Equations of Motion (WJEC GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 3420
Equations of Motion
The equations of motion are used for objects in constant acceleration (or deceleration)
For example, an object falling under gravity without air resistance
Properties of this motion are calculated with the following variables:
u = initial velocity (m/s)
v = final velocity (m/s)
a = acceleration (m/s2)
x = distance travelled (m)
t = time (s)
An Example of the Use of Motion Variables

A ball is dropped from rest, so the initial velocity is 0. The distance fallen is the distance travelled by the ball. The ball is falling and it is assumed there is no air resistance, so acceleration due to free fall is 10 m/s2.
How to use the equations of motion
Step 1: Write out the known and unknown variables given and use the context of the question to deduce any quantities that aren’t explicitly listed. For example:
In vertical motion a = g = ±10.0 m/s2 when an object is falling due to gravity
An object which starts at rest will have u = 0 when x = 0 and t = 0
An object that finishes at rest will have v = 0
Step 2: Choose one of the following equations which contain:
The one unknown quantity you need to find
The remaining variables are known quantities
Step 3: Convert any quantities into standard (SI) units, substitute into the equation and calculate the answer
For example, any distances in km must be converted into m or time in minutes converted into s
Equation 1:
Equation 2:
Worked Example
The diagram below shows an arrangement to stop trains that are travelling too fast.
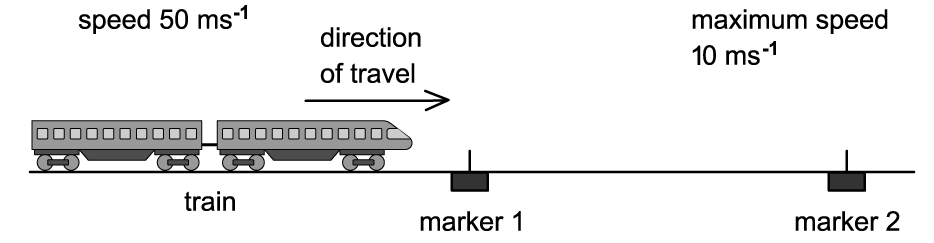
At marker 1, the driver must apply the brakes so that the train decelerates uniformly to pass marker 2 at no more than 10 m/s.
The train carries a detector that notes the times when the train passes each marker and will apply an emergency brake if the time between passing marker 1 and marker 2 is less than 20 s.
Trains coming from the left travel at a speed of 50 m/s.
Determine how far marker 1 should be placed from marker 2.
Answer:
Step 1: Write down the known and unknown variables
u = 50 m/s
v = 10 m/s
a = unknown
x = ? m
t = 20 s
Step 2: Choose the correct equation
u, v and t are known
We are asked to find x
So the correct equation is:
Step 3: Substitute the known quantities and solve to calculate the distance
Worked Example
Higher Tier Only
Show that v = u + at is consistent with the definition of acceleration.
Answer:
Step 1: Define acceleration
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity
Step 2: Rearrange to obtain the given equation
at = (v − u)
at + u = v
So, v = u + at
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This topic can seem a little daunting at first, but the best way to master this section is to practice as many questions as possible! You will normally be given the value of acceleration relevant to the question but you should be aware of the value of g = 10 m/s2.
Remember only students studying the higher tier will be required to rearrange equations like in the second worked example.
More Equations of Motion
Higher Tier Only
The following two equations of motion are to be used by higher-tier students only
Equation 3:
Equation 4:
Worked Example
A cyclist is travelling directly east through a village, which is completely flat, at a velocity of 6 m/s. They then start to constantly accelerate at 2 m/s2 for 4 seconds.
(a) Calculate the distance that the cyclist covers in the 4 s acceleration period.
(b) Calculate the cyclist's final velocity after the 4 s interval of acceleration.
Answer:
(a)
Step 1: List the known quantities
Initial velocity, u = 6 m/s
Acceleration, a = 2 m/s2
Time, t = 4 s
Distance travelled = x (this needs to be calculated)
Step 2: Identify the best equation of motion to use
In this problem, the equation that links x, u, a, and t is
Step 3: Substitute the known quantities into the equation
x = (6 × 4) + (0.5 × 2 × 42) = 24 + 16
Displacement: x = 40 m
(b)
Step 1: List the known quantities
Initial velocity, u = 6 m/s
Acceleration, a = 2 m/s2
Time, t = 4 s
Final velocity = v (this needs to be calculated)
Step 2: Identify and write down the equation to use
In this problem, the equation that links v, u, a, and t is:
Step 3: Substitute the known quantities into the equation
v = 6 + (2 × 4)
Final velocity: v = 14 m/s
Worked Example
A science museum designed an experiment to show the fall of a feather in a vertical glass vacuum tube.
The time of fall from rest is 0.5 s.

Use an appropriate equation of motion to calculate the length L of the tube.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
u = 0 m/s
v = unknown
a = 10 m/s2
x = L = ? m
t = 0.5 s
Step 2: Determine the equation that links these variables
Step 3: Substitute the known quantities to calculate the length L
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are not sure how to rearrange equations or substitute values into an equation then review this skill from your GCSE maths notes.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?