Cosmological Red Shift (WJEC GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 3420
Cosmological Redshift
Usually, when an object emits waves, they spread out symmetrically
If the source of the waves moves, the waves can become squashed together or spread out
If a source of light moves towards an observer, the waves become squashed, causing the wavelength to decrease
The wavelength of light shifts towards the blue end of the spectrum
This is called blueshift
If a source of light moves away from an observer, the waves spread out, causing the wavelength to increase
The wavelength of light shifts towards the red end of the spectrum
This is called redshift
Redshift and Blueshift of Light
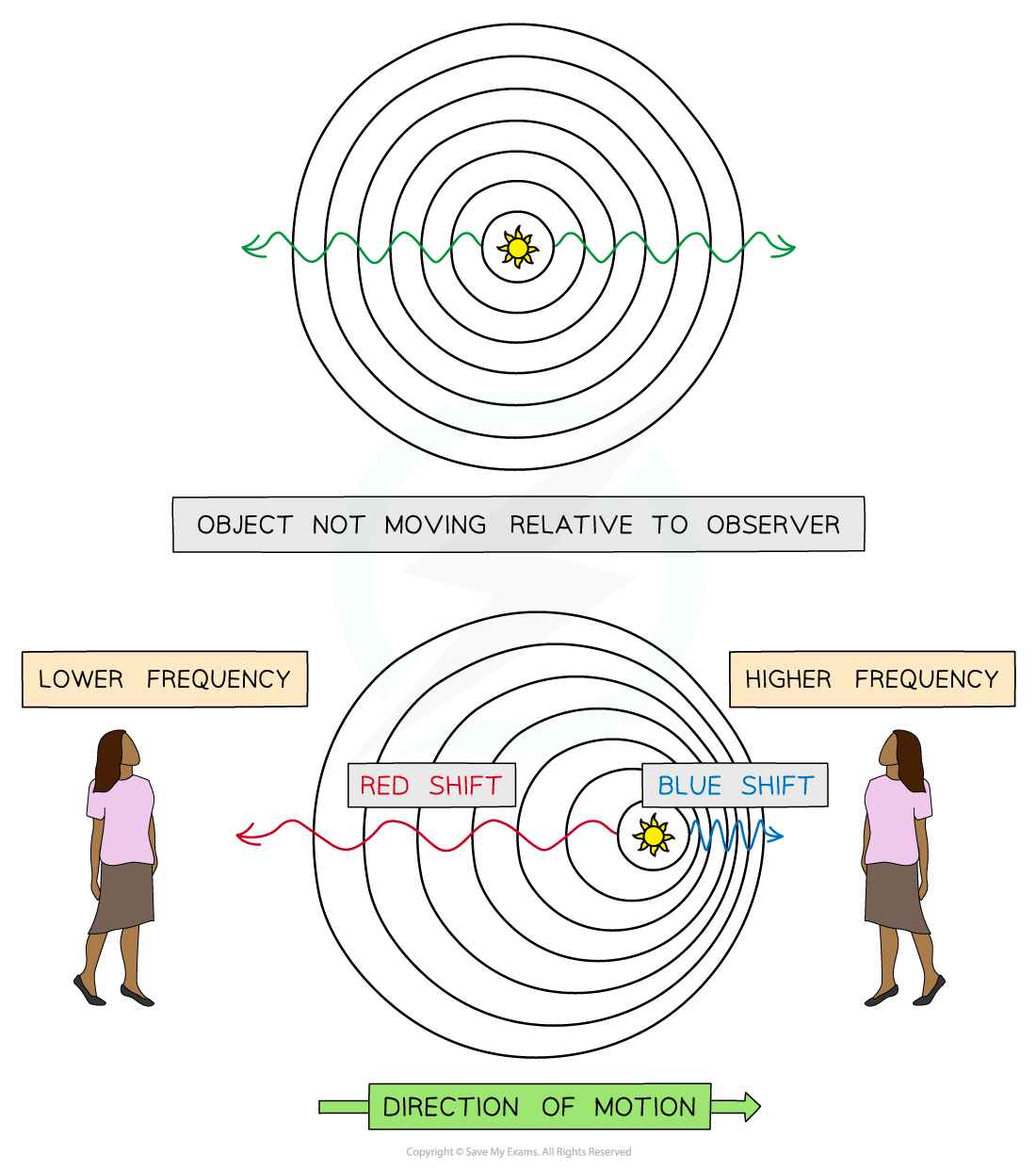
When light moves away from an observer, they observe redshift and when light moves towards an observer, they observe blueshift
When astronomers compare the absorption spectra of light from distant galaxies with spectra from nearby objects, such as the Sun, they observe the dark lines are shifted towards the red end of the spectrum
This means the wavelength has increased as the light travelled from the galaxy to the Earth
This shows that distant stars and galaxies are moving away from the Earth
Redshift of Light from a Distant Galaxy

Comparing the absorption spectra produced by the Sun and a distant galaxy shows the light from the distant galaxy has been shifted towards red wavelengths (it has stretched) due to it moving away
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You need to know that in the visible light spectrum, red light has the longest wavelength and the smallest frequency.
Absorption spectra usually display wavelength as increasing from left to right, so the red end (longer wavelength) is usually on the right and the violet end (shorter wavelength) is usually on the left
The Expanding Universe
Cosmological redshift indicates that distant galaxies are moving away from us
If galaxies are moving away from us, this means the Universe must be expanding
Expansion of the Universe

Observations of light from galaxies show they are moving away from us which means the Universe is expanding
When Edwin Hubble looked at the absorption spectra of distant galaxies, he determined a relationship between the speed of a galaxy and its distance from Earth
Comparing Redshifts of Galaxies
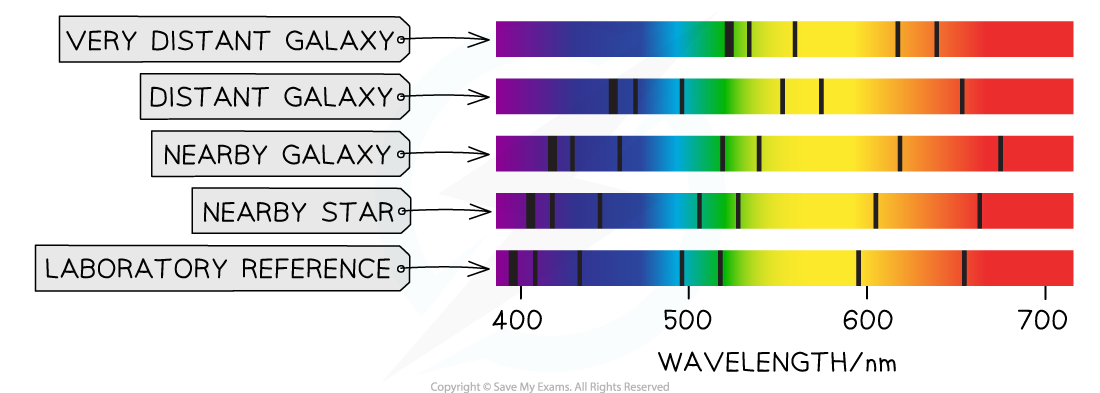
Hubble discovered that all galaxies show redshift, but the galaxies that are further away show a greater increase in redshift
This is Hubble's law, which states
The speed of recession is proportional to the distance of the galaxy away from Earth
'Recession' speed means the speed at which something is moving away
This means that the further away a galaxy is from Earth:
The faster it is moving away
The greater the increase in redshift
Relationship between Redshift and Galaxy Distance

Hubble's law tells us the greater the distance to a galaxy, the greater the redshift, or the speed it moves away from Earth
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure that you understand that the stretching of the wavelength of light is due to the expansion of the Universe, not the motion of stars and galaxies themselves.
This can be visualised by imagining a balloon with equally spaced points on it. The balloon represents space and the points represent galaxies.

When the balloon is deflated (i.e. the Universe was smaller), the points (galaxies) are closer together and are at an equal distance apart.
As the balloon (Universe) expands, all the points (galaxies) become further apart by the same amount.
This is because the space between the galaxies itself has expanded.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?