Current, Resistance & Potential Difference (AQA GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy): Revision Note
Exam code: 8464
Did this video help you?
Current, Resistance & Potential Difference
Potential difference is the work done by a unit charge passing through a component, measured in units of volts (V)
The potential difference between two points in a circuit is a measure of the amount of energy transferred between those points
Electric current is the flow of electrical charge measured in units of amperes (A) or amps
The size of the electric current is the rate of flow of electrical charge
In other words, how many electrons pass through a fixed point each second
Resistance is defined as the opposition to current:
The vibration of the atoms in the wire slows down the flow of electrons
The higher the resistance of a circuit, the lower the current
This means that good conductors have a low resistance and insulators have a high resistance
Resistance
The symbol for resistance is R
It is measured in Ohms (Ω)
Ω is the Greek capital letter ‘Omega’
An Ohm is defined as one volt per ampere (1 V / A)
The resistance of a circuit can be increased by adding resistors (or variable resistors) to it
Every electrical component has a resistance, even wires
In exam questions, the resistance of the wires and batteries are assumed to be negligible
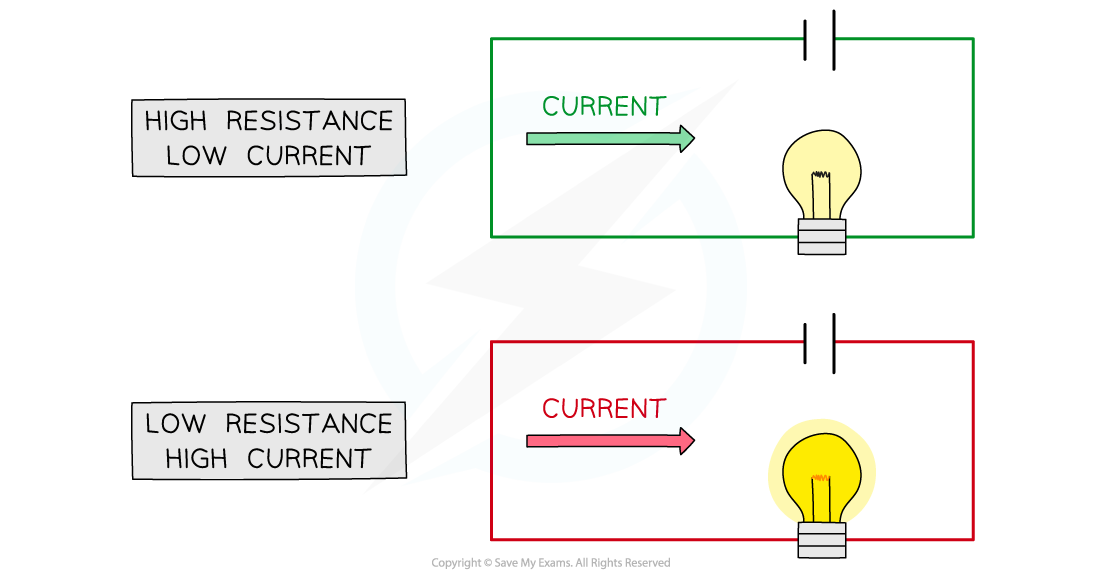
High resistance means there is lower current and vice versa
The current I through a component depends on both the resistance R of the component and the potential difference V across the component
The greater the resistance R of the component, the lower the current I for a given potential difference V across the component
The lower the resistance R of the component, the greater the current I for a given potential difference V across the component
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Resistance can be tricky to grasp conceptually because the definition 'opposition to current' is a bit difficult to pin down.
From the point of view of a tiny electron flowing through a wire, the wire is this huge structure of metal ions arranged in a lattice. There are millions of other electrons flowing through the wire too. Every time an electron hits the lattice, the electron transfers some of its energy to the lattice. The electron loses energy and slows down a bit, and the lattice gains energy and vibrates more and more with each collision. The more it shakes, the more the electrons collide with it.
The wire heats up due to the collisions of electrons with the lattice of the metal ions in the wire. The hotter it gets, the more it vibrates, the more collisions there are. The more collisions there are, the hotter it gets... and on and on and on.
Calculating Current, Resistance & Potential Difference
The current, resistance and potential difference of a component in a circuit are calculated using the equation:

This equation can be rearranged with the help of the following formula triangle:
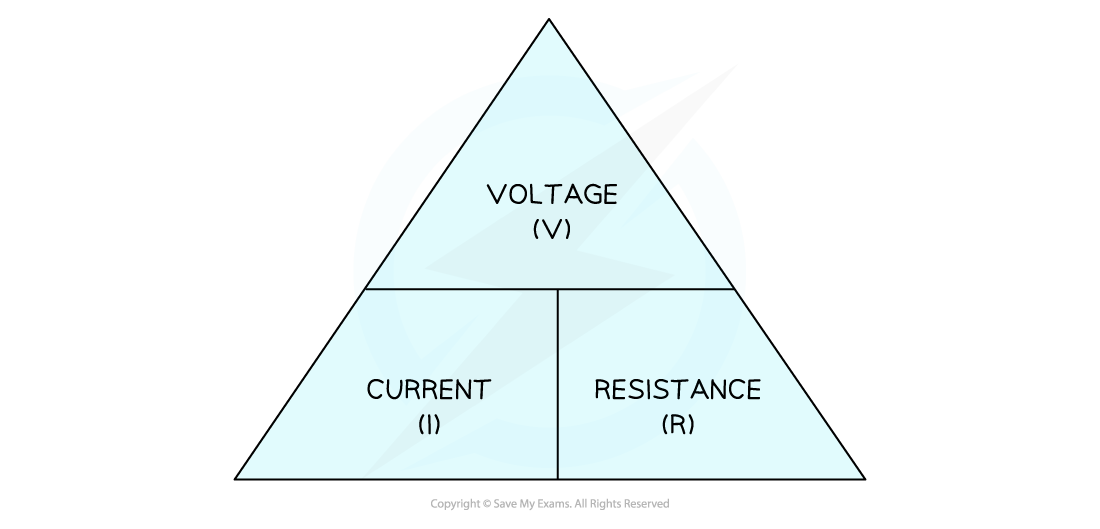
Voltage, current, resistance formula triangle
Worked Example
Calculate the potential difference through a resistor of resistance 10 Ω if there is a current of 0.3 A through it.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Resistance, R = 10 Ω
Current, I = 0.3 A
Step 2: Write the equation relating resistance, potential difference and current
V = IR
Step 3: Substitute in the values
V = 0.3 × 10 = 3 V
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember that 'voltage' and 'potential difference' are the same, either wording will be accepted in your exam answers

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?