Uses of Optical Fibres (WJEC GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 3420
Comparison of Optical Fibres & Satellites
Communication using Optical Fibres
Optical fibres can be used to transmit:
Home (landline) telephone signals
Internet signals
Cable television signals
In phone calls from landline phones:
Electrical signals are converted to light pulses by an infrared laser that flashes at high speed
Repeaters boost the signal every 30 km along the fibre
At the receiving end, the digital signal is converted into sound
Landline Telephone Signal Path

Sound from a landline telephone travels through optical fibres and is boosted every 30 km to the landline of the person listening
Optical fibres can transmit both visible and infrared signals
These signals travel at a speed of 2 × 108 m/s
This is not the same as the speed of light in space
Optical fibres are installed:
In cables attached to telephone (or telegraph) poles in the street
Underground from the service box to the telegraph pole or under the sea
Telegraph Poles

Fibre optic cables can be found in the phone cables attached between the telephone poles and the street
Optical fibres transmit signals over long distances at high speeds
The fastest internet available in Wales is called superfast broadband
It uses optical fibres to transmit internet signals from the telephone exchange to a roadside cabinet in each area and then to homes or businesses
Slower internet speeds are the continued use of old copper cables to carry the internet signal some, or all the way from the telephone exchange
Installation of Optical Fibres for High-Speed Internet

The speed of your internet depends on whether you have all, part or none of your signal transmitted via fibre optic cable from the telephone exchange
Optical fibres have many advantages over copper cables:
They use less energy to transmit the signal
They need fewer boosters to increase the signal
There is no interference with nearby cables
They are difficult to intercept
Their weight is lower, so they are easier to install
Fibre Optic and Copper Cables

Copper cables are heavier and more difficult to install than fibre optic cables
Communication Using Satellites
Many types of communication use satellites or a combination of satellites and cables:
Long-distance landline phone calls
Mobile phone calls
TV broadcasts
Satellites can orbit the Earth in one of two orbits:
Geosynchronous - at an angle between the equator and the north/south poles
Geostationary - above the equator
Geosynchronous and Geostationary Orbits

A geostationary orbit is directly above the equator
Communication involving satellites uses microwaves or radio waves to transmit the signal from Earth to a satellite
Microwave signals must leave Earth and are reflected back to Earth from the satellite
So, signals travel twice the height of the satellite in space
They are not reflected from satellite to satellite
Microwave signals travel huge distances in space
This creates a time delay
Sending & Receiving Signals via Satellite

Signals are transmitted to a satellite and then reflected back to Earth meaning they travel twice the distance of the height of the satellite
Remember the following equations when answering questions on this topic:
The wave equation: wave speed = frequency × wavelength
The speed, distance & time equation:
Where time can refer to time taken or time delay (s)
Worked Example
An optical fibre between Wales and Australia has a length of 16 000 km. Information is sent along this optical fibre with a speed of 1.5 × 108 m/s. A geostationary satellite is at a height of 30 000 km above the Earth.
The speed of light in space is 3 × 108 m/s.

A top-secret message needs to be sent from the Welsh government in Wales to the Australian government in Australia.
Compare the two methods of sending the message.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Optical Fibre
Distance = length = 16 000 km
Speed of signal = 1.5 × 108 m/s
Satellite
Height above the Earth = 30 000 km
Speed of signal = 3 × 108 m/s
Step 2: Convert the distances into m
There are 1000 m in 1 km
Length of cable = 16 000 × 1000 = 1.6 × 107 m
Height above the Earth = 30 000 × 1000 = 3 × 107 m
Step 3: State the equation needed to calculate the time of transmission for both signals
Step 4: Calculate the time for transmission of the signal in the optical fibre
Step 5: Calculate the total distance for transmission of the signal to and from the satellite
total distance = 2 × height of satellite
total distance = 2 × (3 × 107)
total distance = 6 × 107 m
Step 6: Calculate the time for transmission of the signal to and from the satellite
Step 7: Compare the time taken for the transmission of the signal using both methods
The time delay of the signal in the optical fibre is less than for the satellite OR
The time delay of the satellite is 1.9 times longer than for the optical fibre
So, the optical fibre will take less time to transmit the signal
Step 8: Compare other factors involved in sending the signal
Optical fibres are more secure than satellites
The error rate of signals transferred in optical fibres is much less than in satellites
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In your exam, you could be asked to compare with calculations communication via satellite and optical fibre having been given information on them.
Uses of Optical Fibres
Optical fibres are also used in medicine to see within the human body
An endoscopy is a medical procedure that uses an endoscope to look inside the body
An endoscope contains a camera on a long, thin flexible tube containing an optical fibre
It can be inserted down your throat or up where you go to the toilet
As a result of these images, doctors can see what might be wrong with a patient
An endoscopy is invasive, as it involves going inside a person
It may cause some damage to areas or cells it comes into contact with
An Endoscope
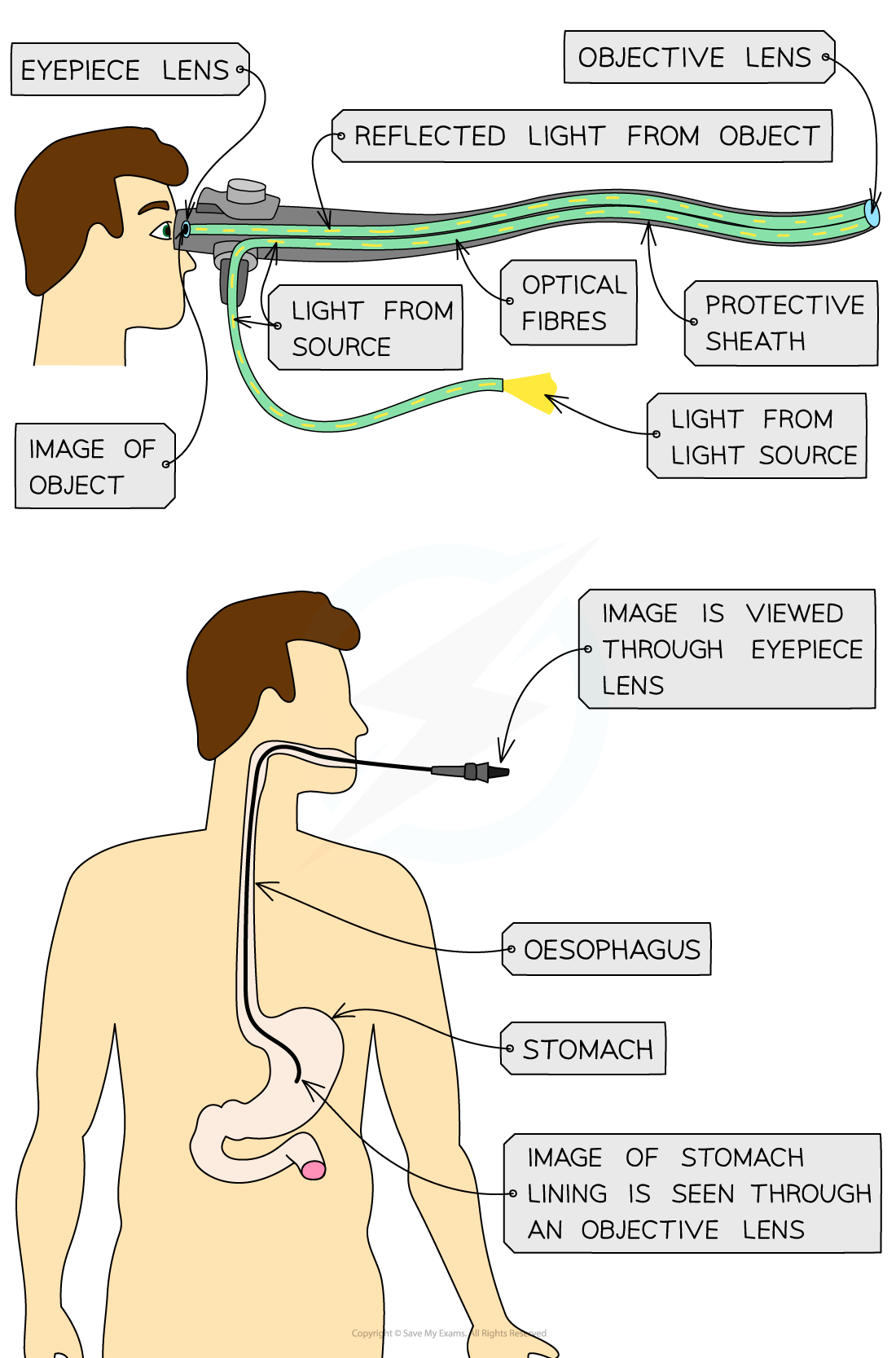
Endoscopes utilise total internal reflection to see inside a patient's body
CT Scans
CT stands for Computerised Tomography
CT scans use X-rays to take many images of a body section at different angles
A 3D image can be built up when all the images are put together
This 3D image can be rotated and viewed from different angles
A CT Scan

CT scans take 2D images from multiple positions to create a 3D image
An Example Image Created by a CT Scan

This 3D image is viewed on a screen and can be rotated to enable doctors to see clearly inside the body
Unlike an endoscopy, a CT scan is non-invasive (no instruments are inserted into the body)
Due to the use of X-rays, it carries an exposure risk as X-rays are ionising
People should limit their exposure to X-rays because, in high amounts, they can cause damage to cells such as mutations and possibly lead to cancer
Worked Example
A child is suffering from severe stomach pains. The doctor would like to perform an endoscopy or a CT scan so they can see what is going on inside the child.
Explain a disadvantage of using a CT scan to obtain medical information compared to using an endoscope.
Answer:
CT scans / X-rays are ionising
X-rays can cause damage to cells / mutations / cancer
OR
Endoscopes use visible light which is not ionising
Visible light does not mutate cells / damage cells / cause cancer
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In your exam, you may be asked to compare the advantages and disadvantages of using an endoscopy or a CT scan to treat a patient. You are not expected to know a great deal of information on CT scans, as you are likely to be given some to help you answer the question.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?