Pressure (WJEC GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 3420
Written by: Leander Oates
Updated on
Pressure
Pressure is exerted when a force acts over an area
Therefore, pressure can be calculated using:
Where:
p = pressure measured in pascals (Pa)
1 pascal is equivalent to 1 newton per meter squared
1 Pa = 1 N / m2
F = force measured in newtons (N)
A = area measured in metres squared (m2)
The area should always be the cross-sectional area of the object
So that the force is at a right angle to the surface it is acting upon
Higher Tier students will need to be able to rearrange the pressure equation
Pressure, Force, Area Equation Triangle
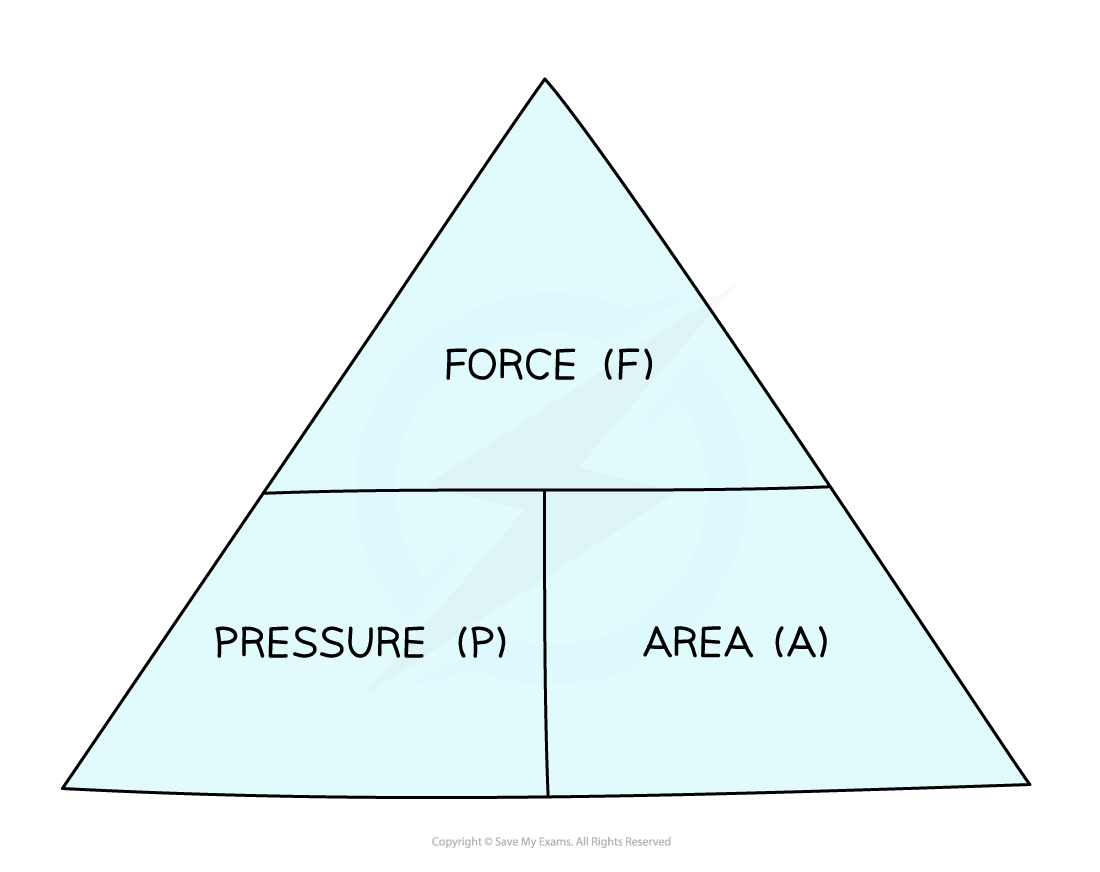
Cover up the variable you need to calculate, and the triangle shows you how the equation is arranged
Pressure can be exerted by a solid on another solid
For example the pressure exerted by a person standing on the ground
Pressure can be exerted by a gas on a surface
For example when gas particles collide with the surfaces of a container
Gas Particles Colliding with the Walls of a Container

Gas particles collide with the surfaces of a container producing a force that acts over an area
Worked Example
The particles in a gas exert a force of 0.3 N on a surface of 0.025 m2.
Calculate the pressure exerted on the surface by the gas.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Force, F = 0.3 N
Area, A = 0.025 m2
Step 2: Write out the equation for pressure
Step 3: Substitute in the known values to calculate

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
