Absolute Zero & Temperature (WJEC GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 3420
Absolute Zero & Temperature
The Kelvin Temperature Scale
The Kelvin temperature scale begins at absolute zero
0 K is equal to -273 °C
Because it is not possible to have a temperature lower than 0 K, a temperature in kelvin will never be a negative value
To convert between temperatures in Celsius, and temperatures in kelvin:
The divisions on both the Kelvin scale and the Celsius scale are equal. This means:
A change in a temperature of 1 K is equal to a change in temperature of 1 °C
Comparison of the Kelvin Scale and the Celsius Scale

Absolute zero is the lowest possible temperature, a change in temperature in K is equal to the same change in temperature in °C
Absolute Zero
The temperature of a gas is related to the average speed of the molecules:
The hotter the gas, the faster the molecules move
Faster moving molecules collide with the surface of the walls more frequently and with more force
This increases the pressure
Gas Molecules in Random Thermal Motion Inside a Sealed Box
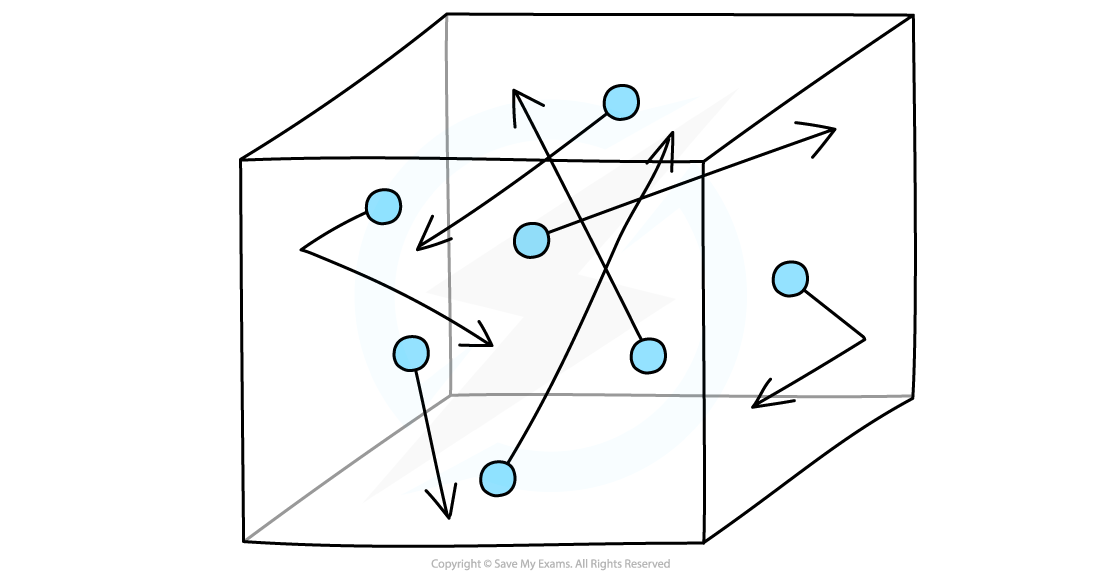
Gas molecules hit the sides of the container which creates pressure. A higher temperature increases the average speed of the molecules, increasing the pressure
As the temperature of the gas decreases, the pressure exerted on the surfaces of the container also decreases
In 1848, Mathematician and Physicist, Lord Kelvin, recognised that there must be a temperature at which the particles in a gas exert no pressure
At this temperature the particles must no longer be moving, and hence not colliding with their container
This temperature is called absolute zero and is equal to -273 °C

At absolute zero, or -273 °C, particles will have no net movement. It is therefore not possible to have a lower temperature
Absolute zero is defined as:
The temperature at which the molecules in a substance have zero kinetic energy
So for a system at absolute zero, it is not possible to remove any more energy from it
This means that absolute zero is the lowest temperature possible
Even in space, the temperature is roughly 2.7 °C above absolute zero
Worked Example
The room temperature of a science lab is measured to be 295 K.
Determine the room temperature in °C.
Answer:
Step 1: Recall the conversion equation for K → °C
Step 2: Convert the temperature to °C
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you forget whether you need to add or subtract 273, just remember that:
0 K = −273 °C
Therefore, °C = K −273
If you get a negative value in K, you know you have gone wrong!

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?