Kinetic Energy (AQA GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Kinetic Energy
Energy in the kinetic store is defined as:
The amount of energy an object has as a result of its mass and speed
This means that any object in motion has energy in its kinetic store
If an object speeds up, energy is transferred to its kinetic store
If an object slows down, energy is transferred away from its kinetic store
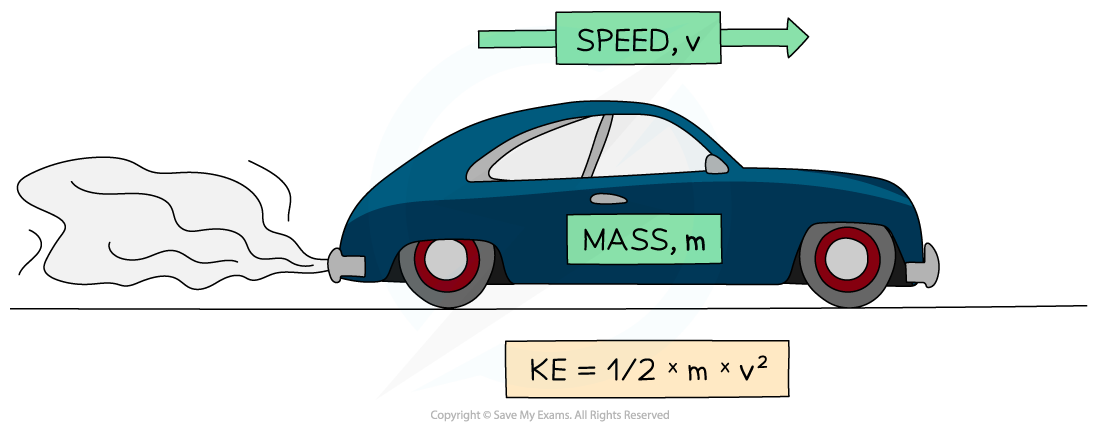
Kinetic energy can be calculated using the equation:
Ek = ½ × m × v2
Where:
Ek = kinetic energy in joules (J)
m = mass of the object in kilograms (kg)
v = speed of the object in metres per second (m/s)
Worked Example
Calculate the kinetic energy stored in a vehicle of mass 1200 kg moving at a speed of 27 m/s.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Mass of the vehicle, m = 1200 kg
Speed of the vehicle, v = 27 m/s
Step 2: Write down the equation for kinetic energy
EK = ½ mv2
Step 3: Calculate the kinetic energy
EK = ½ × 1200 × (27)2
EK = 437 400 J
Step 4: Round the final answer to 2 significant figures
EK = 440 000 J
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When performing calculations using the kinetic energy equation, always double-check that you have squared the speed. Forgetting to do this is the most common mistake that students make.
The kinetic energy equation is one of the most difficult rearrangements you will have to do in AQA GCSE Physics, so if you take the time to learn how to master this one, all the others will be easy by comparison! Remember the rules for rearranging equations; to undo an operation, you do the opposite operation, and whatever you do to one side of the equation, you must also do to the other side.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
