Celsius, subtract 273
To convert from Celsius → Kelvin, add 273
K − 273 = oC
oC + 273 = K
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Sometimes marks in an exam question are given for the unit, so make sure you remember which is the correct one for the quantity in your answer e.g. If the answer is a force, it must have the units of Newtons (N).
You will often see very large or very small numbers categorised by powers of ten, so it is very important you become familiar with these as getting these prefixes wrong is a very common exam mistake!

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?