Describing Waves (WJEC GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 3420
Describing Waves
When describing wave motion, there are several terms which are important to know, including:
amplitude,
wavelength,
frequency,
wave speed,
Amplitude
Amplitude is defined as:
The distance from the undisturbed position to the peak (crest) or trough of a wave
It is given the symbol
and is measured in metres (m)
Amplitude is the maximum or minimum displacement from the undisturbed position
Wavelength
Wavelength is defined as
The distance from one point on the wave to the same point on the next wave
In a transverse wave:
The wavelength can be measured from one peak to the next peak
In a longitudinal wave:
The wavelength can be measured from the centre of one compression to the centre of the next
The wavelength is given the symbol
(lambda) and is measured in metres (m)
Graphical Representation of Transverse Waves
The amplitude and wavelength of a transverse wave can be represented graphically
The distance along a wave is typically put on the x-axis of a wave diagram
A Diagram of a Transverse Wave
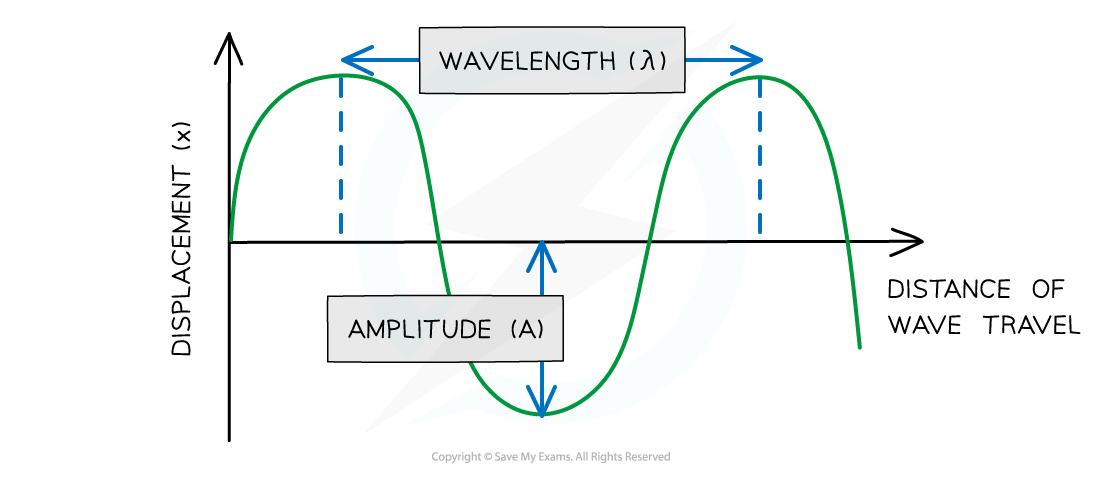
Diagram showing the amplitude and wavelength of a transverse wave
Frequency
Frequency is defined as:
The number of waves passing a point in a second
Frequency is given the symbol
and is measured in hertz (Hz)
Wave Speed
Wave speed is the speed at which energy is transferred through a medium
Wave speed is defined as:
The distance travelled by a wave each second
Wave speed is given the symbol
and is measured in metres per second (m/s)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The wavelength is often shown graphically between the peaks of two consecutive waves. However, the wavelength can be shown between any two corresponding points on two consecutive waves - the distance will still be the same!

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?