Conservation & Dissipation of Energy (AQA GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy): Revision Note
Exam code: 8464
Did this video help you?
Conservation of Energy
The law of conservation of energy states that:
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be transferred from one store to another
This means the total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant
Energy can be transferred from store to store usefully (to do work)
Or energy can be dissipated to the thermal store of the surroundings
Examples of Energy Conservation
Conservation of energy applies to all energy transfers
Example 1: A bat hitting a ball
The moving bat has energy in its kinetic store
Some of that energy is transferred usefully to the kinetic store of the ball
Some of that energy is dissipated by heating to the thermal store of the bat, the ball, and the surroundings
The impact of the bat and the ball causes the particles of the bat and ball to vibrate
The sound wave causes the air particles to vibrate


Conservation of energy: a bat hitting a ball
Example 2: An electric heater
Energy is transferred electrically from the mains supply to the thermal store of the heating element
Some of that energy is usefully transferred to the thermal store of the surroundings by heating the air particles in the room
Some of that energy is dissipated to the thermal store of the surroundings by radiation (light)

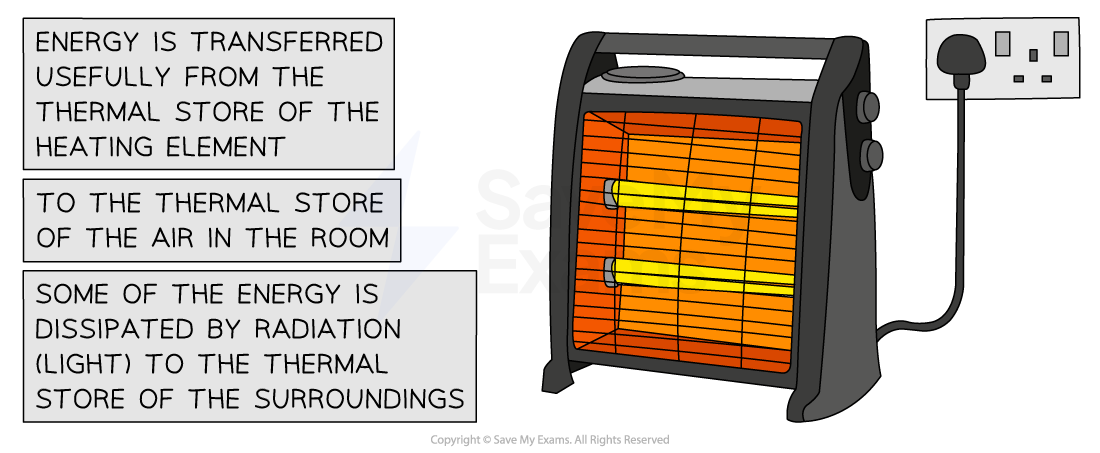
Conservation of energy: electric heater
Example 3: Rollercoasters
When the rollercoaster is on an elevated piece of track, it has energy in its gravitational potential store
When the rollercoaster descends to a lower piece of track, energy is transferred usefully to the kinetic store as the rollercoaster gains speed
When the rollercoaster ascends again, energy is transferred from the kinetic store to the gravitational store as the rollercoaster loses speed
Energy is dissipated to the thermal store of the surroundings by heating due to
friction heating the wheels and track
sound waves vibrating the air particles

As the rollercoaster in the diagram travels from A to D, the useful energy transfers that take place are:
gravitational potential store → kinetic store → gravitational potential store → kinetic store
This is sometimes also described as
GPE → KE → GPE → KE
Example 4: Trampoline
Whilst jumping, the person has energy in their kinetic store
When the person lands on the trampoline, most of that energy is transferred to the elastic potential store of the trampoline
That energy is transferred usefully back to the person's kinetic store as they bounce upwards
Energy is transferred from the person's kinetic store to their gravitational potential store as they gain height
Some of the energy is dissipated by heating to the thermal store of the surroundings (the person, the trampoline and the air)
The useful energy transfers taking place are:
elastic potential store → kinetic store → gravitational potential store

Useful energy transfers: person on a trampoline
Worked Example
Describe the energy transfers in the following scenarios:
a) A falling object
b) A battery powering a torch
c) A mass on a spring
Answer:
Part (a)
For a falling object:
Energy is transferred mechanically from the gravitational potential store of the object to the kinetic store of the object
Part (b)
For a battery powering a torch:
Energy is transferred electrically from the chemical store of the cell to the thermal store of the bulb
Part (c)
For a mass on a spring:
Energy is transferred mechanically from the elastic potential store of the spring to the kinetic store of the mass

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?