Calculating KE & Changes in GPE (WJEC GCSE Science (Double Award)): Revision Note
Exam code: 3430
Calculating KE & Changes in GPE
Higher Tier Only
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy can be calculated using the equation:
Where:
KE = kinetic energy in joules (J)
m = mass of the object in kilograms (kg)
v = speed of the object in metres per second (m/s)
Kinetic Energy of a Moving Car
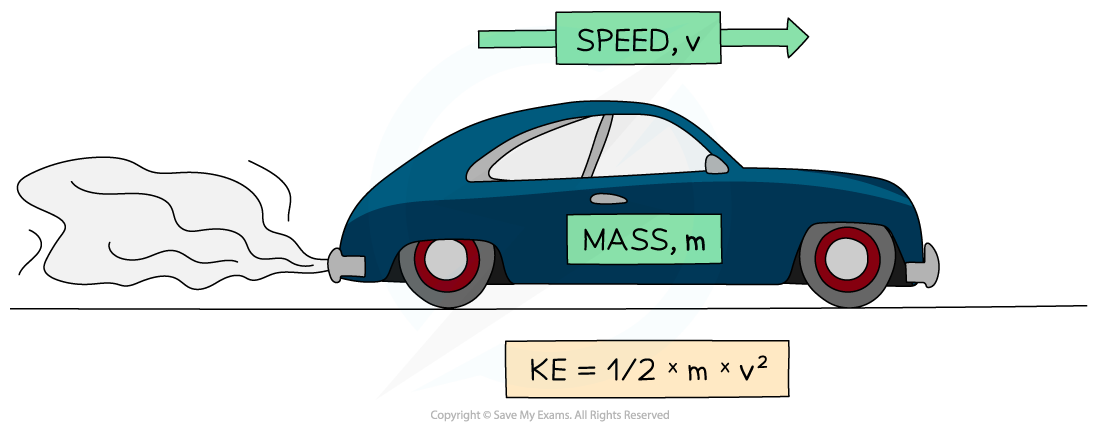
A moving car has kinetic energy because of its mass and speed
Worked Example
Calculate the kinetic energy of a vehicle of mass 1200 kg moving at a speed of 27 m/s.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Mass of the vehicle, m = 1200 kg
Speed of the vehicle, v = 27 m/s
Step 2: Write down the equation for kinetic energy
Step 3: Calculate the kinetic energy
KE = 437 400 J
Step 4: Round the final answer to 2 significant figures
KE = 440 000 J
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When performing calculations using the kinetic energy equation, always double-check that you have squared the speed. Forgetting to do this is the most common mistake that students make.
Change in Gravitational Potential Energy
The change in gravitational potential energy, PE, of an object can be calculated using the equation:
change in gravitational potential energy = mass × gravitational field strength × height
PE = mgh
Where:
PE = change in gravitational potential energy, in joules (J)
m = mass, in kilograms (kg)
g = gravitational field strength in newtons per kilogram (N / kg)
h = change in height metres (m)
Gravitational Potential Energy of a Mass

Raising a mass to a height above the ground gives it gravitational potential energy
Worked Example
A man of mass 70 kg climbs a flight of stairs that is 3 m higher than the floor.
Gravitational field strength, g = 10 N/kg.
Calculate the change in the man's gravitational potential energy.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Mass of the man, m = 70 kg
Gravitational field strength, g = 10 N/kg
Change in height, Δh = 3 m
Step 2: Write down the equation for gravitational potential energy
PE = mgh
Step 3: Calculate the gravitational potential energy
PE = 70 × 10 × 3
PE = 2100 J

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
