Wasted Energy (OCR GCSE Combined Science A (Gateway)): Revision Note
Exam code: J250
Wasted Energy
In practice, most systems tend to be open systems
When energy transfers occur that are not useful, these are described as energy being dissipated to the surroundings
Dissipated just means spread out
This is considered to be wasted energy
Often these less useful energy transfers often involve heating, light and sound
When energy is transferred to the thermal stores of the objects, the temperature of the objects increases
The particles that make up the objects vibrate more, hence the transfer pathway is by heating (of the particles)
Visible light is electromagnetic radiation
Therefore, when light is produced, energy is transferred by radiation
When sound is produced, the sound waves make the air particles vibrate as the wave carries energy away
This increases the energy in the thermal store of the air, hence the transfer pathway is by heating (of the particles)
Useful energy can be defined as:
The energy that is transferred from store to store and used for an intended purpose
Wasted energy can be defined as:
The energy that is not useful for the intended purpose and is dissipated to the surroundings
Worked Example
A student uses an electric motor to lift a load.

The motor turns a mechanism that lifts the load. Some of the energy transfers are useful and the rest of the energy is wasted.
a) State the useful energy transfer occurring in this system.
b) State the wasted energy transfer occurring in this system.
Answer:
Part (a)
The motor turns the mechanism that lifts the load
Therefore, the useful transfer is:
Energy in the kinetic store of the motor is transferred to the gravitational potential store of the load
Part (b)
As the motor operates, friction causes a rise in the temperature of the components and the surroundings
In this case, the energy transfer from the kinetic store of the motor to the thermal store of the motor and the surroundings is not useful, hence it is a wasted energy transfer
Energy is dissipated, by heating, to the surroundings
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you are able to identify "useful" and "wasted" energy as this is commonly tested in exams! When describing wasted energy, make sure to say the energy is dissipated to the surroundings, if you say the energy is simply "lost", this will not gain you the mark as it implies energy is not conserved.
Reducing Energy Loss
Mechanical processes can become wasteful when they cause a rise in temperature
These processes often involve friction
When friction acts, it has the effect of transferring energy from the kinetic store by heating to the objects and the surroundings
This energy cannot be used in a useful way, therefore it is called wasted energy
Energy that is transferred to the surrounding is said to be dissipated (spread out) to the surroundings
Lubrication
Friction is a major cause of wasted energy in machines
For example, the gears on a bike can become hot if the rider has been cycling for a long time
Energy is wasted as it is transferred from the kinetic energy store of the bike to the thermal energy store of the gears and the chain
This friction makes them become hot and transfers energy by heating to the thermal energy store of the surrounding air
This wasted energy can be reduced if the amount of friction can be reduced
This can be achieved by lubricating the parts that rub together
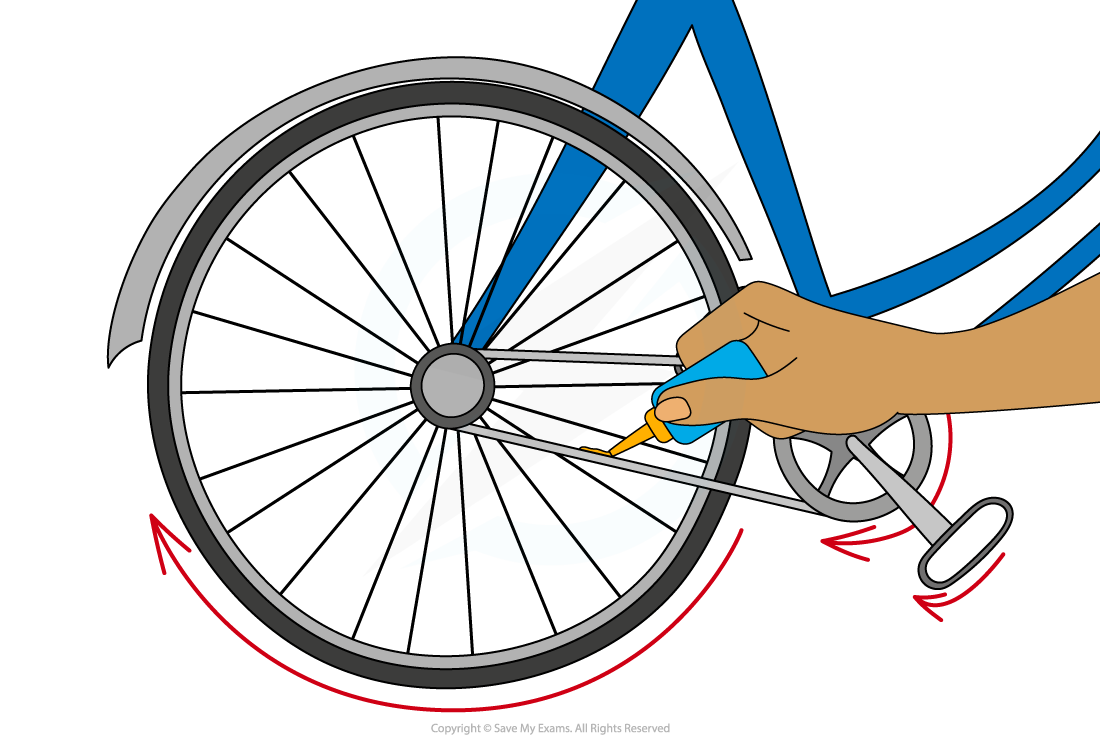
Lubrication helps reduce friction in the parts of a cycle
Insulation
In many situations, the energy transferred by heating is wanted. For example:
When heating a home
When boiling a kettle
If this energy can be prevented from dissipating, then less energy will be needed to replace the wasted energy
This can be achieved by surrounding the appliance with insulation
The effectiveness of insulation depends upon:
How well the insulation conducts heat
How thick the insulation is

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?