Total Internal Reflection & Optical Fibres (WJEC GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 3420
Total Internal Reflection of Light
Sometimes, when light is moving from a denser medium towards a less dense one, instead of being refracted, all of the light is reflected
This phenomenon is called total internal reflection
Total internal reflection (TIR) occurs when:
The angle of incidence > the critical angle
The incident material is denser than the second material
Refraction and Total Internal Reflection
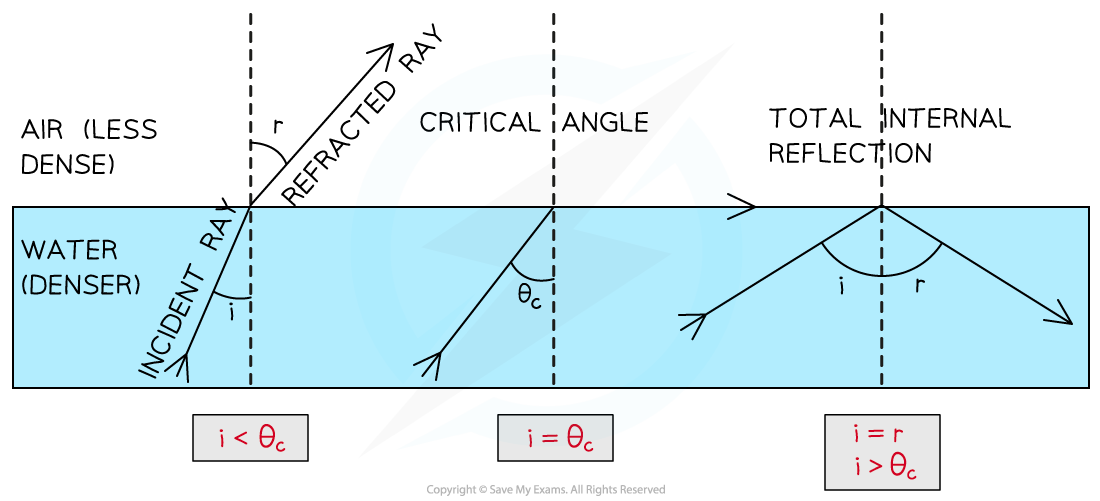
Light is refracted when it passes from a more dense to a less dense medium when the critical angle is greater than the incident angle. Light is internally reflected when it passes from a more dense to a less dense material when the critical angle is less than the incident angle
Worked Example
A glass cube is held in contact with a liquid and a light ray is directed at a vertical face of the cube. The angle of incidence at the vertical face is 39° and the angle of refraction is 25° as shown in the diagram. The light ray is totally internally reflected for the first time at X.
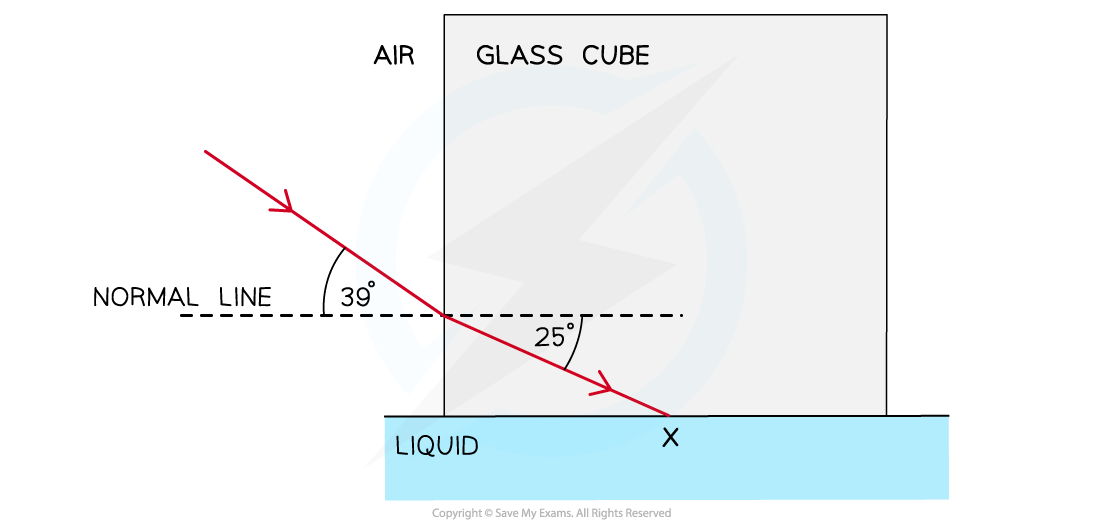
Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray beyond X to the air and calculate the critical angle for the glass-liquid boundary.
Answer:
A correctly drawn diagram would look like this:
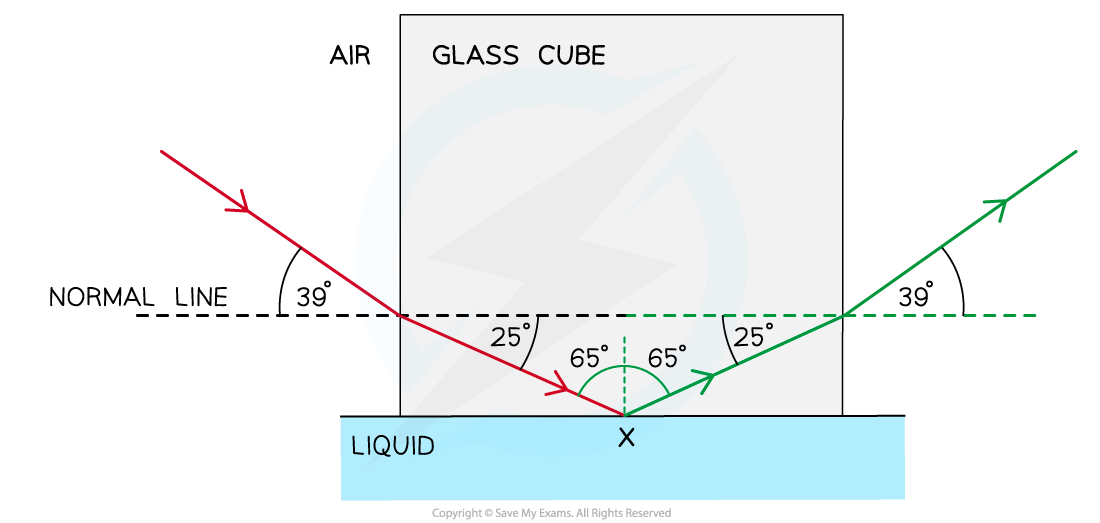
Step 1: Draw the reflected angle at the glass-liquid boundary
When a light ray is reflected, the angle of incidence = angle of reflection
Therefore, the angle of incidence (or reflection) is 90° – 25° = 65°
Step 2: Draw the refracted angle at the glass-air boundary
At the glass-air boundary, the light ray refracts away from the normal
Due to the reflection, the light rays are symmetrical on the other side
Step 3: Calculate the critical angle
The question states the ray is “totally internally reflected for the first time” meaning that this is the lowest angle at which TIR occurs
Therefore, 65° is the critical angle
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If asked to name the phenomena make sure you give the whole name – total internal reflection and not just TIR
Remember: total internal reflection occurs when light travels from a denser material to less dense material and ALL of the light is reflected.
If you are asked to explain what is meant by the critical angle in an exam, you can be sure to gain full marks by drawing and labelling the diagram shown in the notes above.
Optical Fibres
Total internal reflection is used to reflect light along optical fibres
Light refracts when it enters the optical fibre at one end
It undergoes repeated total internal reflection against the sides until it reaches the other end
Where it is refracted back out
In this process light travels long distances without losing information or speed
Total Internal Reflection Along an Optical Fibre
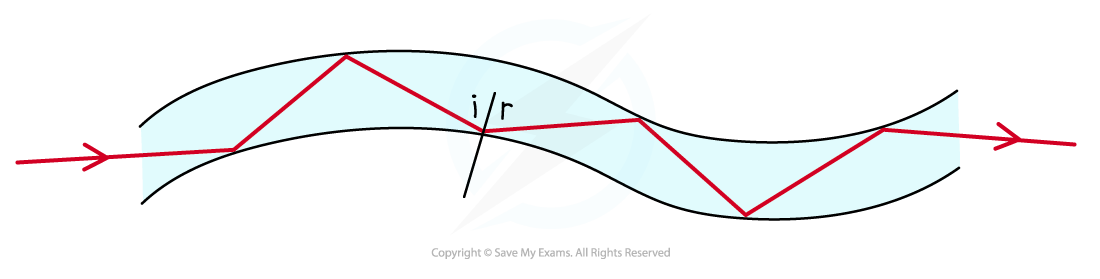
Optical fibres utilise total internal reflection where the angle of incidence on the side of the fibre is greater than the critical angle

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?