Collisions (AQA GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy) : Revision Note
Collisions
Examples of momentum in an event are collisions
Objects will either:
Collide and move in opposite directions - this is an elastic colision
Collide and move in the same direction together - this is an inelastic collision
When the objects move in opposite directions:
Each object will have a different velocity depending on its mass and initial momentum of the system
When the objects move in the same direction together:
They will have a combined mass and velocity
Momentum is always conserved in a collision
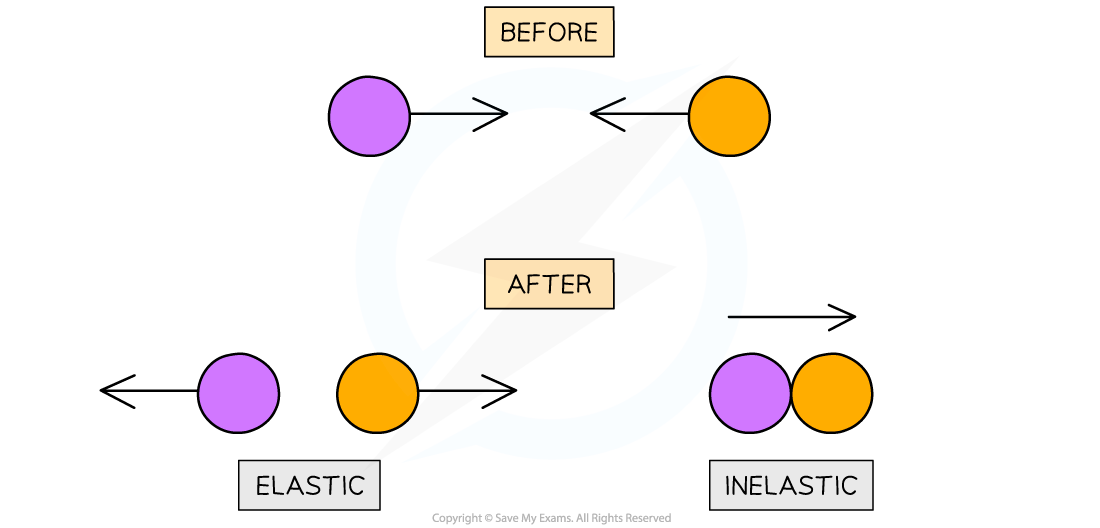
Types of collisions
If an exam question asks you to analyse a collision, follow these tips for full marks:
Always consider the motion before and after the collision and state:
The velocities of each object
The direction each object moves
State whether the collision was elastic or inelastic and explain your reasoning
In a perfectly elastic collision, the kinetic energy is the same before and after
In a perfectly inelastic collision, the two objects stick together after colliding
Describe any energy transfers that occur if kinetic energy is not conserved
For example, it may be converted into heat, sound, elastic potential energy etc

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
