Calculating Work Done in Stretching (WJEC GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 3420
Calculating Work Done in Stretching
Higher Tier Only
When a spring is stretched by a force work is done by the spring
The work done in stretching a spring is equal to the elastic energy stored in the spring
Work Done in Stretching a Spring
Work is done on a spring when it is stretched
Work done is calculated using the equation:
Where:
W = work done by the spring or elastic potential energy (J)
F = force applied to stretch the spring (N)
x = extension of the spring (m)
This is only valid for springs not stretched beyond their limit of proportionality
Calculating Work Done from the Force-Extension Graph
Work done is calculated from the area under a force-extension graph
The area under the graph forms a triangle shape
Where the area of a triangle is
So, the work done = area =
Area Under a Force-Extension Graph
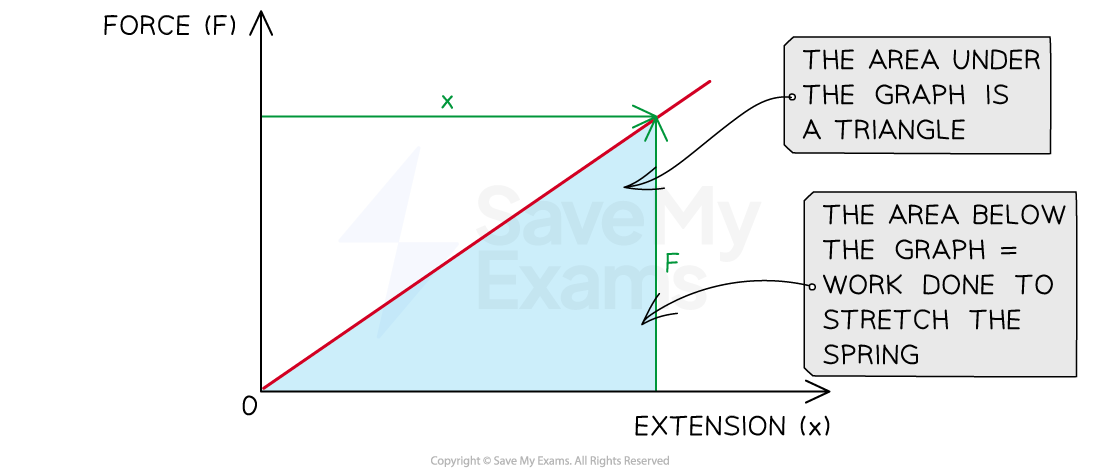
The area under the force-extension graph is a triangle. Calculating the area of the triangle gives the work done by the spring when stretched
Worked Example
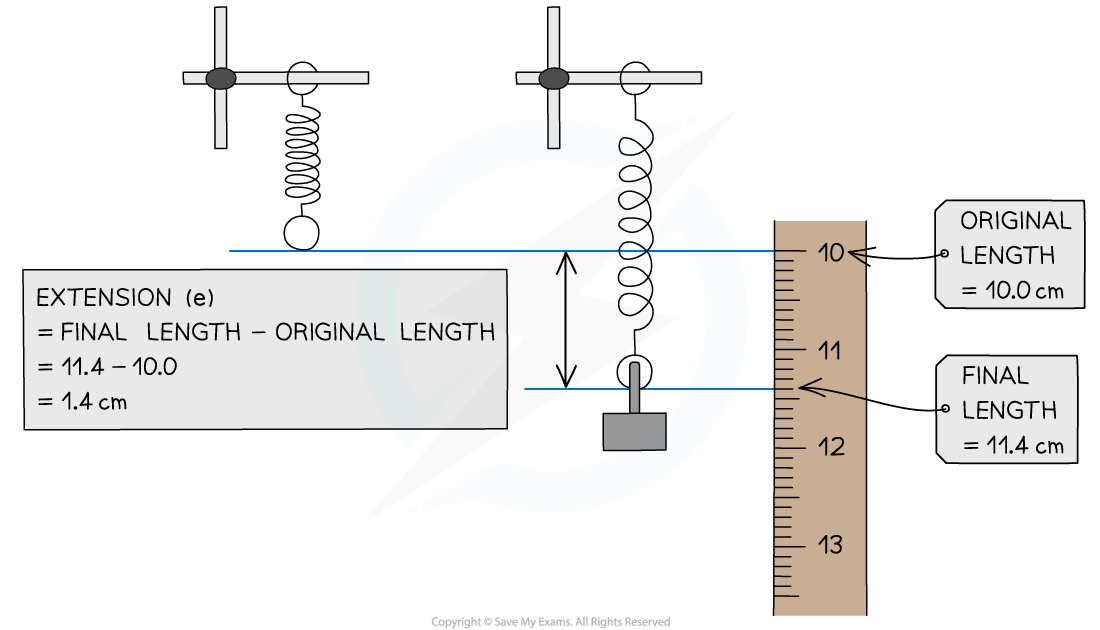
A 250 g mass is attached to the bottom of a hanging spring. It stretches from 10.0 cm to 11.4 cm.
Gravitational field strength = 10 N/kg
Calculate the elastic potential energy stored by the stretched spring.
Answer
Step 1: Draw a diagram of the situation
Step 2: List the known quantities
Mass added, m = 250 g
Original length = 10.0 cm
Final length = 11.4 cm
Gravitational field strength = 10 N/kg
Step 3: Determine the extension of the spring in m
There are 100 cm in 1 m
extension, x = final length − original length
x = 11.4 − 10.0 cm
x = 1.4 cm
x = 1.4 ÷ 100 = 0.014 m
Step 4: Determine the force on the spring
Weight = F = mg
F = 0.250 × 10
F = 2.5 N
Step 5: Recall the equation for work done
Step 6: Calculate the work done
J

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?